File
advertisement

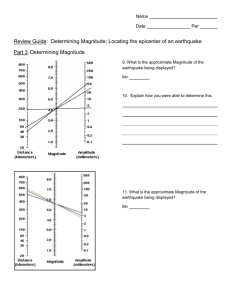
Lab: Locating an EQ Epicenter Steps: Name: NOTE: To locate an epicenter, you need data from 3 different seismic stations. 1. On each seismogram, estimate the time interval (in seconds) between the arrival of the P waves and S waves. This is called the S-P interval. Measure the interval to the closest second and BE VERY ACCURATE! 2. Use an S-P interval graph to convert each S-P interval into a distance (km). 3. On a map, find the location of each seismic station. Using a compass and the map’s scale, draw a circle around each recording station. The radius of the circle must be EQUAL to the distance found in Step 2. 4. After completing Step 3, you will have drawn 3 circles. The earthquake epicenter is where the 3 circles intersect. Sample Calculation: Seismic Station at San Francisco, CA, USA 1. On the sample seismogram from the San Francisco recording station, the S-P time interval for an earthquake is equal to 36 seconds. 2. Based on the graph below, an S-P time interval of 36 seconds is equal to a distance from the recording station of 350 km. 3. On a map, find the location of the recording station at San Francisco. Using a compass, draw a circle around the station with radius of 350 km, according to the map’s scale. Do this step three times, for each of the three seismic stations you have listed. 4. Where the three circles best intersect is the location of the epicenter of the earthquake. 36 s 350 km WebLab: Virtual Earthquake! Name: Instructions: Go to the website: http://vcourseware3.calstatela.edu/VirtualEarthquake/VQuakeExecute.html Read the instructions and the questions below. As you read the correct information on the computer screen, write your answer in the spaces below. NOTE: To complete this lab, you must print out a copy of the CERTIFICATE OF COMPLETION (shown left) with your name on it and today’s date. Staple the certificate to the back of this assignment. Lab forms without the certificate will be deemed INCOMPLETE. A. Introduction Page 1. Where do most earthquakes take place? 2. The point of origin of an earthquake is called the: 3. What is the name of the instrument used to detect earthquakes? 4. Name two things that will affect the speed at which seismic waves will travel: a. b. 5. How many seismic stations do you need to detect an earthquake accurately? B. Perform An Earthquake Simulation Now, pick an earthquake simulation to perform. Choose the Japan region first and complete the tasks given to you by the website. While performing your simulation, answer the following question: 6. According to the graph of seismic wave travel times, how long does it take P waves to travel 300 km? How long does it take for S waves to travel the same distance? P waves = S waves = C. Compute The Earthquake’s Richter Magnitude Once you have found the location of the epicenter, the program will ask you to find the Richter magnitude of the earthquake. Answer the following: 7. The “magnitude of an earthquake is defined as: 8. In what year was the Richter scale introduced? 9. Humans can begin to feel earthquakes at WHAT Richter magnitude? D. Using the Richter Nomogram 10. On the Richter Nomogram, what would be the MAGNITUDE of an earthquake be that has an amplitude of 10 mm on a seismogram and is 600 km away? 11. What would be the MAGNITUDE of an earthquake be that has an amplitude of 50 mm on a seismogram and is 100 km away? E. Printing Your Certificate Congratulations, you have finished the simulation! Print out your certificate of completion with your name and today’s date and attach it to this document.