Atmospheric Effects - Saginaw Valley State University
advertisement

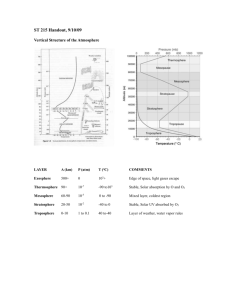
Unit Design For Atmospheric Effects Developed by Sarah E. Bradley Name of My Charter: Marvin L. Winans Academy of Performing Arts Understanding by Design UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 1 Unit Design Worksheet Subject: 7th Grade Science Unit Title: Atmospheric Effects Topic: Atmosphere Composition Grade: Seventh Name: Sarah E. Bradley Stage 1 - Desired Results Established Goals: Content Goals (Grade Level Content Expectations): 1. E.ES.07.71 Compare and contrast the difference and relationship between climate and weather. 2. E.ES.07.72 Describe how different weather occurs due to the constant motion of the atmosphere from the energy of the sun reaching the surface of the earth. 3. E.ES.07.73 Explain how temperature of the oceans affects the different climates on Earth because water in the oceans holds a large amount of heat. 4. E.ES.07.74 Describe weather conditions associated with frontal boundaries (cold, warm, stationary, and occluded) and the movement of major air masses and the jet stream across North America using a weather map. 5. E.FE.07.71 Describe the atmosphere as a mixture of gases. 6. E.FE.07.12 Compare and contrast the composition of the atmosphere at different elevations. Literacy Goals (Common Core State Standards): RI.7.1 Cite several pieces of textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as inferences drawn from the text. RL.7.2 Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze its development over the course of the text; provide an objective summary of the text. SL.7.4 Present claims and findings, emphasizing salient points in a focused, coherent manner with pertinent descriptions, facts, details, and examples; use appropriate eye contact, adequate volume, and clear pronunciation. SL.7.5 Include multimedia components and visual displays in presentations to clarify claims and findings and emphasize salient points. W.7.2 Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/experiments, or technical processes. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 2 Understandings: Students will understand 1. the relationship between weather and climate. 2. that different weather occurs due to the constant motion of the atmosphere from the energy of the sun reaching the surface of the earth. 3. that water in the oceans holds a large amount of heat and that the temperature of the oceans affects the different climates on earth. 4. that weather conditions are affected by many factors and that frontal boundaries and air masses affect weather conditions. 5. that the atmosphere is a mixture of gases divided into layers. 6. that the atmosphere has a different composition at each layer. Students will know 1. the relationship between weather and climate. 2. that different weather occurs due to the constant motion of the atmosphere from the energy of the sun reaching the surface of the earth. 3. that water in the oceans holds a large amount of heat and the temperature of the oceans affects the different climates on earth. 4. that weather conditions are affected by many factors and that frontal boundaries and air masses affect weather conditions. 5. that the atmosphere is a mixture of gases divided into layers. 6. that the atmosphere has a different composition at each layer. Essential Questions: 1. How are weather and climate associated? 2. How does the movement of the atmosphere determine our daily weather? 3. How do oceans affect temperature and climate? 4. How can a weather map be used to analyze and predict weather? 5. How does each layer of the atmosphere affect us? 6. How does the composition of the atmosphere change at different elevations? Students will be able to 1. compare and contrast the relationship between weather and climate. 2. interpret weather maps that show atmospheric motion. 3. compare climates with warm ocean temperatures and cold ocean temperatures. 4. look at current weather and forecast the weather for the following week. 5. identify the different layers in the atmosphere. 6. describe the composition of each layer of the atmosphere. Unit Enduring Understanding: Unit Questions: Students will understand that other factors such as ocean temperatures, movement of the atmosphere, and the relationship between weather and climate. What factors affect the weather and climate in a region? Students will understand that the sun’s heat, oceans temperatures, and cloud coverage play a role in weather prediction. What roles does the atmosphere play in weather prediction? Students will gain confidence in speaking and presenting their prepared information in front of others. Students will cite textual evidence and determine central themes of text throughout unit. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 3 Stage 2 - Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: Goal: Your task is to draw and interpret the weather of all four seasons based on your chosen location. Role: Meteorologist from your chosen location. Audience: The people of your community. Situation: You are a new meteorologist in your town. You need to predict the weather of all four seasons. You must take into account the following factors that affect weather: climate, energy of the sun reaching the surface of the earth, temperature of the oceans, and the movement of major air masses. Chosen location choices: Perth, Australia; Cape Town, Africa; London, England; and New York, New York. Product: Newscast – Weather for the Four Seasons. Newscast presentation will require spoken and visual components. Visual component examples can be, but are not limited to, PowerPoint presentations, Prezi.com presentations, poster, etc. Standards: Rubric below. Key Criteria: Newscast - Presentation and Planning : Weather for the Four Seasons Teacher Name: __________________________ CATEGORY Accuracy of Facts Student Name: 4 ________________________________________ 3 2 All supportive facts are Almost all facts are reported accurately (3 of reported accurately (2 of 3). 3). Research Student researched the subject and integrated 3 or more details from their location. Visuals Visuals include some original material and are clearly related to the content being presented. Graphics are clearly related to the content being presented, but none are original. Duration of presentation The newscast was between 1.5 and 3 minutes and did not seem hurried or too slow. The newscast was between 1.5 and 3 minutes but seemed SLIGHTLY hurried or too slow. Speaks clearly Speaks clearly and distinctly all of the time and mispronounces no words. Speaks clearly and distinctly all of the time but mispronounces 1 or more words. This section’s score will be multiplied by 4. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University One fact is reported accurately. 1 No facts are reported accurately OR no facts were reported. Student researched the Student researched the Either no research was subject and integrated 2 subject and integrated 1 done or it was not clear details from their detail from their location. that the group used it in location. the newscast. Graphics include some Graphics are not related original material but are to the content being only somewhat related to presented. the content being presented. The newscast was between 1.5 and 3 minutes but seemed VERY hurried or too slow. The newscast was too long or too short. Speaks clearly and Does NOT speak clearly distinctly most of the and distinctly most of the time and mispronounces time AND/OR no words. mispronounces more than 1 word. 4 Posture and Eye Contact Stands or sits up straight Stands or sits up straight. Slouches or appears too and looks confident and Establishes eye contact casual but establishes relaxed. Establishes eye with audience during good eye contact with contact with audience most of newscast. audience during most of during most of newscast. newscast. Enthusiasm Facial expression and body language show a strong interest and enthusiasm about the topic throughout the newscast, but it is not overdone. Point of View - Purpose Newscast establishes a purpose at the beginning and maintains that focus throughout! Cohesive newscast. Science Content This sections score will be multiplied by 4. All science content is 1 scientific fact is 2 scientific facts are 3 or more scientific facts portrayed correctly. incorrect. One of the incorrect. 2 of the are incorrect. 3 or more Students will present following is omitted: following are omitted: of the following are information that the suns Students will present Students will present omitted: Students will heat, oceans information that the suns information that the suns present information that temperatures, and cloud heat, oceans heat, oceans the suns heat, oceans coverage play a role in temperatures, and cloud temperatures, and cloud temperatures, and cloud weather prediction. coverage play a role in coverage play a role in coverage play a role in weather prediction. weather prediction. weather prediction. Other Evidence: Before Pre-Assessment Test What do you know about the atmosphere? Discussion and visual discovery of a picture of the atmosphere divided into layers. Facial expression and body language show a strong interest and enthusiasm about the topic throughout the newscast, but it is somewhat overdone. Facial expression and body language show some interest and enthusiasm about the topic throughout the newscast. Slouches or appears too casual AND establishes little eye contact with audience during newscast. Establishes a purpose at The purpose is somewhat It was difficult to figure the beginning, but clear but many aspects of out the purpose of the occasionally wanders the newscast seem only newscast. from that focus. slightly related. During After Journaling Students will have a section in the back of their science booklets explaining what they understood specifically about that day’s concept or what they are having trouble with. Plane Ride Story Students will write a story of them being on a plane ride and how they are going through the different parts of the atmosphere. Visual discovery Visual discovery of a picture of the atmospheres differentiation at elevations. Quick Write What is the atmosphere composed of? Why is this combination important to living things? What do you know about: In social studies, I know you have learned about the word climate. What is climate? What is weather? How are these two different? Quick Write How does the composition of the atmosphere change at different elevations? How do these changes affect the properties and temperature of the air? Visual discovery Visual discovery of a picture showing the sun hitting the oceans, which contributes to the convection cycle. What do you observe? Visual Discovery Facial expression and body language depict apathy or boredom with the topic. Think-Pair-Share What are some similarities and differences between climate and weather? Think-Pair-Share How does the movement of the atmosphere determine our daily UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University Interview Activity Students will read a story during the lesson and will write interview questions to the athlete to ask them why training at altitude helps them become a better athlete. Students will then pair up and interview each other. The interview questions with answers will be turned in. Tracking Daily Weather Students will track daily weather for a period of time and afterward discuss how climate affected the weather. Draw a picture Students will draw a picture of how convection contributes to the water cycle. 5 Visual discovery of a picture of a heat sink. What do you know about…? How does the temperature of oceans affect weather and climate? Visual Discovery Show a weather map and have students visually discover what they observe. This will activate prior knowledge and allow students to assess what they already know. Discuss that the map key can help students out. weather? Think-Pair-Share How do oceans affect temperature and climate? Vocabulary Activities Jigsaw on these vocabulary terms: What is a frontal boundary? What is a cold front? What is a warm front? What is a stationary front? What is an occluded front? What is a jet stream? Draw a picture Students will draw a picture of two toilets and explain why the toilets flush a different way in each hemisphere. Forecast Have students look at current weather and forecast the weather for the following week. Students will actually present like a forecaster on the news. GRASP Presentation and Graphic Organizer on describing weather conditions Quizzes Quiz One Over GLCE’s 1 Quiz Two Over GLCE’s 2-3 Quiz Three Over GLCE 4 Quiz Four Over GLCE’s 5-6 Unit Test Over all essential questions in unit. GRASPS Assessment (above) Describe the assessment/s and state the prompt if applicable. xF xS What type of scoring tools will be used for evaluation? x Analytic rubric x Holistic rubric x Criterion rubric x Checklist x Answer Key x Other Student Self-Assessment and Reflection: Students will have a section in the back of their science booklets explaining what they understood specifically about that day’s concept or what they are having trouble with (Science Journal). They may be asked to describe what they found to be the best part of that days lesson, or the unit as a whole. Stage 3 - Learning Plan Differentiated Instruction: C Level (30 points) 1. Vocabulary Dictionary of key terms from the unit (in booklet) * (10 points) 2. “Do Now” log of bell work “before” activities* (10 points) 3. Foldable of the atmosphere at different elevations* (10 points) UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 6 B Level (60 points) (Students need to pick one activity each from the following clusters: cluster 1 and 2, cluster 4 and 5, cluster 7 and 8. 3, 6, and 9 are required activities. Students will turn all work in.) 1. Create a graphic organizer comparing and contrasting the relationship between weather and climate. (10 points) 2. Pretend weather and climate are people, and create a Facebook page for each. Then create a “things friends have in common” list, with 5 things that weather and climate have in common. (10 points) 3. Create a story board to describe how different weather occurs due to the constant motion of the atmosphere from the energy of the sun reaching the surface of the earth. (10 points) * 4. Create a story, comic strip, or story board that explains how the temperature of the oceans affects the different climates on Earth because water in the oceans holds a large amount of heat. (10 points) 5. Create a graphic organizer that explains how the temperature of the oceans affects the different climates on Earth because water in the oceans holds a large amount of heat. (10 points) 6. GRASP: Presentation and Graphic Organizer on describing weather conditions. (10 points) * 7. Create a diagram to describe the atmosphere as a mixture of gases. (10 points) 8. Create a brochure to describe the atmosphere as a mixture of gases. (10 points) 9. Create a graphic organizer that compares and contrasts the composition of the atmosphere at different elevations. (10 points) * A Level (60 points) 1. Unit Test* (30 points) 2. GRASP: Newscast – Weather for the Four Seasons * (20 points) *denotes mandatory activity Learning Activities: W Where are we going? To a deeper understanding of the factors that affect the weather and climate in a region. Why? Students will better understand weather forecasting in their daily life. What is expected? Students will have a complete understanding of how weather and climate are created and related. H I will hook student interest by showing them a weather forecasting clip at the very beginning of the unit, and posing the question: “Do you understand WHY this weather is occurring?” I will hold student interest through interactive activities, such as: artistic expression and creating a facebook page, student choice in layered curriculum, and alternative methods of the student “showing what they know.” E Students will be equipped to do well on this unit through journaling, a variety of lessons and assignments (both artistic and writing-based), class discussions, and their end of unit GRASP. R Students will be asked to rethink and revise their work through journaling before, during, and after the unit is completed, as well as by giving peers “two stars and a wish” after their various presentations and after going over work in peer relations. E Students will self-evaluate through journaling and a post-test reflection activity. T Learning will be tailored by using the differentiated instruction above. O The unit will be organized so that key concepts build upon one another, assignments tailored to the learning goals, and an overall aligned unit. See calendar below for day-by-day schedule. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 7 Essential Vocabulary Air mass: a widespread body of air, the properties of which can be identified as: having been established while that air was situated over a particular region of the earth's surface (air mass). Atmosphere: the gaseous envelope surrounding the earth; the air. Climate: the composite or generally prevailing weather conditions of a region, as temperature, air pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloudiness, and winds, throughout the year, averaged over a series of years. Cold front: the leading edge of an advancing mass of cold air. Compare: to examine (two or more objects, ideas, people, etc.) in order to note similarities and differences. Composition: a material formed from two or more substances. Contrast: to differ in a way that can serve to distinguish meanings. Describe: to tell or depict in written or spoken words; give an account of. Elevation: the altitude of a place above sea level or ground level. Energy: the ability to do work. Exosphere: the region of the upper atmosphere in which temperature increases continuously with altitude, encompassing essentially the entire atmosphere above the mesosphere. Explain: to make known in detail. Factor: one of the elements contributing to a particular result or situation Frontal boundary: the zone where the air masses meet when two different air masses approach each other. Gases: a substance possessing perfect molecular mobility and the property of indefinite expansion, as opposed to a solid or liquid. Heat sinks: Jet stream: any of the high-speed, high-altitude air currents that circle the Earth in a westerly direction. Mesosphere: the mesosphere is above the stratosphere. Here the atmosphere is very rarefied, that is, thin, and the temperature is decreasing with altitude, about –130 Fahrenheit (-90 Celsius) at the top. Meteorologist: the science dealing with the atmosphere and its phenomena, including weather and climate. Mixture: any combination or blend of different elements, kinds, qualities. Occluded front: occurs when a cold front overtakes a warm front at the surface and a temperature contrast exists between the advancing and retreating cold air masses. Solar energy: energy derived from the sun in the form of solar radiation. Stationary front: a boundary between air masses that is neither advancing nor retreating. Stratosphere: found from about 7 to 30 miles (11-48 kilometers) above the Earth’s surface. In this region of the atmosphere is the ozone layer, which absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. The temperature increases slightly with altitude in the stratosphere. The highest temperature in this region is about 32 degrees Fahrenheit or 0 degrees Celsius. Thermosphere: starts at about 55 kilometers. The temperature is quite hot; here temperature is not measured using a thermometer, but by looking at the motion and speed of the rarefied gases in this region, which are very energetic but would not affect a thermometer. Temperatures in this region may be as high as thousands of degrees. Troposphere: the lowest atmospheric layer and is about seven miles (11 km) thick. Most clouds and weather are found in the troposphere. The troposphere is thinner at the poles (averaging about 8km thick) and thicker at the equator (averaging about 16km thick). The temperature decreases with altitude. UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University 8 Warm front: the trailing edge of a retreating mass of cold air. Weather: the state of the atmosphere with respect to wind, temperature, cloudiness, moisture, pressure, etc. Sequencing the Learning Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Pre-Assessment Test Introduce Unit Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Introduce Unit Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 B Level 1 and 2 B Level 1 and 2 B Level 1 and 2 Weather forecasting clip: “Do you understand WHY this weather is occurring?” Quiz over content goal 1 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 B Level 3 B Level 3 B Level 4 and 5 B Level 4 and 5 B Level 6 Quiz over content goals 2 and 3 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 B Level 6 B Level 6 B Level 6 B Level 6 B Level 6 Quiz over content goal 4 Monday Tuesday UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University Wednesday Thursday Friday 9 Vocabulary C: 1, 2, and 3 Vocabulary C: 1, 2, and 3 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 Vocabulary C: 1 and 2 B Level 7 and 8, 9 B Level 7 and 8, 9 Quiz over content goals 5 and 6 A Level 2: work time A Level 1 A Level 2: Explanation and work time UBD Unit Design Worksheet / Saginaw Valley State University A Level 2: Presentations Weather forecasting clip: “Do you understand WHY this weather is occurring?” 10