6th Grade Science Scales * Unit 2: Weather

5 Weeks 6th Grade Science Scales – Unit 2: Weather 2015-2016
Topic
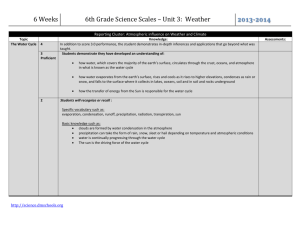
The Water Cycle 4 t
3
Proficien
1
2 http://science.dmschools.org
Reporting Cluster: Atmospheric influence on Weather and Climate
Knowledge:
In addition to score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications that go beyond the target.
Students demonstrate they have developed an understanding of:
how water, which covers the majority of the earth’s surface, circulates through the crust, oceans, and atmosphere in what is known as the water cycle
how water evaporates from the earth’s surface, rises and cools as it rises to higher elevations, condenses as rain or snow, and falls to the surface where it collects in lakes, oceans, soil and in soil and rocks underground
how the transfer of energy from the Sun is responsible for the water cycle
Students will recognize or recall :
Specific vocabulary such as: evaporation, condensation, runoff, precipitation, radiation, transpiration, sun
Basic knowledge such as:
clouds are formed by water condensation in the atmosphere
precipitation can take the form of rain, snow, sleet or hail depending on temperature and atmospheric conditions
water is continually progressing through the water cycle
The sun is the driving force of the water cycle
Student’s performance reflects insufficient progress towards foundational skills and knowledge.
Assessments:
5 Weeks 6th Grade Science Scales – Unit 2: Weather 2015-2016
Topic
Earth’s
Atmosphere and Global
Climate Change
4
3
Proficien t
1
2
Reporting Cluster: Atmospheric influence on Weather and Climate
Knowledge:
In addition to score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications that go beyond the target.
Students demonstrate they have developed an understanding of:
the atmosphere has different properties at different elevations
how global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather
oceans as an influence on climate due to water in the oceans holding a large amount of heat
how clouds, formed by the condensation of water vapor, affect weather and climate
the Sun as the driving force for all weather
collisions between air masses create severe weather
the effect of human behaviors on the levels of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere
Students demonstrate they have the ability to:
make a prediction of an area’s weather based on air pressure and movement
Students will recognize or recall :
Specific vocabulary such as: atmosphere, troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, ozone, wind, jet stream, air pressure, convection, conduction, radiation, altitude, nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, Coriolis effect, weather, climate
Basic knowledge such as:
air is made of a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen and other trace gasses
the difference between weather and climate differences in air pressure create wind
the types of clouds
oceans affect climate
the Sun provides all energy in the atmosphere for weather and climate
Student’s performance reflects insufficient progress towards foundational skills and knowledge.
Assessments: http://science.dmschools.org
5 Weeks
Sample Learner Objectives
6th Grade Science Scales – Unit 2: Weather
Topic
Suggested Instructional Resources
Textbook Resources Labs
2015-2016
PBL Ideas
(projects)
Web Resources – websites or resources on http://science.dmschools.org
definedstem.com
I can identify the sun as the driving force for weather.
I can summarize the steps of the water cycle.
I can explain the difference between weather and climate.
I can describe the composition of
Earth’s atmosphere.
I can differentiate among convection, conduction and radiation.
I can explain the relationships between human activities and global climate change
I can predict whether air masses will float or sink based on their relative densities and/or temperatures.
I can describe the process that causes wind.
The Water Cycle
Earth’s Atmosphere and
Global Climate Change
http://science.dmschools.org