Erosion - Geneva 304

River Systems
Runoff to Rivers
Runoff eventually makes its way into a river system via gullies or small streams
River systems = main stream + several feeder streams (tributaries)
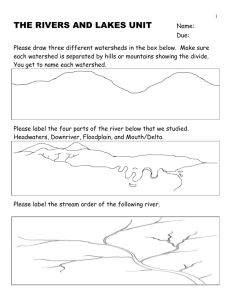
An area drained by a particular system is called a drainage basin
Largest drainage basin in the US is for the Mississippi
River o Drains everything from the Rockies to the
Appalachians
Features of a Stream
Channel – path that a stream follows
Headwaters – origin of a stream
Stream load – the amount of sediment a stream carries
Gradient – slope of the land the stream flows over
Stream Development
Young o V-shaped valleys o Many rapids o Carries all sizes of sediment
(due to rapid water flow) o Rapid down-cutting erosion
(makes river deeper)
Mature o Valley widens o Stream velocity a bit slower o Carries only medium to fine sediment due to slower speed o Begins to develop a floodplain o River begins to curve, creates side cutting erosion (widens river)
Old o U-shaped valley o Slow moving current, but wide channels (move a lot of water) o Carries only fine sediment (due to slow velocity) o Large, wide floodplain o Large curves (called meanders) o Meander cutoffs - large curves that cut themselves off from the main channel o Oxbow lakes - curved lakes left behind by meander cutoffs o Natural levees - sediment humps on the side of the channel left behind by floodwaters
Flooding
Streams and rivers flood every year; severity of flood varies statistically o Small flood => almost a 100% chance each year o Large flood => about a 1% chance each year
The larger and/or older a river, the greater the potential for an extensive and damaging flood