Section 13.1 streams and rivers - Link 308
advertisement

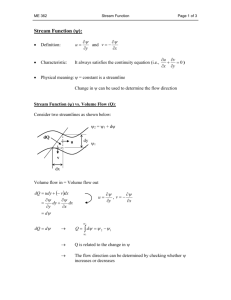
Tributary Is a stream that flows into a larger stream or river. River system is a river and all of its tributaries. - Also referred to as the watershed, is all of the land that drains into a river system A divide is a large landmass that separates two drainage basins. Ex. Rocky mountains. 3 factors that determine a streams velocity. Velocity is the distance water travels in a given amount of time. gradient discharge channel shape Gradient how steep or flat a river is. The steeper the gradient the faster the river will flow. Discharge is the amount of water that passes by a certain point in a given amount of time. Discharge varies depending on the time of year and the weather conditions. Channel is the path that makes up a river. The velocity of a river depends on the depth of the channel, and how winding it is. A shallow river with many boulders has a lot of surface area contacting the river creating friction and slowing the water down Stream Erosion and Deposition Depositon The Process by which the material is deposited Pothole Deep circular basin developed when the river develops small whirlpools Load Downstream Eroded rock and soil By action of the river Suspension Muddy looking Clay, silt and fine sand In between the water molecules. Bed Load Rock transport Capacity Total amount of sediment the stream can carry Competency Maximum size of particle the stream can carry Increase velocity more movement Decrease velocity more deposition Everything held by the water will be deposited. Deposition Fine sediment River slows down to a body of water Describe how rivers wear down rock material. How does a river’s velocity affect its competence and capacity? Under what circumstances do rivers and streams deposit sediment? A river carrying sediments in suspension curves back and forth sharply. Predict what you might find if you studied deposits on the stream bed. Explain your predictions. River Valleys Land is worn away at the head of a river/stream. The level at which the stream can go down to. Set by the body of water the stream enters Differential erosion. Hard top Soft under-strata What is a flood? When a river or stream overflows it’s banks A floodplain is the area along a river that is most susceptible to flooding. A river flowing through a floodplain typically winds back and forth is broad curves called meanders Created because erosion is most rapid on the outside of a river bend and channel is usually deepened there As the water swings wider it could break through a meander and result in an oxbow lake: a curved body of water when deposited sediments separate a meander from it’s river Natural levees form when thick deposits of sediments form ridges on the side of the river after a flood. Restoring natural plant life in areas along rivers. Dams can help to control the amount of water moving downstream. Artificial levees such as sandbags can be put into place as a temporary solution. Maintain safe floodplains by not allowing people to develop the land in a floodplain.