274400.sazetak
advertisement

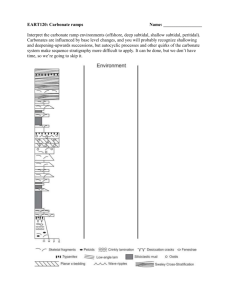
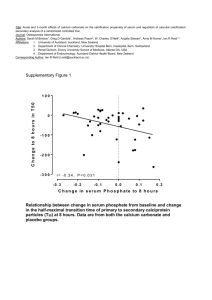
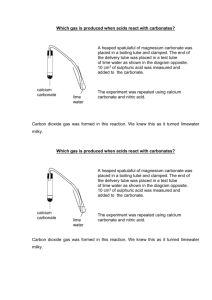
NOVEL METHOD FOR PRECIPITATION OF CALCIUM CARBONATE POLYMORPHS OF UNUSUAL MORPHOLOGIES Ivan Sondi1, Srečo D. Škapin2 , and Branka Salopek-Sondi3 (1) Center for Marine and Environmental Research, Ruđer Bošković Institute, Zagreb, Croatia (sondi@irb.hr), for Advanced Materials, Jožef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia (sreco.skapin@ijs.si), (3) Department for Molecular Biology, Ruđer Bošković Institute, Zagreb, Croatia, (salopek@irb.hr), (2) Department Precipitation processes of carbonate particles of different size, shape, and surface properties have been intensively investigated due to their importance in geo- and biosciences, and in numerous industrial applications. A novel precipitation process, effectuated through catalytic decomposition of urea at elevated temperatures and by using the enzyme, urease, was employed to precipitate calcium carbonate polymorphs in a reacting solution of calcium salts (1-2). The structure and morphology of the obtained precipitates were investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The effects of various experimental conditions on the precipitation processes, such as the concentration of reactants, temperature, aging time, agitation and mixing procedures were investigated. It was found that the formation of different polymorphs of calcium carbonate, characterized by unusual and fascinating morphologies, was effected mostly by agitation and concentration of reactants as well as by mixing procedures. This study also exemplifies recently renewed mechanism in which some of carbonate colloids can be formed through aggregation of preformed nanosize crystalline particles (3,4). Understanding the latter processes may lead to new strategies for the synthesis of calcium carbonate precipitates of desirable structural and morphological properties. Literature: 1. Sondi, I. Matijević E. (2001): Homogenous precipitation of calcium carbonate by enzyme catalyzed reactions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 238, 208-214. 2. Sondi, I., Matijević, E. (2003): Homogeneous precipitation by enzyme-catalyzed reactions. 2. Strontium and barium carbonates. Chem. Mater. 15, 1322-1326. 3. Škapin, S.D., Sondi, I. (2005): Homogeneous precipitation of mixed anhydrous Ca-Mg and Ba-Sr carbonates by enzymecatalyzed reactions. Cryst. Growth Des. 5, 1933-1938. 4. Sondi, I., Salopek-Sondi, B. (2005): The influence of the primary structures of urease enzyme on the formation of CaCO 3 polymorphs: A comparison of plant (Canavlia ensiformis) and bacterial (Bacillus pasteurii) ureases. Langmuir 21, 8876-8882. a b c d e f Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of obtained calcium carbonate particles: (a) spherical vaterite particles, (b,c) “flower-type” vaterite particles, (d) "needle-like" aragonite particles, (e) “root-type” aragonite particles, and (f) "screw-growth" rhombohedra of calcite particles.