European Middle Ages
advertisement

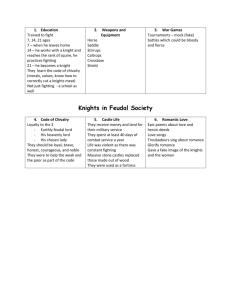
European Middle Ages Section 1: Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms Many Germanic kingdoms that succeeded the Roman Empire are reunited under Charlemagne’s empire Invasions of Western Europe Effects of Constant Invasions and Warfare o Germanic invaders overrun western Roman Empire in 400s o Fighting disrupts trade and government; people abandon cities o Marks the beginning of the Middle Age – period from 500 to 1500 The Decline of Learning o As cities are abandoned, level of learning declines o Knowledge of Greek language and culture is almost completely lost Loss of a Common Language o Introduction of German language changes Latin; dialects develop (French and Spanish) Germanic Kingdoms Emerge Years of Upheaval Between 400 and 600 o Germanic kingdoms replace Roman provinces o Continual wars change borders between kingdoms o The Church provides order and security The Concept of Government Changes o Germans held together by family ties and loyalty, not government o Small communities are governed by unwritten rules and traditions o Germanic warriors pledge loyalty to their chief; live in lord’s hall Clovis Rules the Franks o Germanic people called Franks hold power in Roman province of Gaul o Clovis, leader of the Franks, converts to Christianity in 496 o Leads warriors against other Germanic tribes o Unites Franks into one kingdom with Church’s help by 511 Germans Adopt Christianity How the Church Spread o Frankish rulers convert Germanic peoples to Christianity o Missionaries travel to convert Germanic and Celtic groups Monasteries, Convents, and Manuscripts o Church builds monasteries – where monks live to study and serve God o Italian monk, Benedict, writes rules that govern monastic life o His sister Scholastica adapts rules for nuns living in convents o Monks establish schools, preserve learning through libraries Papal power Expands Under Gregory I o In 590, Gregory I, also called Gregory the Great, becomes pope o Under Gregory, church becomes secular – a political power o Pope’s palace becomes center of Roman government o Uses Church money to raise armies, care for poor, negotiate treaties o Establishes a Christendom – churchly kingdom fanning out from Rome An Empire Evolves Europe’s Kingdoms o The Franks control largest and strongest of Europe’s many kingdoms o By 511, Frankish rule extends over what is now France Charles Martel Emerges o Most powerful official in kingdom is major domo – mayor of the palace o In 719, major domo Charles Martel becomes more powerful than the king o Defeats Muslims from Spain at Tours in 732; becomes a Christian hero o Son, Pepin, begins Carolingian Dynasty – family that ruled 751-987 Charlemagne Becomes Emperor Charlemagne Leads a Revival o Charlemagne limits noble’s power by governing through royal agents o Encourages learning and orders monasteries to open schools Charlemagne’s Heirs o Charlemagne dies in 814; his son, Louis the Pious, rules poorly o Louis’s 3 grandsons fight for the control of empire o In 843 they divide empire into three kingdoms; sign Treaty of Verdun Section 2: Feudalism in Europe Feudalism, a political and economic system based on land-holding and protective alliances, emerges in Europe Invaders Attack Western Europe The Vikings Invade from the North o Warlike Vikings raid Europe from Scandinavia – Denmark, Norway, Sweden o Viking long ships sail in shallow water, allowing raids inland o Eventually, many Vikings adopt Christianity and become farmers Magyars and Muslims Attack from the East and South o Magyars (Hungarian nomads) invade western Europe in late 800s o Muslims strike north from Africa, attacking through Italy and Spain o Vikings, Magyar, Muslim invasions cause widespread disorder, suffering A New Social Order: Feudalism Feudalism structures society o 850 to 950, feudalism emerges – political system based on land control o A lord (landowner) gives fiefs (land grants) in exchange for services o Vassals – people who receive fiefs – become powerful landholders Feudal Pyramid o Power in feudal system much like a pyramid, with king at the top o Kings served by nobles who are served by knights; peasants at bottom o Knights – horseman – defend their lord’s land in exchange for fiefs Social Classes are well defined o Medieval feudal system classifies people into 3 social groups Those who fight: nobles and knights Those who pray: monks, nuns, leaders of the Church Those who work: peasants o Social class is usually inherited; majority of people are peasants o Most peasants are serfs – people lawfully bound to place of birth o Serfs aren’t slaves, but what they produce belongs to their lord Manors: The Economic Side of Feudalism The Lord’s Estate o The lord’s estate, a manor, has in economic system (manor system) o Serfs and free peasants maintain the lord’s estate, give grain o The lord provides housing, farmland, protection from bandits A Self-Contained World o Medieval manors include lord’s house, church, workshops, village o Manors cover a few square miles of land, are largely self-sufficient The Harshness of Manor Life o Peasants pay taxes to use mill and bakery; pay a tithe to priest o Tithe – a church tax – is equal to one-tenth of a peasant’s income o Serfs live in crowded cottages with dirt floors, straw for beds o Daily grind of raising crops, livestock; feeding and clothing family o Poor diet, illness, malnutrition make life expectancy 35 years o Serfs generally accept their lives as part of God’s plan Section 3: The Age of Chivalry The code of chivalry for knights glorifies combat and romantic love. Knights: Warriors on Horseback The Technology of Warfare Changes o Leather saddle and stirrups enable knights to handle heavy weapons o In 700s, mounted knights become most important part of an army The Warrior’s Role in Feudal Society o By 1000s, western Europe is a battleground of warring nobles o Feudal lords raise private armies of knights o Knights rewarded with land; provides income needed for weapons o Knights other activities help train them for combat Knighthood and the Code of Chivalry The Code of Chivalry o By 1100s knights obey code of chivalry – a set of ideals on how to act o They are to protect the weak and poor; serve feudal lord, God, chose lady A Knight’s Training o Boys begin to train for knighthood at age 7; usually knighted at 21 o Knights gain experience in local wars and tournaments – mock battles Brutal Reality of Warfare o Castles are huge fortresses where lords live o Attacking armies use wide range of strategies and weapons The Literature of Chivalry Epic Poetry o Epic poems recount a hero’s deeds and adventures o The Song of Roland is about Charlemagne’s knights fighting Muslims Love Poems and Songs o Knights duties to ladies are as important as those to their lords o Troubadours – traveling poet-musicians – write and sing short verses o Most celebrated woman of the age is Eleanor of Aquitaine (1122 – 1204) o Eleanor’s son, Richard the Lion-Hearted, also wrote songs and poems Women’s Role in Feudal Society Status of Women o According to the Church and feudal society, women are inferior to men Noblewomen o Can inherit land, defend castle, send knights to war on lord’s request o Usually confined to activities of the home or convent Peasant Women o Most labor in home and field, bear children, provide for family o Poor, powerless, do household tasks at young age Section 4: The Power of the Church Church leaders and political leaders compete for power and authority The Far-Reaching Authority of the Church The Structure of the Church o Power within Church is organized by statues; pope is supreme authority o Clergy – religious officials – includes bishops, priests, and others o Bishops supervise priests, settle Church disputes Religion as a Unifying Force o Religion important in Middle Ages; shared beliefs bond people o Clergy administers the sacraments – rites to achieve salvation o Village church is place of worship and celebration The Law of the Church o The Church has system of justice to guide people’s conduct o All medieval Christians expected to obey canon law – Church law o Canon law governs over political leaders through threat of Excommunication – banishment from Church, denial of salvation Interdiction – king’s subjects denied sacraments and services o Kings and emperors expected to obey pope’s commands o European Middle Ages (Ch. 13) Section 1: Charlemagne Unites Germanic Kingdoms Invasions of Western Europe Effects of Constant Invasions and Warfare o Germanic invaders overrun western __________________________________________________ o Fighting disrupts trade and government; ______________________________________________ o Marks the beginning of the _________________________period from ______________________ The Decline of Learning o As cities are abandoned, level of ____________________________________________________ o Knowledge of Greek language and culture is almost completely lost Loss of a Common Language o Introduction of German language changes Latin; ____________________________ develop (French and Spanish) Germanic Kingdoms Emerge Years of Upheaval Between 400 and 600 o ________________________________________________________ replace Roman provinces o ______________________________________________ change borders between kingdoms o The Church provides order and security The Concept of Government Changes o Germans held together by _____________________________________________, not government o Small communities are governed by unwritten rules and traditions o Germanic warriors pledge loyalty to their _______________________; live in lord’s hall Clovis Rules the Franks o Germanic people called Franks hold power in Roman province of Gaul o _______________________________, leader of the Franks, converts to Christianity in ________ o Leads warriors against other Germanic tribes o Unites Franks into one kingdom with Church’s ______________________________________ Germans Adopt Christianity How the Church Spread o Frankish rulers convert Germanic peoples to __________________________________________ o Missionaries travel to convert Germanic and Celtic groups Monasteries, Convents, and Manuscripts o Church builds monasteries – ___________________________________________________________________ o Italian monk, Benedict, writes rules that govern ________________________________________ o His sister Scholastica adapts rules for nuns living in convents o Monks establish schools, preserve learning through libraries Papal power Expands Under Gregory I o In 590, Gregory I, also called __________________________________________________________________ o o o Under Gregory, church becomes secular – ________________________________________________________ Pope’s palace becomes center of Roman government Uses Church money to raise armies, care for poor, negotiate treaties o Establishes a _________________________________________ – churchly kingdom fanning out from Rome An Empire Evolves Europe’s Kingdoms o The Franks control largest and strongest of Europe’s many kingdoms o By 511, Frankish rule extends over what is now France Charles Martel Emerges o Most powerful official in kingdom is _________________________________________________ o o In 719, major domo ________________________________ becomes more powerful than the king Defeats Muslims from Spain at Tours in 732; becomes a Christian hero o Son, Pepin, begins __________________________________ Dynasty – family that ruled 751-987 Charlemagne Becomes Emperor Charlemagne Leads a Revival o Charlemagne limits noble’s power by governing through royal agents o Encourages learning and orders _____________________________________________________ Charlemagne’s Heirs o Charlemagne dies in 814; his son, Louis the Pious, ______________________________________ o Louis’s _______________________________________________ fight for the control of empire o In 843 they divide empire into three kingdoms; sign _____________________________________ Section 2: Feudalism in Europe Invaders Attack Western Europe The Vikings Invade from the North o Warlike Vikings raid Europe from Scandinavia – _________________________________________________ o Viking long ships sail in shallow water, allowing raids inland o __________________________________________________________________________________________ Magyars and Muslims Attack from the East and South o Magyars (Hungarian nomads) invade western __________________________________________ o Muslims strike north from Africa, attacking through Italy and Spain o ____________________________________________________ invasions cause widespread disorder, suffering A New Social Order: Feudalism Feudalism structures society o 850 to 950,_______________________________________ emerges – political system ________ ______________________________________________________________________________ o A ___________________(landowner) gives ________________________ (land grants) in exchange for services o __________________________________________________________________________________________ Feudal Pyramid o Power in feudal system much like a pyramid, __________________________________________ o Kings served by nobles who are served by knights; peasants at bottom o __________________________________________________________________________________________ Social Classes are well defined o Medieval feudal system classifies people into 3 social groups ________________________________________________________________________ Those who pray: monks, nuns, leaders of the Church o ________________________________________________________________________ Social class is usually inherited; majority of people are peasants o __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o Serfs aren’t _________________________________, but what they produce belongs to their lord Manors: The Economic Side of Feudalism The Lord’s Estate o The lord’s estate, _______________________________, has in economic system (manor system) o Serfs and free peasants maintain the lord’s estate, give grain o The lord provides housing, farmland, protection from bandits A Self-Contained World o Medieval manors include lord’s house, church, workshops, village o __________________________________________________________________________________________ The Harshness of Manor Life o Peasants pay taxes to use mill and bakery; pay a tithe to priest o __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o o o o Serfs live in crowded cottages with dirt floors, straw for beds Daily grind of raising crops, livestock; feeding and clothing family Poor diet, illness, malnutrition make life expectancy ____________________________________ Serfs generally accept their lives as part of God’s plan Section 3: The Age of Chivalry Knights: Warriors on Horseback The Technology of Warfare Changes o __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o In 700s, mounted knights become most important part of an army The Warrior’s Role in Feudal Society o By 1000s, western Europe is a battleground of _________________________________________ o Feudal lords raise private armies of knights o Knights rewarded with land; _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ o Knights other activities help train them for combat Knighthood and the Code of Chivalry The Code of ________________________________________ o By 1100s knights obey code of chivalry – _____________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ o They are to protect the weak and poor; _______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ A Knight’s Training o Boys begin to train for knighthood at age ________; usually knighted at ___________ o Knights gain experience in local wars and tournaments – mock battles Brutal Reality of Warfare o _______________________________________________________________________________ o Attacking armies use wide range of strategies and weapons The Literature of Chivalry Epic Poetry o Epic poems recount a hero’s deeds and adventures o __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Love Poems and Songs o Knights duties to ladies are as important as those to their lords o __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o Most celebrated woman of the age is _______________________________________________ (1122 – 1204) o Eleanor’s son, ____________________________________________________, also wrote songs and poems Women’s Role in Feudal Society Status of Women o According to the Church and feudal society, women are _________________________________ Noblewomen o Can inherit land, defend castle, send knights to war on lord’s request o Usually confined to activities of the __________________________________________________ Peasant Women o Most labor in home and field, bear children, provide for family o _______________________________________________________________________________ Section 4: The Power of the Church The Far-Reaching Authority of the Church The Structure of the Church o Power within Church is organized by statues; _______________________ is supreme authority o Clergy – religious officials – _______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ o Bishops supervise priests, settle Church disputes Religion as a Unifying Force o Religion important in Middle Ages; shared beliefs bond people o Clergy administers the ____________________________________ – rites to achieve salvation o Village church is place of worship and celebration The Law of the Church o __________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ o o All medieval Christians expected to obey _____________________________________________ Canon law governs over political leaders through threat of _________________________________________ – banishment from Church, denial of salvation Interdiction – ____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ o Kings and emperors expected to obey pope’s commands