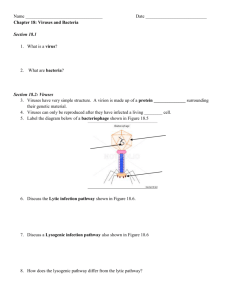
18.2 Viruses
advertisement
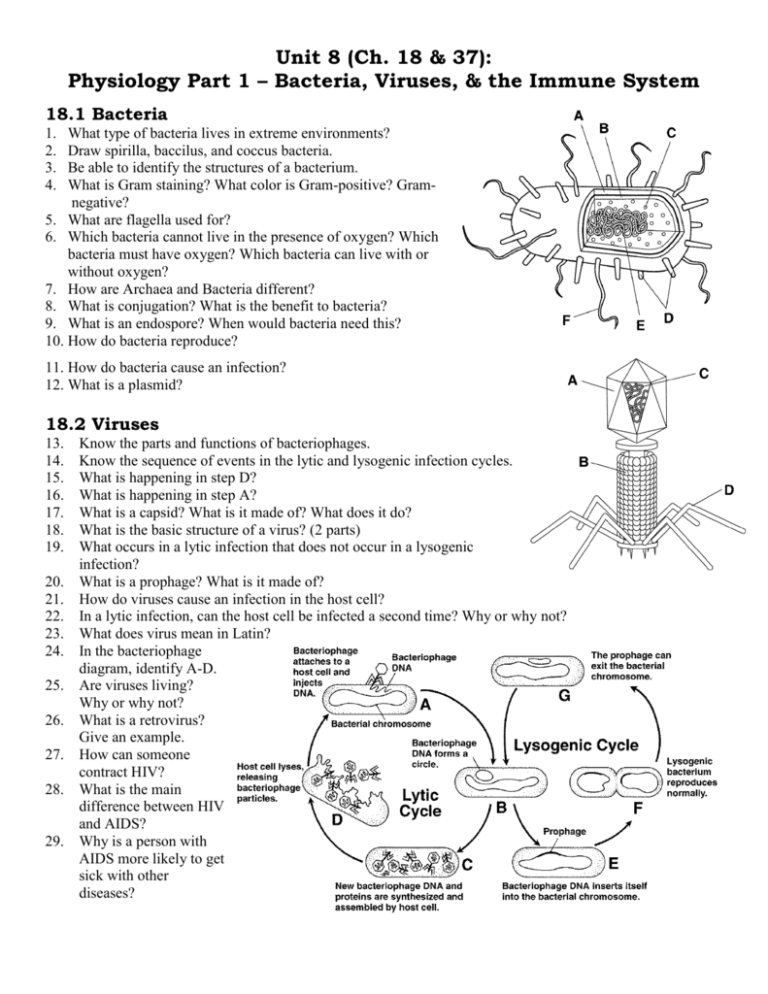
Unit 8 (Ch. 18 & 37): Physiology Part 1 – Bacteria, Viruses, & the Immune System 18.1 Bacteria 1. 2. 3. 4. What type of bacteria lives in extreme environments? Draw spirilla, baccilus, and coccus bacteria. Be able to identify the structures of a bacterium. What is Gram staining? What color is Gram-positive? Gramnegative? 5. What are flagella used for? 6. Which bacteria cannot live in the presence of oxygen? Which bacteria must have oxygen? Which bacteria can live with or without oxygen? 7. How are Archaea and Bacteria different? 8. What is conjugation? What is the benefit to bacteria? 9. What is an endospore? When would bacteria need this? 10. How do bacteria reproduce? 11. How do bacteria cause an infection? 12. What is a plasmid? 18.2 Viruses 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. Know the parts and functions of bacteriophages. Know the sequence of events in the lytic and lysogenic infection cycles. What is happening in step D? What is happening in step A? What is a capsid? What is it made of? What does it do? What is the basic structure of a virus? (2 parts) What occurs in a lytic infection that does not occur in a lysogenic infection? What is a prophage? What is it made of? How do viruses cause an infection in the host cell? In a lytic infection, can the host cell be infected a second time? Why or why not? What does virus mean in Latin? In the bacteriophage diagram, identify A-D. Are viruses living? Why or why not? What is a retrovirus? Give an example. How can someone contract HIV? What is the main difference between HIV and AIDS? Why is a person with AIDS more likely to get sick with other diseases? 37.1 & 37.3 Infectious & Noninfectious Diseases 30. What does it mean for a disease to be infectious? 31. What is a noninfectious disease? Give at least 2 examples. 32. Who was Pasteur? What was his theory? 33. Who was Koch? How did he contribute to germ theory? 34. What is a vector? Give an example. 35. What is a pathogen? List 5 of them. 36. How are diseases spread through direct contact? 37. How are diseases spread through indirect contact? 38. What are antibiotics? 39. Antibiotic resistance can occur when bacteria _____________________ (change). 40. What is an allergen? 41. What is an allergy? 42. What is anaphylaxis? 43. What substance do white blood cells release too much of in allergic reactions? 44. What is an autoimmune disease? 37.2 The Immune System 45. What are the 2 physical barriers that keep pathogens out of the body? 46. How do immunizations work? 47. What are phagocytes? 48. How do antibodies help phagocytes destroy pathogens? 49. The type of immunity that is produced in response to a pathogen infecting your body is called ____________________ immunity. 50. What are the characteristics of inflammation? Is inflammation a specific or nonspecific response? 51. Why are antigens important to the immune system? 52. What function do T cells play in antibody-mediated immunity? 53. How does interferon help protect the body? GOOD LUCK!!!!