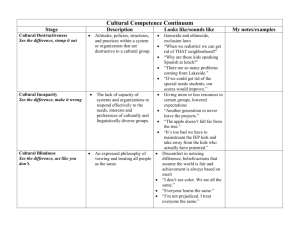
skill cultures
advertisement

Review of Current Cultural and Linguistic Diversity and Cultural Competence Reporting Requirements, Minimum Standards and Benchmarks for Victoria Health Services Project Literature Review Published by the Statewide Quality Branch Victorian Government Department of Health Melbourne Victoria August 2009 © Copyright State of Victoria, Department of Health, 2009 The publication is copyright. No part may be reproduced by any process except in accordance with the provisions of the Copyright Act 1968. Authorised by the State Government of Victoria, 50 Lonsdale Street, Melbourne. This document can be downloaded from the Department of Human Services web site at:www.dhs.vic.gov.au Acknowledgements This report was written by the Institute for Community, Ethnicity and Policy Alternatives, Victoria University Edited by: Patrice Higgins Funded by: The Department of Human Services The text represents the views of the authors and may not represent the views of the State Government. 2 CONTENTS EXECUTIVE SUMMARY .............................................................. 5 1. INTRODUCTION .................................................................... 7 2. LITERATURE REVIEW METHODS ........................................... 8 3. DEFINING CULTURE, CULTURAL COMPETENCE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY .............................................................. 9 4. RELEVANCE OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE TO HEALTH AND WELLBEING ............................................................................ 11 5. MODELS OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE.................................. 13 5.1 Discussion and Analysis: How do the models guide intervention? ......... 17 6. CULTURE AS A FACTOR IN SAFETY AND RISK MANAGEMENT IN HEALTH SYSTEMS .............................................................. 20 7. GOVERNMENT POLICY AND REPORTING FRAMEWORKS FOR CULTURAL DIVERSITY ............................................................ 28 7.1. Mapping Cultural Diversity Policy, Planning and Reporting Arrangements for Cultural Diversity ............................................................................ 28 Health Service Cultural Diversity Plan (HSCDP) ....................................... 30 7.2 Discussion ..................................................................................... 32 7.3 Selected Commonwealth and State Policies and Reporting Frameworks 35 8. STANDARDS OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE FOR HEALTH SERVICES ............................................................................... 40 8.1 Australian Standards ...................................................................... 41 8.2 International standards................................................................... 45 8.3 Discussion ..................................................................................... 46 9. INDICATORS AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS .............................. 49 10. TOWARDS A FRAMEWORK OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE ASSESSMENT .......................................................................... 55 11. CONCLUSION .................................................................... 58 REFERENCES ........................................................................... 60 RESOURCES ............................................................................ 68 Appendix 1 ......................................................................................... 68 Minimum Reporting Requirements Under HSCDP .................................. 68 Appendix 2 ......................................................................................... 70 Core Strategies of the Cultural diversity plan for Victoria’s specialist mental health services 2006–2010 ................................................................ 70 Appendix 3 ......................................................................................... 71 Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services and Standards (USA) ... 71 Appendix 4 ......................................................................................... 73 3 Lewin Group Cultural Competence Domains (2002) .............................. 73 Appendix 5 ......................................................................................... 75 Cultural Competence Assessment Tools ............................................... 75 Mental Health Assessment Tools ......................................................... 84 4 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This literature review was prepared by the Institute for Community, Ethnicity and Policy Alternative (ICEPA), Victoria University. The review was commissioned by the Statewide Quality Branch of the Victorian Department of Human Services (the department). Its main aim was to conduct a review of cultural and linguistic diversity and cultural competence reporting requirements, minimum standards and benchmarks for health services incorporating: Mapping and analysis of current department cultural diversity and cultural competence reporting requirements for Victorian health services from department and health service perspectives; Mapping and analysis of current national and international literature on cultural diversity and cultural competence focusing on reporting requirements, minimum standards and benchmarks for health services; and Examination and identification of key interventions and their enablers for cultural diversity and cultural competence together with evidence of the efficacy of these interventions within health services. A systematic approach was adopted to identify, critically evaluate and synthesise relevant information from international, Commonwealth and state documents, academic databases, refereed journal articles, government policy statements and government and non-profit organisation publications. The review included documents available from on-line sources, reports, conference papers, keynote speeches, discussion papers and websites which are commonly referred to as grey literature. Various definitions of culture, diversity, cultural diversity and cultural competence arose throughout the literature. Through analysis of these definitions, it was determined that there is no conclusive and agreed upon definition of these concepts. Cultural competence in healthcare has emerged partially as a strategy to address racial and ethnic disparities that may lead to health inequalities. Several studies, both Australian and international, have documented the benefits of a culturally competent health care system to potentially reduce health disparities among populations from culturally and linguistically diverse (CALD) backgrounds. However, there is little conclusive evidence on cultural competence framework/s and their efficacy in reducing health inequalities. Several studies document that failure to consider a patient’s cultural and linguistic issues can present risk/s to health services and their clients, especially in terms of preventable adverse events in patients of minority backgrounds. Some studies suggested that in order to minimise risks, health care organisations needed to integrate cultural competence into their internal quality improvement activities. In the review of policy and reporting frameworks for cultural diversity it was noted that there are many complex reporting and planning arrangements within the Department of Human Services. A review on standards of cultural competence found a lack of national standards in relation to the provision of culturally and linguistically appropriate health services. The National Quality Framework suggested that a standardised core set of performance measures based on cross-cultural quality issues that is broadly applicable across all healthcare settings should be adopted. 5 A number of cultural competence assessment frameworks were reviewed in the context of health care services and it was found that models of cultural competence needs to be embedded within organisational processes. From the existing models and strategies reviewed in the literature, some key headings are provided to assist in developing a range of agency specific measures and indicators. An example from the Migrant-friendly Hospitals Project highlights the initiative of the European Union in putting migrant-friendly, culturally competent health care and health promotion higher on the European health policy agenda, and in supporting other hospitals through compiling practical knowledge and instruments. The recommendations from this project were launched as the ‘Amsterdam Declaration towards Migrant Friendly Hospitals in an ethno-culturally diverse Europe’. A core recommendation from this declaration is the need to define what cultural competence means; and at a service level to: ‘find consensus on criteria for migrant-friendliness, cultural competence and diversity competence that are adapted to their specific situation; and to integrate them into professional standards and to enforce their realisation in everyday practice’. The review concludes that there is much written on cultural diversity and cultural competence in healthcare. Research indicates there are benefits of integrating cultural competence into health care delivery systems. Effective outcomes of integrating cultural competence into health services can be achieved by developing and implementing a customised holistic approach and embedding it into the organisational context with an ongoing monitoring and review system. 6 1. INTRODUCTION The Department of Human Services (the department) has commissioned Victoria University’s Institute for Community, Ethnicity and Policy Alternatives (ICEPA) to develop and implement a project plan incorporating a review of Cultural and Linguistic Diversity (CALD) and cultural competence reporting requirements, minimum standards and benchmarks for health services. The key objectives of the project are: 1. Mapping and analysis of current department cultural diversity and cultural competence reporting requirements for Victorian health services, from department and health service perspectives. 2. Mapping and analysis of current national and international literature on cultural diversity and cultural competence focusing on reporting requirements, minimum standards and benchmarks for health services. 3. Examination and identification of key interventions and their enablers for cultural diversity and cultural competence, together with evidence of the efficacy of these interventions within health services. 4. Using the results of Objectives 1-3, develop a practical strategic framework for the development of appropriate standards for cultural diversity and cultural competence interventions for Victorian health services and make recommendations as to a minimum set of standards. 5. Test the strategic framework and recommended minimum set of standards with health services and members of Cultural Diversity Committees (CDCs) at one statewide workshop and report on project findings to the Statewide Quality Branch. This literature review component of the project report incorporates the first three objectives and forms the first step in the Review of Current Cultural and Linguistic Diversity and Cultural Competence Reporting Requirements, Minimum Standards and Benchmarks for Victoria Health Services Project. The review has two overlapping and interrelated purposes: The first is to synthesize and examine the current understanding of cultural and linguistic diversity and cultural competence; measurement of cultural competence amongst health care personnel; documentation of organisational frameworks that support cultural competence, and the establishment of cultural competence reporting methodology. The second purpose of this literature review is to generate a framework to inform decisions about the scope, content, and mechanisms to enhance any existing frameworks for culturally competent health care services. 7 2. LITERATURE REVIEW METHODS Approach: This literature review adopts a systematic approach to identify, critically evaluate and synthesise relevant information. Search Strategy: A search of international, Commonwealth and state documents was conducted using various combinations of key words and phrases for example cultural diversity and cultural competence; reporting requirements and minimum standards, safety and culture in health care, measurement of cultural responsiveness, racism and safety and risk in health care settings and benchmarks for health services. A further search was carried out using academic databases for example Medline, CINAHL, and a range of ‘on line’ full text journals. The types of references used include refereed journal articles, government policy statements as well as government and non-profit organisation publications. Documents commonly referred to as grey literature available from on-line sources, reports, conference papers, key note speeches, discussion papers and websites are also included. The review notes that while there is a plethora of articles on ‘cultural competence’ there is less material on reporting and monitoring of cultural competence, and scant literature on benchmarks and indicators. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Articles were included if they defined cultural competence and cultural diversity in health settings, provided models of cultural competence in health care and explored issues in implementation of cultural competence in health settings such as planning, reporting, standards, indicators and challenges/enabling factors. As there are a large number of articles on cultural competence, those that did not relate to health settings were generally excluded. Articles covered were in English only, excluding materials that were in other languages. Limitations: The searches were conducted for publications dating back to 1990. No other limitations were set. Information Sources: A wide range of information sources were searched including: Medline Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAH) The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality website Multicultural Australia and Immigration Studies (MAIS) Cochrane Library Proquest Sage Journals on-line Google Scholar Georgetown University- National Centre for Cultural Competence website European Commission Migrant Friendly Hospitals Project website American Government Websites Commonwealth Government Websites State Government Websites (NSW, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia). 8 3. DEFINING CULTURE, CULTURAL COMPETENCE AND CULTURAL DIVERSITY Various definitions of culture, diversity, cultural diversity and cultural competence were generated from relevant literature. However before defining cultural diversity and cultural competence, it is vital to understand the concept of culture. Culture is a much written about concept; as early 1871 Edward Tylor defined it as: ‘…that complex whole which includes knowledge, belief, arts, morals, law, custom, and any other capabilities and habits acquired by man as a member of society.’ In 1952, Kroeber and Kluckhohn claimed to have identified 160 different definitions representing different groups, for example, Topical, Behavioural, Normative, Functional, Mental, Structural, and Symbolic. Given the scope and complexity of the concept, culture, resists any exhaustive or conclusive definition (Effa-Ababio, 2005). Diversity as a concept is broad and tends to refer to groups or individuals that are perceived to be different from the general community (Centre for Culture Ethnicity and Health, 2003). Cultural diversity is also another broad concept; however it tends to focus on the rights of individuals and groups. UNESCO’s Universal Declaration on Cultural Diversity, adopted unanimously in 2001, is the most articulated understanding of cultural diversity. The declaration promotes cultural diversity to the level of common heritage of humanity, implying it as ‘a source of exchange, innovation and creativity…as necessary for mankind as biodiversity is for nature’ (UNESCO, 2002). The term cultural and linguistic diversity refers to the range of different cultures and language groups represented in the population. In popular usage, culturally and linguistically diverse communities are those whose members identify as having nonmainstream cultural or linguistic affiliations by virtue of their place of birth, ancestry or ethnic origin, religion, preferred language or language spoken at home. Aboriginal organisations prefer that the needs of Australian Aborigines be considered separately, rather than under the framework of cultural and linguistic diversity (Department of Human Services, 2006 pp. 43). Although the notion of cultural competence is not conclusive there is some acceptance in the academic community about its definition as suggested by Cross et al (1989). Accordingly, cultural competence is a set of congruent behaviours, attitudes and policies that come together in a system, agency or among professionals and enable that system, agency or those professionals to work effectively in cross-cultural situations (Cross et al, 1989). Cultural competence can be viewed at an individual level whereby it is the ability to identify and challenge one’s cultural assumptions, values and beliefs (Fitzgerald, 2000). As well, it can be more than an awareness of cultural differences, as it can be used to improve health and well being by integrating culture into the delivery of health services (National Health and Medical Research Council, 2005). Efforts to define cultural competence and its application within the health care context are continuing. The National Quality Forum notes (2002) that there is an absence of standardised frameworks, logic and definition of cultural competence. While the case for the benefits of cultural competence from a clinical and business standpoint is accepted, the major challenge is how to define, assess and measure 9 cultural competence (Betancourt et al 2002, Brach and Fraser 2000). Definitions have focused on the individual or clinician level, and the organisational level. Some definitions recognise both the individual, organisational or structural aspects of cultural competence. The definition of cultural competency ‘culture’ is often reified and not treated as a dynamic and changing factor increasing the risk of perpetuating cultural stereotypes (Greg and Saha, 2006). Various definitions of cultural competence exist however, the definition by Cross et al (as noted above) seems to be most widely quoted. Although there is no consensus on a single defining there is some agreement that building cultural competence capacity will improve health care delivery to diverse populations. 10 4. RELEVANCE OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE TO HEALTH AND WELLBEING Australia is a multicultural country with approximately one in four people being born overseas. Victoria is among the fastest-growing states in Australia and according to the 2006 ABS Census, had a resident population of almost five million people. Net overseas migration has consistently accounted for more than half of Victoria’s population increase. In Victoria 23.8 per cent of the population were born overseas and an additional 19.7 per cent of Victorians, born in Australia, had either one or both parents born overseas. This diversity is growing faster than at any other time in Victoria’s history and the trend is expected to continue. The National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) points out that: All Australians have the right to access health care that meets their needs. In our culturally and linguistically diverse society, this right can only be upheld if cultural issues are core business at every level of the health system-systemic, organisational, professional and individual (NHMRC 2006, pp.1). For many migrants and refugees the impact of settlement and acculturation varies widely depending on their experience and circumstances. Health and wellbeing are governed by many factors, some outside the health system, such as housing, employment, education, community networks and supports and access to essential services. In reality the health and wellbeing of culturally and linguistically diverse communities depends on a complex balance of social, economic, and environmental factors. The promotion of healthier living for culturally diverse communities is linked to both ‘risk’ and ‘protective’ behaviours that are related to immigration, ethnicity, ‘race’ and culture. Risk factors are characteristics, variables, or hazards that, if present for a given individual, make it more likely that this individual, rather than someone selected at random from the general population, will develop a disorder (Multicultural Mental Health Australia, 2005). Protective factors reduce the likelihood of a person suffering a disease, or enhance their response to the disease should it occur (AIHW, 2002). The health status of migrants can vary according to a range of factors, which include not only country of birth and levels of English but also the process of migration, stage in the life course, community capital and support and each individual’s balance of protective and risk factors. While immigrants and refugees often enter Australia with better physical health due to screening processes (NSW Health, 2004) they may have worse levels of mental health that are associated with the stressors of migration (Reid and Tromph, 1990) and any health advantage shown by immigrants usually disappears over time. This effect has been documented for physical health outcomes such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and mental health (AIHW, 2004). The Institute of Medicine (2008) concludes that one major contributor to health inequalities is a lack of culturally competent care and that by providing culturally 11 appropriate services there is potential to reduce disparities and improve outcomes, increase efficiency of clinical and support staff and improve satisfaction among patients. ‘Culture’ is central in the delivery of health care services, since it can influence patients’ health beliefs, medical practices, attitudes towards medical care, and levels of trust. Cultural differences can impact on how health information is provided, understood, and acted upon. Clinical barriers in health care delivery could be overcome by addressing cultural differences, and result in improved access and quality of care for culturally diverse populations. Cultural competence in healthcare has emerged partially as a strategy to address racial and ethnic disparities that may lead to health inequalities. Betancourt, Green and Carrillo (2002) conclude cultural competence in healthcare systems shows the ability of systems to provide care to patients with diverse values, beliefs, and behaviours, including meeting patients’ social, cultural and linguistic needs. They state that the goal of cultural competence is to create a health care system and workforce that are capable of delivering the highest-quality care to every patient regardless of race, ethnicity, cultural background and English proficiency. Cultural competence has been promoted as a way for health services and organisations to respond effectively to the cultural and linguistic needs that patients bring to the health care encounter (US Department of Health and Human Services, 2001). It focuses on the capacity of the health system to improve health and wellbeing by integrating culture into the delivery of health services (NHMRC, 2005). Cultural competence then requires organisations to have a clearly defined and matching set of values and principles, as well as policies and structures that enable them to work effectively in cross-cultural situations. Brach and Fraser (2000) are able to demonstrate that health systems and clinicians’ ability to deliver appropriate services to diverse populations can be improved; they conclude that cultural competence should work, and found health systems have limited evidence to suggest otherwise. Anderson, Scrimshaw, Fullilove, Fielding, and Normand (2003) reviewed five interventions to improve cultural competence in health care systems, but they could not determine the effectiveness of any of these interventions because there were either too few comparative studies, or the studies did not examine the outcome measures their review was evaluating. In the Australian context, NHRMC (2006:4) notes that a health system that is culturally competent: acknowledges the benefits that diversity brings to Australian society; helps health Services and consumers to achieve the best, most appropriate care and services; enables self-determination and ensures a commitment to reciprocity for culturally and linguistically diverse consumers and their communities; and holds governments, health organisations and managers accountable for meeting the needs of all members of the communities they serve. 12 5. MODELS OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE In the closing plenary of a convention on ‘Building Culturally Competent Health Systems in California’ Joseph Betancourt, Director of the Disparities Solutions Centre, Massachusetts, General Hospital stated, ‘…ultimately what we want is a health care system that can respond to the need of any patient’. This statement begs the question, ‘what needs to be done to create a health care system that has the ability to respond to any patient’s need?’ This section will explore potential answers to that question through key models of cultural competence and their outcomes in the context of both Australian and overseas health care systems. A number of models of cultural competence have been developed, which encompass the different dimensions that cultural competence should address. In an influential model, developed by Cross et al (1989) cultural competence is envisaged as a continuum through: Cultural Cultural Cultural Cultural Cultural Cultural destructiveness incapacity blindness pre-competence competence proficiency. A key model is that developed by Campinha-Bacote (1999, 2002) who argues that cultural competence has five interdependent elements: Cultural Cultural Cultural Cultural Cultural Awareness Knowledge Skills Encounters Desire. Cultural awareness involves a process of self-examination of one’s own cultural and professional background and biases towards others and being aware of one’s own prejudices that may affect health care delivery. Cultural knowledge is gaining an understanding of the world-views of different cultural and ethnic groups, and seeking information on how diseases and health conditions affect particular groups. Cultural skill is the ability to collect relevant data on the client’s presenting problem and to know their overall health status. Cultural encounters are the process of engaging with individuals from other cultures with the view to modifying existing assumptions about a cultural group and prevent stereotyping. Finally, cultural desire is the motivation of an individual to engage in each of the stages of being coming culturally competent as described above. The progression from cultural destructiveness whereby the attitudes, policies and practices are destructive, systems not being intentionally destructive, systems being perceived as fair for all to the knowledge that systems have flaws in dealing with minority issues, respect for differences, and finally to cultural proficiency holding cultural differences and diversity in high esteem. This model represents an 13 interesting view that perceives organisations moving through two extremes on the continuum through time. Muriel Bamlett (2007) has applied this as a useful concept to understanding cultural competence in Aboriginal Children’s Services and has illustrated how this model can be used to analyse approaches by mainstream agencies to Aboriginal culture and history such as the Stolen Generations. The National Health and Medical Research Council (2006:29) model acknowledges four dimensions of cultural competence: Systemic — effective policies and procedures, mechanisms for monitoring and sufficient resources are fundamental to fostering culturally competent behaviour and practice at other levels. Policies support the active involvement of culturally diverse communities in matters concerning their health and environment. Organisational — the skills and resources required by client diversity are in place. A culture is created where cultural competence is valued as integral to core business and consequently supported and evaluated. Management is committed to a process of diversity management including cultural and linguistic diversity at all staffing levels. Professional — over-arching the other dimensions, at this level cultural competence is identified as an important component in education and professional development. It also results in specific professions developing cultural competence standards to guide the working lives of individuals. Individual — knowledge, attitudes and behaviours defining culturally competent behaviour are maximised and made more effective by existing within a supportive health organisation and wider health system. Individual health professionals feel supported to work with diverse communities to develop relevant, appropriate and sustainable health promotion programs. Health care systems, embracing this model, need to allocate appropriate resources to ensure cultural competence is embedded into organisations, for example to conduct policy, organisational and professional training and assessment procedures. Andrulis (2003) identified five dimensions that address the major causes of disparities that can exert significant influence over the success and quality of the patient-physician relationship, treatment plans, and health outcomes. These are: biological and genetic influences; differential access to care; quality of care disparities; clinical-patient perceptions and realities; language and communication barriers. In another study that focussed on reducing ethnic children’s health disparities, Andrulis (2005) suggests the need to: collect and use race/ethnicity data for the review of program, service, and Health Service effectiveness; bridge the communication divide to reduce language and communication barriers; and 14 develop knowledge and skills that integrate factors affecting children from diverse backgrounds. In doing so, oral and written materials must accommodate a diverse range of health literacy needs and reflect an understanding of life course experience. For example, understanding the role and legacy of racism and discrimination on health and familial relationships, recognising the significant influence of culture on health, and understanding the cultural context for health care decision-making is critical for effective clinical encounters. Understanding the role, norms, or customs of the family in medical decisions, healing practices, rituals, and other culturally influenced priorities must be integrated into health care interactions, as well as integrating cultural competence into quality of care. Andrulis talks of the need ‘for research to extend through and beyond the clinical encounter to address the role of the health care setting and system’ (Andrulis 2005, pp. 377), with each health care setting recognising its importance to the process. The framework proposed by Brach and Fraser (2000) is developed based on knowledge gained from fieldwork undertaken across sectors and so captures realistic issues and offers practical suggestions. It is a holistic framework that incorporates nine categories of cultural competence in health settings: Interpreter services, as the most common way to improve communication among persons who speak different languages. Recruitment and retention of minority staff or, more generally speaking, staff who reflect the demographics of the patient population. Training in cultural competence, aimed at increasing cultural awareness, knowledge and skills, leading to changes in staff (both clinical and administrative) behaviour and patient-staff interactions. Coordinating with traditional healers, health professionals needing to coordinate with these healers, as they would with any other care provider. In addition, presenting patient education in a conceptual framework that harmonises with traditional healing practices may increase the chances that patients will concur with treatment recommendations. Use of community health workers as they are known and respected by the community, and can serve as guides to the health system, (their advocacy and empowerment function is important). Culturally competent health promotion. This can take several forms: health professionals’ screening tools, brief interventions, public information campaigns. The health promotion messages can be made more culturally competent and specific. Including family and/or community members. While patient autonomy has become a core principle of Western health care, some minority groups involve family members in health care decision-making. Immersion into another culture. Immersion enables participants (health professionals) to overcome their ethnocentrism. Administrative and organisational accommodations. A variety of administrative and organisational decisions related to clinic locations, hours of operation, network membership, physical environments and written materials can also affect access to and use of health care These categories attempt to provide rigor from various points of health provision that can work at multiple levels such as organisational, community, and in education and training, recruitment, and interface between traditional healers and health 15 professionals. The conceptual framework does not address the need for additional resources to make many of these activities possible. The authors also note that there is insufficient research evidence to suggest the effect of particular cultural competence techniques on any outcomes, including racial and ethnic disparities (Brach and Fraser, 2000). Betancourt et al (2002) identified benefits of cultural competence to the health care systems by interviewing health care experts in government, managed care, academia, and community health care delivery. Based on their exploratory exercise they came up with some key suggestions for developing the cultural competence framework. Accordingly, health care requires an understanding of the communities being served including the impact of socioeconomic influences on individual patients’ health beliefs and behaviors, and how these factors interact with the health care system in ways that may prevent diverse populations from obtaining health care. Then, there is a need to devise strategies to reduce and monitor potential barriers through interventions. The authors provide a framework for the implementation of culturally competent practices based on these suggestions. The framework includes the following components: Organisational cultural competence: This involves reflection of racial and ethnic diversity in health care leadership and work force. Inclusion of community members in health care process and formally including community health advocates and recruiting staff from diverse communities would enhance cultural competence in the organisation. Systemic cultural competence: Systemic barriers such as a lack of interpreter services, culturally and linguistically appropriate health education materials can lead to patient dissatisfaction, poor comprehensive and compliance, and lower quality care. Clinical cultural competence: The role of cross-cultural education and training including education in cultural competence for senior management, health services, and staff is vital in the provision of quality care. The focus of training should be on socioeconomic factors, communication skills, and mechanisms for addressing racism and bias. Patient empowerment is also a source of cultural competence. Strategies for attaining cultural competence included: using health care purchasers (government and private), developing contractual requirements (federal and state), and formulating accreditation standards (for example, for hospitals and medical schools). Jirwe, Gerrish and Emami (2006) identified nine most frequently cited models of cultural competence and undertook a content analysis that revealed four themes: 1. An awareness of diversity among human beings to provide a culturally competent care; this is based on the premise that to know the other culture one needs to know one’s own. 2. An ability to care for individuals requires the need to communicate effectively with the clients to know the client needs and their belief systems and to develop a mutually acceptable health management plan; 16 3. A non-judgemental openness—an aspiration on the part of the health service to overcome their own prejudices, in order to provide culturally sensitive care; and 4. Enhancing cultural competence as a long-term continuous process that requires learning, reflection and improvement on the part of Health Services. Romeo (2007, pp. 206) states that cultural competence is a ‘learning process that enables individuals and organisations to function effectively in the midst of cultural difference’. He points to the need to view cultural competence as an ongoing process of organisational transformation in a continuum from early to later stages of development. This means, that for health care organisations to become more culturally competent they will need to engage in a change process of organisational transformation. This entails engaging in a change process from a monoculture to a pluralistic environment, or an environment that accepts and integrates people from diverse cultural backgrounds. A number of models of organisational change for cultural competence have been put forward which develops cultural competence in agencies. Tirado (1998) proposes a five-stage model of organisational change: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Culturally Culturally Culturally Culturally Culturally resistant unaware conscious insightful versatile. Similarly, Dreachslin (1996) proposes a five-stage change model from affirmative action to valuing diversity encompassing a number of dimensions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Discovery Assessment Exploration Transformation Revitalisation. 5.1 Discussion and Analysis: How do the models guide intervention? All these models have both strengths and weaknesses. The models point to elements of change: Identifying where and how change can occur along a continuum; and Suggesting that the cultural continuum is not an end point but an ongoing process. The usefulness of the models lies in unpacking the different dimensions of what they suggest might constitute cultural competence and in determining strategies for action. As noted earlier in the paper there is no conclusive definition of cultural competence, and that the notion of culture tends to be oversimplified in the notion of cultural competence (Gregg and Saha, 2006). Cultural competence models tend not to consider the structural causes of health care inequalities (Gregg, Bussey-Jones, Fernandez and Lemon, 2005). However as cultural competence is gaining popularity 17 in health care and social policy there is a need for a clearly defined and agreed upon definition, framework, and criteria to implement and assess its efficacy. There are a number of assessment tools that have been developed (see below) as instruments to measure change. Berson and Iscel (2006) advocate a case for a culturally inclusive holistic approach to implementing cultural competence through various initiatives, projects and strategies in order to reach different target groups in the community. This approach has been used at the Ethnic Disability Advocacy Centre, in Western Australia, and has resulted in many positive outcomes for individuals, industry and the community. The approach includes provision of services such as: employment, independent living, education, home care, health, recreation, transport, and advocacy taking into consideration cultural care, cultural values, cultural responsibilities and cultural practices. At the same time vital feedback from the consumers and carers is received and utilised to further improve services. This inclusive system of service delivery strives for substantive equality with both health service and the consumers. It illustrates provision of services in a culturally competent manner, as consideration is given to cultural care, values, responsibilities and practices. In some ways this approach is similar to a quality assurance system whereby quality of a system is improved through monitoring and feedback. The Centre for Cultural Ethnicity and Health (2003) conclude that quality improvement can provide a broad framework for responding to the needs of individuals and groups from non-English speaking backgrounds. They suggest the following characteristics to be associated with organisations that continually improve their performance: a patient/client group focus; strong leadership; a culture of improving; evidence of improved outcomes and a commitment to striving for best practice. From the above example, it can be assumed that in order to ensure that the needs of individuals and groups from Non-English speaking and CALD backgrounds are met the issue of equity needs to be treated in the same manner as the issue of quality. In an effort to address cultural diversity in Australian health services, a study was undertaken by Allotey, Manderson and Reidpath (2002) that used applied anthropological approaches to negotiate style and content for a set of resource materials designed to be used by health Services in community health and hospital settings. The resulting guide shows best practice for clinical care regardless of cultural or linguistic diversity, and would assist health services to avoid stereotyping by encouraging staff to ask their patients questions. This approach is based on the philosophy that rather than using a pre-existing checklist on cultural imperatives to obtain cultural knowledge a health care professional would ask their patient ‘who is the cultural expert’ not them. It requires a respect for the ‘expertise’ of the patient and incorporates the active involvement of each patient and their family/carers. Australian Health Minister’s Advisory Council (2004) advocated an Indigenous framework that included knowledge and awareness, skilled practice and behaviour, strong relationships and equity of outcomes. This model was grounded on the premise that an understanding of cultural heritage coupled with formal education and training would instigate a change in attitudes and behaviour that then needs to be endorsed through a strong management process. The model requires a balanced workforce inclusive of Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islander people; management 18 being sensitive to cultural needs and risk management that reflects cultural differences. It proposed the need for equity of outcomes for both individuals and communities achieved through quality assurance mechanisms. Anderson et al (2003) reviewed five interventions to improve the cultural competence of health care systems. The interventions included: 1. programs to recruit and retain staff reflecting cultural diversity of the community served 2. use of interpreter services for clients with limited English proficiency 3. cultural competence training for healthcare worker 4. use of linguistically and culturally appropriate health education material 5. culturally specific health care settings. The authors state they could not determine the effectiveness of these interventions because there were either too few comparative studies, or the studies did not examine the outcome measures evaluated in the review. These outcomes were: client satisfaction with care, improvement in health status, and inappropriate racial or ethnic differences in use of health services or in received and recommended treatment. The major drawback of this review is that the interventions were carried out over time and in different settings. Perhaps the results would have been different if the interventions were undertaken in conjunction with other changes at organisational level such as commitment at senior management level with a defined plan and allocation of resources. The models described in this section provide some guidance for interventions, and specific examples have been provided. While we are aware that there is good practice, the literature on this field is scant. We were unable to find any further studies evaluating the success or impact of these interventions. 19 6. CULTURE AS A FACTOR IN SAFETY AND RISK MANAGEMENT IN HEALTH SYSTEMS The benefits of integrating cultural competence into health care have been well established. According to Stewart (2006) culturally competent health care is a good business practice, a better use of resources, and helps to: improve access and equity for all groups of population; improve consumer health literacy and reduced delays in seeking health care and treatment; improve communication and understanding of meanings between health consumers and Health Services; improve patient safety and quality assurance, and improve public image of a health service. Most of the practice frameworks in Australia have engaged with cultural diversity in heath care from an inclusion and multiculturalism perspective. There are other related ways to consider ‘culture’ in health systems. The following section will discuss key issues and challenges of integrating cultural competence into health care. Safety and Managing Risk Several studies show that minority and migrant patients are not receiving the same level of health care in terms of diagnosis, treatment and preventative services that the average population receive (Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2006; 2007) and are less likely to receive the same level of care for numerous health issues including: less aggressive treatment of colorectal cancer; they receive fewer orthopaedic procedures (Ronsaville and Hakim, 2000) more misdiagnosis of mental illness with less adequate treatment (Fiscella, 2002). More recently, Paradies (2006) found that the relationship between discrimination and poor mental health is well established. Overall, this literature suggests that that in Australia and internationally the health status of racial and ethnic minority groups tends to be poorer than that of the average population of the countries in which they reside (Anderson et al 2003; Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2007; Kelly and Bancroft, 2007; Kreps, 2007; King et al, 2008; Like, 2007; Serizawa, 2007; Smith and Betancourt et al, 2007). From these studies, we can conclude that the health disparities may be a result of inadequate interaction between health and culture and/or due to the inability of healthcare systems to address the health care needs of individuals from CALD background. With regard to the Australian context, Johnstone and Kanitsaki (2006) contend that those responsible for the design and delivery of health care can do more to improve the status quo in regard to ensuring the responsiveness of the Australian health care system to the health and care needs of resident minority racial and ethnic groups, and that much more needs to be done. 20 These issues offer insights into what health services in Australia should be doing. NHMRC (2005:16) point out that for the health sector in Australia will need to: Address similarities and differences within communities based on gender, age, length of stay, literacy and beliefs; Implementing policies to ensure equity and access to health services and promotion for a diverse population; Plan and delivering culturally competent and appropriate health promotion and health services; Address systemic attitudes to cultural diversity that can influence how communities survive and succeed; Address research gaps about the contribution of systemic risk factors (such as access to health services) to inequalities in health for CALD background communities; and Develop and maintain a culturally competent health workforce. According to Bischoff (2003) a number of factors are likely to be relevant in culture as a factor in safety and risk management. These can include a trajectory of errors and risks in health systems relating to: Diagnostic testing Medication Pain management Medical follow-up Admission Referral Food and diets Patient adherence Patient information/understanding Patient reporting/complaints Patient participation. The Institute of Medicine (2002) in USA argues that patient safety is not solely about addressing general systems issues to prevent the failure of a planned action to be completed as intended or the use of a wrong plan to achieve an aim (such as administering the wrong medication or dosage). It also entails: avoiding misdiagnosis; preventing patients from exposure to unnecessary risks; and ensuring informed consent. Similar issues are confirmed by Flores (2000) in that failure to consider a patient’s cultural and linguistic issues can result in: Inaccurate histories Decreased satisfaction with care Non-adherence Poor continuity of care Less preventive screening Miscommunication Difficulties with informed consent Inadequate analgesia A lower likelihood of having a primary care provider Decreased access to care Use of harmful remedies; delayed immunisations Fewer prescriptions. 21 These issues clearly suggest risk to both health services and their clients. The stated mission of the Australian Council on Healthcare Standards (ACHS), the national independent bodies which determines accreditation standards for health services, is to ‘improve the quality and safety of health care’ this includes cultural safety (http://www.achs.org.au). However, there is no doubt that every aspect of care delivered to culturally and linguistically diverse clients has the potential to be less than optimal if language and cultural barriers are not addressed as a matter of priority. A recent study conducted by Johnstone and Kanitsaki (2007) found that most participants interviewed had not previously heard of the term ‘cultural safety’ before receiving information from the researchers. On a more positive note however, it was also noted that participants had a sense that cultural safety was a complex process primarily concerned with health services ‘doing things safely’. This they believed could be achieved by ensuring that patients from minority racial and ethnic backgrounds got safe care and did not suffer mishaps and harm because of ineffective communication or because of lack of cultural awareness on the part of staff. A lack of risk management of cultural differences can lead to major issues for both health services and recipients. According to Johnstone and Kanitsaki (2006) issues of culture and language and the risks associated with cultural misunderstandings and failure to use professional health interpreters have long had legal implications in terms of preventable adverse events in patients of minority backgrounds. These authors cite many examples of litigation. They highlight the need for a more strategic and systematic approach to health service delivery to culturally and linguistically diverse groups and the need to set as a national priority the ‘alignment of cultural safety and cultural competence initiatives with national and local organisational clinical risk management programs and related patient safety and quality care initiatives.’ Proposed Strategic Framework and Standards Developing and implementing a national strategic framework for improving culturally and linguistically appropriate services in healthcare in Australian states and territories. Developing and operationalising national standards for culturally and linguistically appropriate services in healthcare in Australian states and territories. The standards developed should have their focus mandates, guidelines, and recommendations pertaining to: o Culturally safe and culturally competent care (including culturally competent and safe organisations) o Language access services o Organisational supports for cultural safety and cultural competence (including mandates for funding bodies to ensure the provision of appropriate human resources and funding). Central to this, Johnstone and Kanitsaki (2007 pp.181) highlight the need to develop and implement a national agenda for research on cultural safety and cultural competence in healthcare under the auspices of NHMRC/ARC. 22 Quality of Care and Culture It is noted by Omeri (2004:26) that governments hold health services accountable for delivering services that are appropriate for consumers from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds, with the aim to reduce racial, ethnic and social disparities in health care and health outcomes. This raises the question of cultural competence as an issue of quality and quality assurance. Organisations need to integrate cultural competence into their internal quality improvement activities; this can be fundamental to an organisation-wide approach to planning and implementation of continuous improvement in performance. Performance measures that relate cultural competence as part of overall performance management will assist in ‘culture’ being included in quality assessments. Including these measures in performance management systems elevates their importance for the institution. There is substantial evidence that language barriers and miscommunication have adverse affects on the quality of care received, patient satisfaction and patient health outcomes (Bischoff, 2003; Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2007; Kelly and Bancroft, 2007; Markove and Broom, 2007). The quality of physician/patient communication affects outcomes, with many at double risk: at risk of receiving less optimal care because they are part of a minority community and the additional risk posed by language barriers (Stewart et al, 2000; Bischoff, 2003). The standard of patient-provider communication is a strong indicator of the quality of health care provided. According to Bischoff (2003) less satisfactory aspects of care in language discordant consultations lead to issues with quality such as: meeting patients’ needs giving explanations showing respect during the consultation process giving follow-up information. Lack of explanation about medication correlated with later non-adherence and patient dissatisfaction (Manderson and Allotey, 2002); poor compliance to medications and health promotion strategies, poorer health outcomes (Brach and Fraserirector, 2000; Flores, 2000) was also noted. In addition, it was found that patients were more likely to miss follow-up appointments and skip medication and more likely to use hospital emergency rooms and have longer median in-patient days in hospital (Levin-Zamir, 2007). Research tells us that there is a conclusive link between cultural and language considerations in clinical contexts. However, Johnstone and Kanitsaki, (2006:383) point out that, researchers are slow to demonstrate that link. These authors argue that patient safety programs tend to underestimate or understate the critical relationship that exists between culture, language and safety and quality of care and that if this issue is not addressed patients from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds are exposed to preventable risks. Betancourt (2006a) reviews specific quality improvement approaches, such as disease management (DM) and the chronic care model (CCM), and identifies areas where cultural competence could be embedded: Identify patients who need care: Since both the CCM and DM create registries of patients with specific chronic conditions (for example, diabetes), a culturally competent approach would ensure that these registries are stratified by race, 23 ethnicity, and language proficiency and thus geared to identify racial/ethnic disparities in health care. Provide care by tailoring the methods used to the patient's needs: In CCM and DM programs, physicians, case management nurses, and other members of multidisciplinary care teams seek to communicate with patients outside of the traditional office visit, for example, through telephone contact, e-mail, and group visits. A culturally competent approach would establish ways to communicate with patients with limited English proficiency, limited health literacy, alternative health beliefs, and other needs. Support physicians and multidisciplinary teams in their clinical decision-making: Once sociocultural barriers to care are identified and interventions to address them are put in place, physicians could be enlisted to help. For example, physicians could be provided with information solicited by other health care team members regarding patients' understanding of their conditions or their fears and concerns about a medication. Thus, physicians' clinical decision-making and care management strategies could be informed by information about patients' sociocultural barriers to care and can engage in culturally competent approaches to address them. Support patients in their ability to help manage their own illnesses: To make this process culturally competent, educational information could be provided to patients in the appropriate languages and reading levels. In addition, selfmanagement advice and strategies should take into account key issues related to patients' social context, such as their physical environment and ability to exercise. Provide physicians, teams, and physician organisations with feedback on their performance: Stratifying performance feedback by race, ethnicity, culture, and language proficiency would enable health teams to identify issues as they arise, and address them as they emerge in distinct populations. Patient Centred Care and Culture Patient centred care is defined as care that is respectful and responsive to individual patient preferences, needs and values and that these values guide all clinical decisions (Beach and Saha et al, 2006). Evidence exists that health services who are at the forefront of caring for people from CALD backgrounds do not have an acceptable level of knowledge and understanding of the nature and implications of cultural competence in health care (Chenoweth, Jeon and Burke, 2006; Campesino, 2006: 298; Cioffi, 2005; Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2007; Smith and Betancourt, 2007; Westwood, 2008). When health services fail to understand socio-cultural differences between themselves and their patients, communication and trust between them may suffer leading to a perceived or actual diminishment in the quality of care expressed by patients (Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2006). Both patient-centeredness and cultural competence aim to improve health care quality, but each emphasizes different aspects of quality. The primary goal of the patient-centeredness movement has been to provide individualised care and restore an emphasis on personal relationships. It aims to elevate quality for all patients. Beach et al (2006) point out that there is congruence between cultural competence and patient-centred care. They state: ‘…to deliver individualised care, a provider must take into account the diversity of patients' perspectives, and so—to the extent that patient-centred care is delivered universally—care should become more equitable. Likewise, to the extent cultural 24 competence enhances the ability of health care systems and providers to address individual patients' preferences and goals, care should also become more patientcentred’ (2006). Smith (2002) and the Department of Human Services (2008) suggest that migrant and minority health care issues need to be framed as quality issues; and that interventions need to focus on the quality of overall care at both individual and organisational levels. Congruent with this view Johnstone and Kanitsaki (2007) note, that cultural safety should be viewed both from the perspective of the consumer and the Health Service. Therefore changing the attitudes and behaviour is necessary in order to achieve results in the medium and long term, as there is evidence that institutional discrimination has an influence both on health outcomes and on community attitudes (VicHealth, 2007). It is noted in the Lewin Report (2002) that the multifaceted and interconnected nature of cultural competence domains tend to overlap and do not occur in mutually exclusive categories. Congruent with this view the Australian Resource Centre for Healthcare Innovations (ARCHI: 1) provide this definition of a culturally competent health care system: ‘…staff within a culturally competent health care system honour and respect beliefs, interpersonal styles, attitudes, and behaviours of individuals, families and communities they serve. Cultural competence is a life-long process which includes the examination of one’s own attitudes and values, and the acquisition of knowledge and appreciation of cultural differences and similarities within, among, and between groups. A culturally competent system of care reflects and responds to the communities it serves through its administrative policies and procedures, hiring practices, training and professional development, and the active participation of community members and consumers. Self-assessment, culturally based needs assessments, and the active incorporation of findings from these assessments into practice are essential elements of culturally competent systems.’ Patient-centred care can be described generally as an approach that emphasises attention to patients’ psychosocial as well as physical needs. The implication for CALD clients is that their cultural needs, histories and social contexts that impact on health will be taken into account. This approach also emphasises that treatment choice takes patient preferences into account, and that self-care is supported as well as treatment. Central to this is the development of a sense of partnership in care, and facilitation of patient involvement in decision making about treatment decisions; if a service is not culturally sensitive, then partnership with patients in care will be ignored. This will impact negatively on communication about diagnosis and treatment. Patients have been found to prefer patient-centred care, and those who receive it, also report better health outcomes (Little et al, 2001). According to Smith and Betancourt et al (2007) in order to address racial and ethnic health disparities from the consumer provider perspective it is necessary to examine and understand attitudes, such as mistrust, subconscious bias, and stereotyping, that health service staff and patients may bring to the clinical encounter. In order to attain higher levels of quality of care for CALD clients within hospital systems, health services must firstly be made aware of the impact of social and cultural factors on health beliefs and behaviours; understand the impact of stereotyping (Taylor and Lurie, 2004); be equipped with the tools and skills to manage these factors appropriately through training and education and they should empower patients to be active partners (Betancourt and Carrillo, 2002; Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2007). 25 Lewin, Skea, Entwistle, and Zwarenstein (2001) undertook a study on patientcentred approach in clinical consultations and concluded that interventions to promote patient-centred care within clinical consultations may significantly increase the patient centredness of care. However, there is limited and mixed evidence on the effects of such interventions on patient health care behaviours or health status; or on whether these interventions might be applicable to Health Services other than physicians. The Victorian Government Department of Human Services has commissioned the National Ageing Research Institute to support and evaluate best practice in personcentred health care in Victorian Health Services (Dow, Haralambous, Bremner, and Fearn, 2006). The aim of this initiative is to make sure that older people are being cared for in the context for their individual situation, and to empower them and the people who care for them to be involved in decision-making. The Program delivers a strategic and comprehensive response to assist staff in providing quality care to patients from CALD backgrounds. It includes co-ordination of language services, including interpreting and translating, staff development, and policy and procedure development and implementation. Key issues in person-centered care involve effective participatory approaches. The Department has identified the following key priority actions: Promote the rights and responsibilities of patients to the community, consumers and carers; Communicate clearly and respectfully with consumers and carers; Provide accessible information to consumers, carers and community members about health care and treatment; Communicate and provide information about treatments and care to consumers and carers that is developed with consumers and, where appropriate, carers listen and act on the decisions their consumers make about their care and treatment; Integrate participation of consumers, carers and community members, representatives or nominees into the quality and safety program; Community representatives or nominees to be involved in the review of system level issues regarding consumer and carer feedback and complaints; Include the involvement of consumers, carers, community members, representatives or nominees in all aspects of the organisation’s planning and development; Provide staff training and education on how to use the different types of participation; Ensure position descriptions include participation component ; and Evaluate, monitor and report on participation to the community and the Department of Human Services. The survey found the Health Services lacked the service capacity to providing the person centred care. The issue of capacity was even more pronounced for acute services than sub-acute; the inability to provide care in an environment considered most ideal for that person – that is, in the person’s home was also pronounced. Various organisational support issues were also identified that require attention to achieve both positive culture and practice change. For example, having good management support and working within an organisation that values its staff was identified as important. Barriers included high staff turnover, problems with staff recruitment, staff feeling ‘pressured to discharge’ patients before they are ready and lack of good mentoring. Working within an organisation that values and prioritises 26 the care of the older person, supports ‘top down’ the provision of person-centred care and seeks to both receive and act on consumer feedback was also considered necessary (Dow, Haralambous, Bremner, and Fearn, 2006: 70). Brach and Fraser (2000) have also offered the notion of ‘family centeredness; respecting the potential wish of culturally diverse groups to include their family members in healthcare decision-making. While recognizing that certain privacy regulations and laws exist, person centered approaches can accommodate familycentered care, as determined by the patient. Knowledge and understanding the role that family play in healthcare decisions become important considerations. This includes knowledge of culturally defined composition and roles within families; skills necessary to communicate with family members with attention to age, gender; include family members in decision making when requested; honor patient and family perspectives and choices; and patient and family knowledge, values, beliefs and cultural backgrounds are incorporated into the planning and delivery of care. At the core of both patient centeredness and cultural competence is the emphasis on seeing the patient as a unique person. The general characteristics of patientcentered care (for example, building rapport; exploring patient beliefs, values, and the meaning of illness; finding common ground) may be endorsed as aspects of cultural competence. Beach et al (2006) argue that because cultural context is relevant to the needs of all patients, not only to those of culturally diverse backgrounds, cultural competence has the capacity to enhance patient-centeredness and improve quality for all patients. From the above, it is evident that patient- centered care can provide a mechanism to be inclusive of CALD patients in care delivery. There is a need to develop particular kinds of policies and procedures in hospitals that support cultural competence. In addition, there is a need for organisational commitment to cultural competence and subsequent action at the policy and procedures level, as these initiatives can often be overshadowed by other organisational priorities (Wilson-Stronks, Lee, Cordero, Kopp, and Galvez, 2008). Consumer Knowledge and Empowerment Health literacy is a new concept that focuses on the ability to use the health care system appropriately and to live a healthy lifestyle (Davis et al, 1998). Health literacy is dependent upon education, past experience with the health system, age, gender and culture. It is suggested by Levin-Zamir (2007) that it is important to understand the association between cultural competence, empowerment and health literacy for three specific reasons. First, she argues that the concepts form the basis for improving health indicators. The next argument made is that, the empowerment, cultural competence and health literacy connection has significance regarding the use of public resources for health care and that health costs increase due to costs that stem from the increased need for repeated examinations, treatment, hospitalizations due to mistakes and misunderstandings. Finally, it is noted that the personal cost can be of personal shame and harm that is caused to self-esteem by an unpleasant encounter with a health service. In a study conducted by VicHealth (2007) it was found that the health consequences of discrimination can be moderated if people have a positive ethnic identity and a realistic appraisal of the existence and extent of discrimination affecting their group. It is also important that patients should be aware of their own attitudes, subconscious bias and mistrust in relation to health services (Johnstone and Kanitsaki, 2007; Smith and Betancourt, 2007). 27 7. GOVERNMENT POLICY AND REPORTING FRAMEWORKS FOR CULTURAL DIVERSITY This section will firstly map out the cultural diversity policy, planning and reporting frameworks in the Victorian Department of Human Services. This will be followed by a selected exploration of what other state and Commonwealth governments are undertaking. The purpose of this section links to Objective 1, as set out in the introduction of this literature review. 7.1. Mapping Cultural Diversity Policy, Planning and Reporting Arrangements for Cultural Diversity The Department of Human Services is the largest Victorian government department. It is a complex agency with different areas of responsibility including health, housing, disability, children, aged care and mental health. The large scale of the department and the multiple service delivery areas within entails numerous linkages, frameworks, policies, legislations and planning and reporting arrangements. The department operates within the larger policy and legislative framework of the Victorian Government (in addition to the Commonwealth). The broader policy context for cultural diversity is primarily informed by the principles contained in following Victorian legislation: Equal Opportunity Act 1995 (currently under review); Racial and Religious Tolerance Act 2001; Multicultural Victoria Act 2004 and its proposed amendments; and Charter of Human Rights and Responsibilities Act 2006. The department implements programs and services consistent with the Growing Victoria Together: A Vision for Victoria to 2010 which aims to achieve outcomes relating to economic, social and environmental concerns. This document identifies shared goals are a focus for setting government priorities and includes high-quality accessible health and community services and a fairer society that reduces disadvantage and respects diversity (http://www.growingvictoria.vic.gov.au). The Victorian Government’s overarching multicultural affairs policy, Valuing Cultural Diversity 2002, contains four themes: Valuing diversity Reducing inequality Encouraging participation Promoting the social, cultural and economic benefits of cultural diversity to all Victorians. The department and other Victorian government agencies report on achievements against Victoria’s multicultural affairs policy each year as part of a whole-ofgovernment approach to multicultural affairs. This reporting is stipulated in the Multicultural Victoria Act 2004 where government departments are required to report annually to the Minister for Multicultural Affairs and parliament on their 28 achievements in the multicultural arena. The department of reports through the Diversity Unit against the four broad themes listed above. The objectives of the Departmental Plan 2008-09 are: Building sustainable, well-managed and efficient human services Providing timely and accessible human services Improving human service safety and quality Promoting least intrusive and earliest effective care Strengthening the capacity of individuals, families and communities Reducing inequalities through improving health and wellbeing, particularly for disadvantaged people and communities. The department has tried to address t cultural diversity by developing a comprehensive Cultural Diversity Plan 2007-2008 which maps out actions against particular objectives. In addition it has adopted a Language Services Policy (2005). This policy recognises effective communication to be essential to the delivery of highquality services. It outlines the necessary requirements to enable people who cannot speak English, or who speak limited English, to access professional interpreting and translating services when making significant life decisions and where essential information is being communicated (http://www.dhs.vic.gov.au/multicultural/langservpolicy.htm). In line with its multicultural affairs policy obligations, the department’s Diversity Unit has developed a guide which establishes six strategy areas for improving cultural responsiveness under a Cultural Diversity Guide (2006). The six areas are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Understanding clients and their needs Partnerships with multicultural and ethno-specific agencies A culturally diverse workforce Using language services to best effect Encouraging participation in decision making Promoting the benefits of a multicultural Victoria. While cultural diversity principles are adopted by the department, it notes that ‘Victoria’s cultural diversity provides a significant challenge for the Department and its funded agencies, in ensuring that Victorians from all backgrounds can enjoy access to human services on an equal footing, and are treated with respect and sensitivity’ (DHS, 2006:6). The department’s Cultural Diversity Guide points out that the delivery of culturally responsive, equitable services is a core quality expectation of the department programs and funded agencies. The departmental planning and reporting for cultural diversity form the foundations of the Cultural Diversity Plan 2007-2008 and incorporate the following: Health Service Cultural Diversity Plan (HSCDP); Disability Services Cultural and Linguistic Diversity Strategy; Home and Community Care (HACC) Cultural Planning Strategy; and Cultural Diversity Plan for Victoria’s Specialist Mental Health Services. These will be visited briefly to provide an overview and to analyse the commonalities and differences across these reporting areas: 29 Health Service Cultural Diversity Plan (HSCDP) The Health Service Cultural Diversity Plan’s objective is to improve the quality of service delivery and ensure that health services cater appropriately for culturally and linguistically diverse communities (Department of Human Services, 2008). The minimum reporting requirements identified in this plan are six areas under the Cultural Diversity Plan and health services (hospitals) report against these. Since 2006 every Victorian health service has had to establish a cultural diversity committee; develop and implements a health service cultural diversity plan; lodge the plan with the Director, Statewide Quality Branch and from 2007 onward every service is required to report annually on the plan’s accomplishments. The minimum reporting set out in the cultural diversity guide applies to the HSCDP and includes reporting against areas including: data knowledge skills language engagement education. Please see Appendix 1 for details of the minimum reporting requirements. Disability Services Cultural and Linguistic Diversity Strategy Based on The State Disability Plan 2002-2012 of the Victorian Government this strategy is underpinned by a legislative framework which includes the Disability Discrimination Act 1992 (Commonwealth), Equal Opportunity Act 1995 (Vic), The Intellectually Disabled Person’s Services Act 1986 (Vic) and The Disability Services Act 1991 (Vic). The purpose of the Strategy is to assist all disability support providers to plan and deliver culturally appropriate disability supports. These providers include government and non-government organisations that deliver supports such as accommodation, day programs, case management, respite, advocacy, information, support packages and recreation. There are standards for service providers which are embedded strongly in planning and quality assurance processes. The current Victorian Standards for Disability Services 1999 (the ‘Standards’) represent the minimum operational standards for government and nongovernment disability support services in Victoria. To ensure that the standards are implemented by organisations, a number of strategies have been developed, including: Consumer assessment Service delivery self assessment Management self assessment Development and implementation of quality plans. The Disability Services Cultural and Linguistic Diversity Strategy was launched in 2004 and its objective is to meet the needs of people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds with a disability, their family and carers. The Strategy is located within a more regulated framework and has a stronger legislative and monitoring framework than HSCDP. However, there are similarities in the planning and reporting frameworks for cultural diversity. These are based on the 30 original six principles identified in the Cultural Diversity Plan. The seven goals in the Disability Services CALD Strategy are: Understanding people and their needs Encouraging participation in decision-making Providing culturally relevant and accessible information A culturally diverse workforce Using language services to best effect Meeting the specific needs of different communities Promoting the benefits of a culturally diverse Victoria. The mechanisms for planning, monitoring and implementing the CALD Strategy is through integration into existing practices. The department is a partner to the Commonwealth and State/Territory Disability Agreement (CSTDA). As part of this agreement, the department’s Disability Services Division coordinates the Victorian collection for the National Minimum Data Set. The requirement of this data collection has changed from a single day snapshot approach to an ongoing full year collection. Home and Community Care (HACC) Cultural Planning Strategy (CPS) This strategy has been in place since 1997 and its overall objective is to increase the responsiveness of HACC services to people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds who were identified as one of the five ‘special needs groups; within the broader HACC target population under the Commonwealth Home and Community Care Act 1985. The Act recognises that people from culturally and linguistically diverse might experience difficulties in gaining access to HACC services. The Victorian HACC program is supported by the HACC Program Manual which sets out legislative and policy frameworks and covers issues of implementation. HACC service delivery occurs within the National Quality Assurance Framework which comprises the HACC National Service Standards, HACC Program National Service Standards Instrument and Guidelines, Consumer Survey Instrument and Guidelines, HACC Program National Complaints Policy and Statement of Rights and Responsibilities. As part of the Commonwealth State/Territory Disability Agreement, HACC Services also has to undertake data collection for the National Minimum Data Set. The Victorian HACC Cultural Planning Strategy is designed to be used by HACC service providers to demonstrate and evaluate the provision of culturally appropriate services to people from CALD backgrounds. It is supported by a number of tools and resources such as Cultural Planning Tool guidelines and resources. The Tool conforms to the National Service Standards and seven principles around which planning takes place: Access; Cultural Relevance; Consultation; Information; Special Needs Programs; Service Coordination and Accountability. These areas are then supported by broad indicators. CPS requires HACC providers to develop and submit HACC Cultural Action Plan each year. The department funds 14 HACC Equity and Access Program (HEAP) projects based in community agencies. The ‘HEAP workers’ resource the service providers and support them in the development of Cultural Action Plans. Action on Disability within Ethnic Communities (ADEC) is funded to play a coordination role for HEAP workers across Victoria. 31 Departmental regional offices are responsible for regional planning, monitoring of funding agreements, ensuring Cultural Action Plans are submitted and overseeing implementation more broadly. The Culturally Equitable Gateways Strategy was initiated in 2003 as CALD communities were identified as being under-represented in core HACC services in relation to their numbers. This Strategy was reviewed in 2007 and overall, it identified that the Strategy made a positive influence on participation of CALD communities at the local government level. The HACC Cultural Planning Strategy is currently being evaluated. This evaluation will determine future directions for cultural planning in the development of HACC policy and service delivery. Cultural Diversity Plan for Victoria’s Specialist Mental Health Services 20062010 This plan provides a framework for improving mental health services’ accessibility and responsiveness to Victoria’s culturally and linguistically diverse communities. The key strategies adopted in the plan are listed in Appendix 2. The Victorian Government is a signatory to the National Mental Health Strategy which is an agreement between the Commonwealth and State/territory governments. The national initiatives implemented by Department of Human Services include the National Standards for Mental Health Services and the National Practice Standards for the Mental Health Workforce. These documents emphasise the need for cultural sensitivity, as central to quality mental health care. The Victorian Government has also endorsed the Framework for Implementation of the National Mental Health Plan 2003-2008 which has four key approaches relevant to culturally sensitive care: a population health approach acknowledging the influence of migration experience and culture as risk and protective factors in mental health; improving service responsiveness to cultural diversity; strengthening quality; and fostering culturally inclusive research and innovation. 7.2 Discussion The Victorian Government multicultural affairs policy framework shapes the internal policies and strategies of the department. The Cultural Diversity Guide (2006) provides the skeletal framework for planning and reporting. A number of commonalities exist in each of the different cultural diversity planning and reporting areas deriving from the Guide. These include: understanding clients’ needs; access by culturally and linguistically diverse communities to services; responsiveness of services to cultural diversity including issues of language services, cultural sensitivity, appropriate workforce and recruitment and training; consumer participation; and overall promotion of multiculturalism or a commitment to cultural diversity values. The differences lie, not in the principles, but in operationalising the planning and reporting processes. These are linked to a number of factors including: historical developments of service provision or policy area within the department; Commonwealth State Agreements and the presence of National Service Standards; legislative base which provides a compliance base or a self regulatory (nonmandatory) framework; and internal and external resources available to services to support cultural diversity planning and reporting processes. 32 It is clear from the above mapping processes that there are many complex reporting and planning arrangements within the department and providers may see these as onerous and time-consuming. The planning and reporting processes, while attempting to ensure consideration of cultural diversity, can inadvertently lead to its resentment and it being seen as just another task to be ticked off as being done. Onerous processes can be a prohibitive factor in the continuous improvement cycle. A comparative look at the differences in reporting within the department begs the question of mandatory reporting against self assessment. The exploration of the answers to this question is complicated and patchy. A consultation undertaken by the department in 2003 identified major problems including: better access to information; problems with cultural sensitivity of services; access to language services; better workforce planning and stronger monitoring and reporting (DHS, 2004). While this consultation precedes the adoption of The Disability Services Cultural and Linguistic Diversity Strategy, it is instructive in that it points to problems relating to implementation of cultural competence, reporting and monitoring in a field (that is, disability services) that has long had mandatory processes. Similarly in the mental health area, with legislative and mandatory reporting arrangements and Service Standards, responsiveness of clinical and psychiatric disability rehabilitation and support services were not responsive to needs of CALD clients (Department of Human Services, 2006c). The HACC program, again with National Service Standards and legislative framework identified that cultural responsiveness and access was a major issue which led to further initiatives such as The Culturally Equitable Gateways Strategy. On the other hand, HSCDP does not have legislative and service standards in the same way. While health service are assessed by the Australian Council on Health Care Standards using the tool EQUiP 4 Accreditation standards and guidelines, there is no mandatory elements relating to cultural diversity service standards. The cultural diversity elements of EQUiP 4 are presented in a very broad manner 1.6.3. The reporting against HSCDP has resulted in strong compliance although without a mandatory base. Eighty-four out of 88 health services across Victoria submitted plans to the Statewide Quality Branch relating cultural diversity outcomes (Department of Human Services, 2008a:7). In a consultation held in 2007 by department, four key issues were identified as problematic in these reporting arrangements: variation in the duration of HSCPDs ranging from 1-3 years; practice and scope of cultural diversity committees; variation in the level of detailing of strategies and actions; and different approaches to cultural diversity responsiveness based on geographical location (for example, metropolitan, regional or rural). Additionally there is little or no research about CALD consumer experiences of health services. Work has been commissioned to develop consumer participation indicators. The Victorian Patient Satisfaction Monitor (VPSM) collates surveys regarding peoples’ experiences in health services through a questionnaire mechanism - this is offered in a range of languages. 33 A forum to review Health Service Cultural Diversity Plans titled Present PracticeFuture Opportunities Forum endorsed the value of cultural diversity planning processes as a way to keep the focus on CALD issues in health services. However at this forum, numerous planning and reporting challenges and issues were identified. The key findings were: linking HSCPD with other strategic and management planning; reframing the plans under patient safety and risk management and performance management; linking various cultural diversity planning processes; clearer planning and reporting processes and who has responsibility for it, communication processes within the health service; Strategic planning timeframes (there should be a three or even five year plan not just a one year plan); need to know how to access to expertise, need for sufficient support and resourcing in planning and reporting; need for clarity about whose role it is to evaluate if improvements to be made; need for feedback on reporting and planning; no baseline data and a lack of consistent data and information sources within the department, particularly that there is no baseline data; challenges of a whole-of-organisation approach within a complex departmental environment; need for leadership on cultural diversity within the department senior executive champions, needing to build the status of the issue within competing priorities; better partnerships with community and internal sharing of information; need for a model of consumer participation that works with CALD communities; improvements in language services; streamlining reporting arrangements with auditing and quality improvement processes in the Department of Human Services; benchmarking and setting standards; difficulties of measuring outcomes; and making staff training mandatory and the need for standards on training. In this forum there was a call from practitioners for ‘mandating’ managers on performance and reporting more effectively and with correct reporting processes on cultural diversity outcomes, embedding cultural diversity within risk, accreditation and quality systems, and legislating for language services. This indicates dissatisfaction with existing reporting processes, casting doubt on self reporting and the need to make planning and reporting more effective. Additionally there was a call 34 for indicators, standards and benchmarking to establish stronger systems to measure progress and cultural diversity outcomes in more concrete way (Department of Human Services, 2008a). The department has commissioned work to develop a second set of consumer participation indicators under the ‘Doing it well vs., not for us’ policy framework. 7.3 Selected Commonwealth and State Policies and Reporting Frameworks Information in relation to current systems for reporting disparities for minority groups of health care consumers as they relate to health systems is very difficult to locate in the Australian context. Systems of reporting vary from agency to agency and across the states in Australia. A desk based literature review was not able to adequately identify internal reporting arrangements as many evaluations and reports are not made public. Searches were conducted in the web pages of the Commonwealth and state government departments of health, human services and multicultural affairs. Much of the multicultural affairs reporting is focused broadly on the government achievements against their policies and is not specific enough. Where examples have been found, they have been about one-off initiatives or highlights of a promotional nature, making analysis of their effectiveness difficult. A reference to reporting by health services was noted in the Action Plan for the Royal Adelaide Hospital (2007-2010:13) which indicated that: Procedures would be developed to respond to complaints by patients about staff who are culturally insensitive or discriminatory. A measurement of this intervention would be that procedures would be completed and published, and that reporting would be ongoing. However, King et al (2008 pp. 251) noted that out of 501 hospitals surveyed in the US in 2006 fewer than one in five hospitals that collected race/ethnicity information used it to assess disparities in quality of care, health outcomes, or patient satisfaction. The following represents an attempt to map the current state of cultural diversity in Australia in relation to health. Due to the absence of an appropriate evidence base available in the public domain, the picture, at best, can be described as patchy and incomplete. At present the New South Wales Health Department has published the guide to Health Services for a Culturally Diverse Society: Implementation Plan. The NSW Government and NSW Health point out that they are committed to ensuring public health services meet the needs of all NSW residents, regardless of their cultural origins or their English skills. The Plan is aimed at achieving three consumer based outcomes and outline strategies for the achievement of these outcomes: People of non-English speaking background are aware of the health services which are available to them and the health system which provides these services. People of non-English speaking background make judgements about the health system and their own needs and articulate these to the appropriate organisational component within the health system. Judgements made by people of non-English speaking background about health system and their own health needs are included in the policies and plans of the health system. Health systems services are accessible and appropriate and used by people of non-English speaking background (NSW Health, 2002). 35 Information on the reporting mechanisms for these or what standards are used for reporting was not identifiable from their public information systems. In their website, NSW Health promotes: policies and procedures to allow equal access for all people to health services; programs and health services which recognise the cultural diversity of the people of NSW; and commitment to equal opportunities that reflect the cultural diversity of NSW. All public health system employees are required to follow these guidelines that are explained in the following documents: 1. Health Services for a Culturally Diverse Society: An Implementation Plan (1995); 2. Circular 94/10: Standard Procedures for the Use of Health Care Interpreters (1994); 3. Strategic Directions in Refugee Health Care in NSW (1999); 4. Caring for Mental Health in a Multicultural Society: A Strategy for the Mental Health Care of 5. People from Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Backgrounds (1998); and 6. Guidelines for the Production of Multilingual Health Resources by Area Health Services, NSW Health Department and NGOs funded by NSW Health (2001). The NSW reporting and monitoring of multicultural affairs takes place under the Ethnic Affairs Priorities Statements (EAPS). These reports are whole-of-government reporting on multicultural affairs and take place within four broad headings. These reports highlight key initiatives and are often promotional in nature. The broad criteria are not sufficient to gauge what indicators or standards are being used and it cannot be considered a measurement tool. The NSW Health Plan has seven strategic objectives including meeting consumer needs and developing their workforce. Annual Report 2007 (pp.169-172) reflects an attention to cultural diversity (http://www.health.nsw.gov.au/pubs/2007/pdf/AnnualReport_07.pdf). The South Australian Government Department of Health identifies the notion of ‘cultural accountability’ in their Primary Health Care Policy Statement 2003-2007. The Statement defines cultural accountability as responding to diversity by recognising, respecting and being accountable to the unique cultural needs and values of diverse populations. However there is no information on how this accountability is implemented or monitored. (http://www.health.sa.gov.au/Default.aspx?tabid=62) In Western Australia (WA), the government has adopted a Substantive Equality Framework which agencies have to report against. The policy framework set out a key role for the public sector in addressing systemic discrimination by: ensuring that policies respond to individual and communities’ different needs and priorities; providing services that meet the needs of different Indigenous and ethnic groups; and having effective work practices including recruitment and retention policies. 36 The WA Government reporting framework has been designed as an integral part of the change process to: enable agencies to make gradual transition towards the aims of the Policy Framework for Substantive Equality; develop the Policy Framework aims in a supportive and learning environment; move away from the usual generic ‘one size fits all’ model of reporting, to one which suits the individual needs of agencies; make reporting easier; and increase accountability in relation to providing services to people of different Indigenous and ethnic backgrounds (http://www.equalopportunity.wa.gov.au/pdf/summaryguide.pdf). The interesting element of this model is that it does not implement a generic framework across all agencies to report against. Rather outcomes are negotiated and agencies report against those achievements they negotiated. In Queensland, Queensland Health has been making progress towards embedding cultural diversity into its service and program design and delivery. They have a number of policy frameworks within their portfolio including: Queensland Health Multicultural Policy Statement Queensland Health Language Services Policy Statement Queensland Health NESB Mental Health Policy Statement These policies set out the principles of access and equitable health service delivery to CALD communities. The implementation framework is governed by a number of plans. The Statewide Health Services Plan 07-12 recognises the health needs of people from CALD backgrounds and identifies that improving access to health services will be considered in Area Health Service and other planning processes. In addition, it has developed the Queensland Health Strategic Plan for Multicultural Health 2007-2010. The reporting on the cultural diversity planning takes place through the Queensland Health Multicultural Action Plan 2006-2007 which is a whole of government process on reporting on multicultural affairs. They identify a series of action that build cultural competence of the health system such as: Focus on refugee health Workforce development Training of professionals Building sustainable language services Monitoring and evaluation strategies for particular program areas Raise Queensland Health’s profile in CALD communities Work on culturally appropriate complaints mechanisms Develop and disseminate a guide on information dissemination Establish a state-wide model of multicultural mental health coordinator positions (http://www.health.qld.gov.au/multicultural/policies/ActionPlan_2006_07.pdf). Queensland Health has established a multicultural health site and has identified a five-year strategic plan with key actions against it. The reporting takes place against four broad criteria of the Multicultural Queensland Policy. These are: 37 1. 2. 3. 4. Strengthening Multiculturalism Productive Diversity Supporting Communities Community Relations and Anti-Racism. Since the election of the Rudd Labour Government, there has not been a review of the policy framework for multiculturalism. The Department of Immigration and Citizenship traditionally monitored and reported against access and equity considerations. Between 1996 and 2005, the department published the Access and Equity annual report, which reported on progress in implementing the Charter of Public Service in a Culturally Diverse Society. In 2007, the Charter was replaced by a new strategy, Accessible Government Services for All (AGSFA). This framework was adopted to promote fairness and responsiveness in the design, delivery, monitoring and evaluation of government services in a culturally diverse society. In 2008, AGSFA reverted to the Access and Equity name; however, the strategy remains the same. The reporting criteria for AGSFA are also broad and include: Responsiveness—the extent to which programmes and services are accessible, fair and responsive to the individual needs of clients. Communication—the openness and effectiveness of communication channels with all stakeholders. Accountability—the effectiveness and transparency of reporting and review mechanisms; Leadership—a whole of government approach to management of issues arising from Australia’s culturally and linguistically diverse society. A number of strategies are suggested under each of these categories for implementation and reporting. (http://www.immi.gov.au/about/reports/accessible_government/accessible_gove rnment_2006/_pdf/accessible_government_appendixa.pdf) An examination of cultural competence performance reporting in Indigenous Affairs shows other practices of planning and reporting. The Australian Health Ministers Advisory Council (AHMAC) endorsed the National Cultural Respect Framework for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Health in 2004. This is guided by four broad areas: Knowledge and Awareness Skilled Practice and Behaviour Strong Customer or Community Relationships Equity of Outcomes This framework is useful in that it identifies areas of focus within organisational performance related to culture. Each jurisdiction is to develop its own reporting frameworks. For example, the Western Australia Government Office of Aboriginal Health has developed a Cultural Respect Framework which has four key parts: An Aboriginal impact statement for policy and program development Services reform through cultural partnerships, education, review and practice development Aboriginal workforce development 38 Monitoring and evaluation Planning occurs through an impact statement rather than a generalised plan. In terms of monitoring and evaluation the framework lists potential actions as: Monitor use of the Aboriginal impact statement in program and policy proposals at divisional, area health service and local level; Monitor number of cultural partnerships, cultural education sessions and services reviews by directorates and health services; Assess trends in Aboriginal hospital admission data; Conduct periodic Aboriginal patient satisfaction surveys; Consult local Aboriginal community representatives on the cultural appropriateness of local health services (Government of WA b). Reporting and monitoring systems are complex and depend on many organisational developments. Their effectiveness is dependent on factors on a number of factors including: planning processes, resources, specificity of the criteria for performance, utilisation of reports in improvements in service, policy and program development and links to other accountability mechanisms. Bischoff (2003) identifies that it is important to connect systems of reporting with quality of care. He identifies that improving the quality of health care encompasses six aims: safety, effectiveness, patient-centeredness, timeliness, efficiency and equity. Smith (2002) advocates that monitoring for cultural diversity and migrant/minority health care issues require it to be framed as a quality issue. A glance at current practice in Australia indicates that what is happening is fragmented. Reporting frameworks often relate to the principles relating to cultural diversity outlined above. None of these are specific enough to determine measures of progress. This calls into question whether more specific standards and indicators are needed. The reporting process is also fraught with complications and these apply to the department and other government agencies. The key issues include: Lack of quality baseline data; A lack of standard definitions complicates comparability between government agencies and health services; Multiple reporting processes, which are not well integrated; Instruments of reporting often need to be reworked to address linguistic and cultural issues, for example, separation of quality improvement, patient safety, other risk management, patient satisfaction and other processes; The impact of the intervention is often difficult to isolate from other factors; The standards of data collection and assessment of impact are often inappropriate (for example, randomized control trials). Integrating cultural competence reporting into broader national health care objectives, is a challenge but one that should be urgently addressed. 39 8. STANDARDS OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE FOR HEALTH SERVICES A lack of national standards exists in relation to the provision of culturally and linguistically appropriate services in health services. This makes reporting requirements within and between health departments difficult to ascertain, and to measure progress against. Anderson et al (2003) undertook a review of interventions that were designed to take into consideration the health care needs of CALD clients, utilisation of services and levels of satisfaction. They identified a number of strategies including: recruitment and retention of CALD staff that reflect the diversity of client groups; language services, particularly use of interpreters and/or bilingual providers; use of linguistically and culturally appropriate health education materials; training relating to cultural awareness and competence for health services; and provision of culturally relevant healthcare settings. The evaluation of outcomes of before-after or control group studies indicated outcomes relating to improvement in client health status, client satisfaction with care, improved service utilisation by CALD clients and changed treatment regimes for CALD clients. However, the study did not find sufficient evidence to determine the effectiveness of any of the interventions. This highlights the key questions for this section poses a number of key questions: 1. What standards should be used? 2. What are the indicators? 3. How is progress against the standards and indicators to be measured? Standards are published documents setting out specifications and procedures designed to ensure products, services and systems are safe, reliable and consistently perform the way they were intended to. They establish a common language which defines quality and safety criteria (Standards Australia). They also establish protection for consumers, provide opportunity for improvement and innovation and can act as regulatory mechanism. Determining what outcomes have been achieved against standards work well when they are aligned to indicators which are appropriate to measure progress. Standards, explicitly and by implication, set out the knowledge and skills that an individual or an organisation must have to fulfil the requirements for standards of performance. Standards can focus on different levels of the health care system: the patient, the practitioner, the organisation, the region or the country. This is because the conditions for error and harm can occur at all levels. Standards can work towards mitigating risk and achieving quality outcomes. The Lewin Group (2002) undertook a project with the aim to develop an analytical framework for assessing cultural competence in health care delivery, identify specific indicators, and assess the utility, feasibility and practical application of the framework and its indicators. The resulting framework is named as a Cultural Competence Assessment Profile (the Profile) that is a tangible and targeted approach 40 for conducting organisational assessments. It has three major components: a) domains of cultural competence, b) focus areas within domains, and c) indicators relating to focus areas. The domains include organisational values, governance, planning and monitoring/evaluation, communication, staff development, organisational infrastructure, and services/interventions; each domain has focus areas and focus areas have indicators (for example, structure, process and output). Key observations of this project are: Assessment is Not an Isolated Event assessment of cultural competence should not be considered an isolated event, but rather a continuous process that is emphasized and integrated in an organisation’s overall assessment activities. Importance of Assessing Institutionalisation: there is a need to assess the ‘institutionalisation’ of cultural competence in an organisation, that is, the extent to which cultural competence is an integral part of the organisation’s service, management and business functions. Validation of the Components of the Profile: the exploratory process for this project give credence to the Profile’s seven evidence-based domains as appropriate performance areas for assessing cultural competence. The sites emphasized the importance of assessing the domain of organisational values as the necessary precursor to culturally competent performance. Since the development of the Profile involved action research, the site visits supported the credibility of the Profile’s focus areas and specific indicators. The authors suggest the profile can assist organisations to identify the critical elements of measuring cultural competence. It can also be used in structured quality assurance and other performance measurement activities such as mandates and standards. The profile can be useful to organisations serving a single and multiple ethnic groups. In addition, it is potentially useful for organisations at different levels of cultural competence development due to its flexibility organisations can pick and choose aspects that most suit them. 8.1 Australian Standards There are a number of standards that provide the framework for health and allied health service provision in Australia. Commonly recognised providers of health care standards and/or accreditation services include the Australian Council for Health Care Standards (ACHS), the Quality Improvement Council (QIC) and the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). The Standards set by the Australian Council of Healthcare Standards (ACHS). ACHS’s mission is to ‘improve the quality and safety of health care’ through an independent assessment process. The Evaluation and Quality Improvement Program (EQUiP 4) provides a framework for safety and quality for health services. It is a selfassessment undertaken by health services on an annual basis with biennial on-site surveys by external accreditation surveyors. EQUiP4 sets out standards in three broad areas, namely, Clinical, Support and Corporate. These cover the standards relating to continuity of care; access; appropriateness, effectiveness; safety and 41 consumer focus, quality improvement and risk management; human resource management; information management; population health; research; leadership and management; and safe practice and environment. The standards are divided into mandatory and non-mandatory. There are 14 mandatory standards; none specify cultural diversity. Standards relating to cultural diversity are listed under Consumer Focus (non-mandatory) in Article 1.6.3 which states ‘The organisation makes provision for consumers / patients from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds and consumers / patients with special needs.’ (http://www.achs.org.au/pdf/E4A3_poster.mandcriteria.pdf) These standards are provided within a continuous improvement cycle of awareness, implementation, evaluation, excellence and leadership. Some examples are provided under each of these elements. The accompanying guide notes that health services should develop policies and systems to address: Understanding people and their needs Systems to understand and analyse changing demographics Providing relevant and accessible information An appropriately trained workforce Meeting the specific needs of different communities. (http://www.achs.org.au/pdf/E4A3_poster.mandcriteria.pdf) These standards are relevant to HSCDPs as they cover similar criteria about culturally sensitive service provision. Implementation and reporting for HSCDPs can be an important element of meeting accreditation requirements. The National Standards for Mental Health Services outlines a standard which specifically relates to cultural awareness. A standard on cultural awareness is that ‘the Mental Health Services (MHS) delivers non-discriminatory treatment and support which are sensitive to the social and cultural values of the consumer and the consumer’s family and community’ (http://www.health.vic.gov.au/mentalhealth/quality/national-standards.pdf, pp.25). These standards are mandatory and have a specific reporting requirement as noted above. There are a number of criteria listed for these standards: MHS staff have knowledge about the social and cultural groups represented in the defined community and an understanding of those social and historical factors relevant to their current circumstances. The MHS considers the needs and unique factors of social and cultural groups represented in the defined community and involve these groups in the planning and implementation of services. The MHS delivers treatment and support in a manner which is sensitive to the social and cultural beliefs, values and cultural practices of the consumer and their carers. The MHS employs staff or develops links with other service providers/organisations with relevant experience in the provision of treatment and support to the specific social and cultural groups represented in the defined community. The MHS monitors and addresses issues associated with social and cultural prejudice in regard to its own staff. Documented policies and procedures exist and are used to achieve the above criteria. 42 The MHS monitors its performance in regard to the above criteria and utilizes data collected to improve performance as part of a quality improvement process. (http://www.health.vic.gov.au/mentalhealth/quality/national-standards.pdf) A scan of the literature was not able to identify an evaluation of the practice of implementation of these standards or their effectiveness for culturally sensitive care. The Evaluation Report of the Second Mental Health Plan noted that there remains, however, a continuing need to improve health outcomes for people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds. The Standards for Disability Services in Victoria set out the expectations of better practice for the delivery of services and supports to people with a disability. The current Victorian Standards for Disability Services 1999 (the ‘Standards’) represent the minimum operational standards for government and non-government disability support services in Victoria. To ensure that the standards are implemented by organisations, a number of strategies have been developed, including: Consumer assessment Service delivery self assessment Management self assessment Development and implementation of quality plans. The HACC National Service Standards were introduced in 1991 to provide agencies with a common reference point for internal quality controls by defining particular aspects of service quality and expected outcomes for consumers in seven key areas: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Access to Services Information and Consultation Efficient and Effective Management Coordinated, Planned and Reliable Service Delivery Privacy, Confidentiality and Access to Personal Information Complaints and Disputes Advocacy. These standards are assessed by the HACC National Standards Instrument and Guidelines covering the seven criteria listed above. The standards are assessed using self assessment and joint assessment methodologies with the relevant State Department. The Instrument has a number of specific questions relating to cultural diversity: Objective 1: How can your agency demonstrate that access to services by special needs groups occurs on a non-discriminatory basis? Objective 4: How does your agency ensure that the consumers’ cultural needs are taken into account when providing care/support? (http://www.health.gov.au) The guidelines are not meant to be prescriptive but rather are intended to provide general guidance to agencies and service quality assessors in collecting the views of consumers as part of the appraisal of service quality. The Royal College of General Practitioners have developed standards for health services in Australian detention centres. They identify that the criteria in these Standards relate to systems and processes that require extra attention to ensure the 43 provision of high quality and safe care to patients within immigration detention centres. These include: Informed patient decision (Criterion 1.2.2) Interpreter services (Criterion 1.2.3) Clinical autonomy for medical, clinical and allied health staff (Criterion 1.4.2) Continuity of comprehensive care (Criterion 1.5.1) Continuity of the therapeutic relationship (Criterion 1.5.2) Engaging with other services (Criterion 1.6.1) Respectful and culturally appropriate care (Criterion 2.1.1) Confidentiality and privacy of health information (Criterion 4.2.1) Transfer of health information (Criterion 4.2.3). (http://www.racgp.org.au) While the context of health service delivery in detention centres is very different from the traditional health service environments, the issues identified in the report are transferable to other CALD populations in relation to care delivery. A number of standards are developed including: Access to Care Information about the health service; Health promotion and prevention of disease; Diagnoses and management of specific health problems; Continuity of Care, Coordination of care Content of Patient Health Records Collaborating with Patients Safety and Quality Education and Training Service Management; Management of Health Information Equipment for Comprehensive Care Clinical Support Processes. Of particular interest is the subset of Collaborating with Patients Standard (2.1.1.) is respectful and culturally appropriate care. This standard has a set of indicators which will be described in the next section. (http://www.racgp.org.au) While not linked directly with health systems standards The Aged Care Standards and Accreditation Agency is the body appointed by the Department of Health and Ageing, under the Aged Care Act 1997, as the accreditation body residential aged care facilities. There are a number of standards specified in the accreditation of residential care facilities. Of interest is the standard 3, titled Resident Lifestyle. The standard defines the general principle of the standard and lists 10 expected outcomes. Outcome 3.8 is Cultural and spiritual life - Individual interests, customs, beliefs and cultural and ethnic backgrounds are valued and fostered (http://www.accreditation.org.au/AccreditationStandards). To assist the implementation of this standard the Department of Health and Ageing has initiated a Program titled Partners in Culturally Appropriate Care (PICAC) to ensure the special needs of older people from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds are identified and addressed. One of the key elements of this is the funding of the Centre for Cultural Diversity and Ageing which provides both community support and service provider support (http://www.culturaldiversity.com.au) 44 8.2 International standards Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS) are the US set of recommendations for national standards with an outcomes-focused research agenda. In 2001, the Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Minority Health (OMH) published standards for culturally and linguistically appropriate services for healthcare organisations. These standards were an initial move to provide structure to what constitutes culturally appropriate healthcare services. The CLAS standards are proposed as one means to correct inequities that currently exist in the provision of health services and to make these services more responsive to the individual needs of all patients/consumers. The standards are intended to be inclusive of all cultures and not limited to any particular population group or sets of groups. However, they are especially designed to address the needs of racial, ethnic, and linguistic population groups that experience unequal access to health services. There are 14 standards, (refer to Appendix 3 for details) which are organised by themes: Culturally Competent Care (Standards 1-3) Language Access Services (Standards 4-7) Organisational Supports for Cultural Competence (Standards 8-14). Within this framework, there are three types of standards of varying stringency: Mandates—CLAS mandates are current federal requirements for all recipients of federal funds (Standards 4, 5, 6, and 7). Guidelines—CLAS guidelines are activities recommended by OMH for adoption as mandates by Federal, State, and national accrediting agencies (Standards 1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13). Recommendations—CLAS recommendations are suggested by OMH for voluntary adoption by health care organisations (Standard 14). (http://www.omhrc.gov/templates/). In the submission to the CLAS standards a number of concerns were expressed by different agencies relating to implementation and reporting. These considerations are central to cultural competence practice and include a range of perspectives. ‘We do not believe that culturally and linguistically appropriate health care services are an area of health care that should be highly regulated. When a guideline or standard is strictly mandated and regulated, all possible opportunities for flexibility and innovation are eliminated. This approach is not in the best interests of the patient or customer needing the service.’ ‘To have any effect in practice, finalised standards must be more than mere ‘guideposts.’ To the extent possible, the final standards should be issued as enforceable regulations. Without an enforcement mechanism to support the final standards, we fear many health care organisations and providers will not prioritize linguistic and cultural competence and our communities will continue to lack access to quality health care.’ 45 ‘The American Academy of Pediatrics agrees with the intent of the DHHS recommendations for cultural competence standards. However, the Academy has concerns regarding the availability of education, training, qualified personnel, adequate reimbursement, evaluation mechanisms and other resources required to implement and comply with the standards.’ ‘Issues related to incentives, costs, reimbursement and other administrative concerns and if CLAS standards are applied if applied literally, they would likely overwhelm most hospitals’ and physicians’ resources — both time and money’ (US Department of Health and Human Services 2001). The implementation of CLAS has met with challenges. These are reflected in a number of forums and documented in the Third National Conference on Quality Health Care for Culturally Diverse Populations: Advancing Effective Health Care through Systems Development, Data, and Measurement, 2002. The conference notes that the two greatest challenges to implementing organisational cultural competence strategies remain persuading leadership and staff, and finding resources. Integrating cultural competence into broader organisational goals and programs was identified, as the key strategy. The Conference resolved that the CLAS standards can guide organisational change and assist with the implementation of cultural competence in a host of health care settings. However, representatives of health care organisations— clinics, hospitals, county health departments, and for-profit and nonprofit managed care organisations—reported on several years of experience implementing cultural competence activities. Gaining support for organisational change was identified as ‘very challenging’, but many Health Services felt that the national standards for CLAS provided a useful guide the interventions they are implementing. (http://www.diversityrx.org) 8.3 Discussion As can be seen from these standards, cultural diversity is either not included or included as a subset of other standards. Where it is included, the standard is very broad and does not provide sufficient guide for agencies for implementation. While some standards have guides or specified outcomes, these are not specific enough. There are also a number of issues that arise from setting and implementation of standards. It is assumed that standards setting results in compliance. The review shows there are no accepted standards or method for reporting on safety and quality in health care organisations. The US Institute of Medicine (2001) Crossing the Quality Chasm notes that a system is high quality if it provides care that does not vary because of personal characteristics such as gender, ethnicity, geographic location, and socioeconomic status. Accreditation is, however, often accepted as providing an indicative measure of quality. Also questions are raised about whether standards can, in reality, prevent ‘risk’ or guarantee the quality of care. As noted by the Australian Council for Safety and Quality in Health Care (2003: 6) it should not be assumed that the higher the standards set by standard-setting agencies the better compliance would be. Whenever a standard is set, some organisations will decide that the costs of compliance exceed the costs of non-compliance. In the various standards explored above, the levels of compliance with the standards related to cultural diversity remains unknown. 46 The expectation of stakeholders who are involved in the accreditation and standards process means that there is more scrutiny of the standards and the expectation of more efficient and streamlined systems to cater for diverse Health Services. In relation to cultural competence in health care there is the debate on whether a national framework should be developed and publicly reported each year against standards and benchmarks. The Australian Council for Safety and Quality in Health Care notes a number of issues for consideration, especially in relation to accreditation and the standards that are developed for accreditation purposes. The pertinent issues are categorised and discussed below. Standards development processes There are a growing number of standards and standards setting bodies in health care, raising concerns about the cost and quality of standards setting processes. There is little coordination to prevent duplication of standards across organisations and service delivery areas, as well as identification of new priority areas. Accreditation agencies that develop their own standards fund that activity (sometimes with ad hoc government assistance) through membership fees from organisations that they will subsequently survey for accreditation. This may create competing imperatives relating to the rigour of the standards versus the subsequent cost of compliance to members. There is a variable level of involvement of consumers or other independent stakeholders in standards setting processes. Whether consumers should be involved in the accreditation or assessment processes; what level of involvement should they have are issues of contention. The Working Group strongly believes that consumers should be involved at all levels including the governance structures of any accreditation/assessment system. Quality of standards Defining a ‘safe health system’ is not an easy task and to date has not been done sufficiently well. The underpinning philosophy of standards varies widely. For example, some define minimum acceptable structures, processes or outcomes, while others are goal oriented/ideal statements. Standards for health care have traditionally focused on organisational structures and processes. They are moving towards an outcome orientation but have not yet comprehensively addressed patient safety. There is no single set of minimum or core standards for health care. Accreditation processes Whilst there are some incentives (including funding incentives), participation in accreditation programs is largely voluntary. Informed consumers are concerned that accreditation based on an organisation’s commitment to continuous quality improvement may overlook the possible inadequacy of the starting point from which improvement is being encouraged. There is little being learned by the health care system from the wealth of data collected through the accreditation processes. There is a variable level of involvement of consumers in accreditation or standards development. Organisational impact There are strong imperatives to reduce the administrative burden of accreditation. Stakeholders are concerned that accreditation is potentially diverting resources from 47 strategies aimed at directly addressing quality and safety concerns. There is particular concern about requirements to be accredited by multiple service providers against multiple sets of standards. In addition, the burden of accreditation on small facilities may be disproportionate to their resources and capacity, and to the outcomes gained from accreditation. In addition to requiring accreditation, most state governments and some third party purchasers require evidence of compliance with specific system and outcome criteria, creating a significant extra burden for health care organisations. The question is whether a more robust accreditation system could completely meet the requirements of these stakeholders, thereby alleviating the administrative burdens created by their additional compliance and reporting requirements. Organisations want a system that reassures the board, management, consumers and clinicians that their facility is providing care of an acceptable standard of safety and quality. (http://www.aasw.asn.au/adobe/publications/mental/MH_Safety_quality.pdf). The US National Quality Framework argues that cultural competence cannot alone deliver outcomes unless it is embedded across all aspects of an organisation. One of the conclusions of 2002 The Third National Conference on Quality Health Care for Culturally Diverse Populations in relation to advancing effective health care through systems development, data, and measurement was that cultural competence must align its objectives with broader quality-of-care initiatives to strengthen its position in the national health care agenda. The implication of this is that cultural diversity issues need to be reconsidered as part of a broader quality of care processes of the department including risk management, patient centered care and appropriate data collection including consumer feedback data (http://www.diversityrx.org/CCCONF/02/PROCEEDINGS_0401.htm#03a). The National Quality Framework also notes that a standardised core set of performance measures based on cross-cutting quality issues that is broadly applicable across all healthcare settings should be adopted (NQF, 2002). 48 9. INDICATORS AND ASSESSMENT TOOLS Indicators are instruments which are used to measure or determine what is happening over time, measure progress made or establish benchmarks for judgement. Indicators are an important element of performance measurement to strive for good practice and ensure continuous quality improvement. A social indicator was defined by the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) as a ‘direct and valid statistical measure which monitors levels and changes over time in a fundamental social concern’ (OECD, 1976:14). The OECD uses social indicators for two purposes: first to describe social developments and second to determine how effective society and government are in altering social outcomes. This is to be contrasted to indicators linked to performance management techniques that measured achievements in terms of outputs and targets (Armstrong et al, 2002:3). The terms outcome and impact are often used interchangeably to denote what is being measured. ‘Outcomes reflect the net effect of the program on the target population. They show the impact the program has on the original problems or identified need, who receives assistance, and the impact of the program on people’s well-being’ (Department of Premier and Cabinet Victoria 1988:16). Beneforti and Cunningham (2002) identify three types of indicators: Program viability and sustainability indicators Participation indicators Outcome indicators Program viability and sustainability indicators measure aspects of program functioning including: turnover; funding levels and stability; community consultation and support; involvement, employment and training of local people; succession planning; adequacy of facilities and equipment; and access to these facilities and equipment at critical times. These indicators enhance understanding of the processes which can lead to positive outcomes (and therefore how they could be repeated). Participation indicators provide a summary measure of community participation in activity or initiative, and where relevant, the participation of target groups (for example, women, adults, youth, and refugees). Outcome indicators provide insight into changes in social areas more broadly. The most comprehensive set of indicators to measure cultural competence has been developed by the Lewin Group in 2002. The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) and the Office of Minority Health (OMH) commissioned the Lewin Group to develop indicators of cultural competence. The resulting Assessment Profile included the domains that provide the underlying construct of cultural competence within a healthcare organisation, and the critical areas in which cultural competence should be evident or manifest in an organisation. The Assessment Profile had the following eight domains: Organisational Values: An organisation’s perspective and attitudes with respect to the worth and importance of cultural competence and its commitment to provide culturally competent care. 49 Governance: The goal-setting, policy-making, and other oversight vehicles an organisation uses to help ensure the delivery of culturally competent care. Planning and Monitoring/Evaluation: The mechanisms and processes used for: a) long and short-term policy, programmatic, and operational cultural competence planning that is informed by external and internal consumers; and b) the systems and activities needed to proactively track and assess an organisation’s level of cultural competence. Communication: The exchange of information between the organisation/providers and the clients/population, and internally among staff, in ways that promote cultural competence. Staff Development: An organisation’s efforts to ensure staff and other service providers have the requisite attitudes, knowledge and skills for delivering culturally competent services. Organisational Infrastructure: The organisational resources required to deliver or facilitate delivery of culturally competent services. Services/Interventions: An organisation’s delivery or facilitation of clinical, public health, and health related services in a culturally competent manner. These domains (refer to Appendix 4 for a further breakdown of these domains) may be considered the dimensions in an agency to which standards can be set. These are then measured by specific indicators which the Lewin Group divides these into four types. Structure Indicators are used to assess an organisation’s capability to support cultural competence through adequate and appropriate settings, instrumentalities, and infrastructure, including staffing, facilities and equipment, financial resources, information systems, governance and administrative structures, and other features related to the organisational context in which services are provided. Process indicators are used to assess the content and quality of activities, procedures, methods, and interventions in the practice of culturally competent care and in support of such care. Output indicators are used to assess immediate results of culturally competent policies, procedures, and services that can lead to achieving positive outcomes. Intermediate outcome indicators are used to assess the contribution of cultural competence to the achievement of intermediate objectives relating to the provision of care, the response to care, and the results of care. The Lewin Group indicators have spawned the development of a range of indicators by different organisations in different domains. For example, the Migrant Friendly Hospitals used the following indicators to measure staff training and to measure how staff are able to better handle cultural encounters (http://www.mfheu.net/public/files/mfh-summary.pdf): Feasibility could be demonstrated for example, acceptability among staff varied in the hospitals but altogether a total of 149 staff members participated. 50 Quality was operationalised in terms of the following dimensions: content, structure, amount of training units, qualification of trainers, composition of participating staff, management support, systematic needs assessment on the department level, integration in ongoing quality assurance etc. Effectiveness could be confirmed by improvement of staff’s self-rated awareness, knowledge, skills and comfort level concerning cultural diversity issues, as well as by increases in interest levels regarding cultural competence and in staff's selfrated ability to cope with work demands. Cost-effectiveness: external training costs were low, but developmental costs rather high, despite personal costs being mainly covered through voluntary work. Sustainability: training was recognised as an effective way to equip staff with important competencies and will be continued but modified in all participating hospitals. The Cultural Competency Standards and Self Assessment Tool Manual developed by the Multicultural Forum of Mental Health Practitioners (2005:pp.s 6-10) also developed broad standards and indicators, as outlined in the following table1. Standard Service planning Collaboration with Key Stakeholders Equitable Access to CALD people 1 Indicators Strategic Business Plan demonstrates commitment Policy for ensuring delivery of culturally appropriate services to all cultural groups in the service region Incorporated cultural competence principles in its recruitment processes for all positions at the service Gazetted specialist multicultural liaison staff position CALD representation on all internal committees Staff representatives on various CALD community organisations Distributed information in English and in key CALD languages Ensured clinicians are aware of existing alternative/complementary providers for example traditional healers; and key individuals in community to consult with concerning religious beliefs influencing treatment Informed CALD consumers about their rights and responsibilities in accessing and using service Promoted awareness of its programs in appropriate languages and places Developed policies and procedures to address and accommodate culture-based needs of CALD consumers Accessed accredited interpreter services when needed Conducted assessment and diagnoses by formally qualified and cultural competent clinicians Some indicators have been para-phrased for the sake of brevity. 51 Language Services Policy Clinical cultural competence Training CALD Consumer and Care Participation Research and Development Fiscal Support The service has a Language Services Policy Negotiated with Interpreter Service agency to ensure accredited interpreters who are trained in health issues and terminology Used accredited mental health trained interpreters when required Provided staff training on use of interpreters Sought to develop a staffing profile which reflects the cultural diversity of the wider community Ensured all staff undergo the state-endorsed clinical cultural competence training program within the first 12 months of employment Made available culturally validated assessment instruments or tools Incorporated cultural competence into staff orientation and performance review requirements The service has consulted with CALD consumers in the development of programs Taken satisfaction survey of CALD clients The service has an organisational culture which promotes research and development to trans-cultural health Linked with external agencies that have research focus on health of CALD communities Patient admission forms collect data compatible with the definition of CALD An annually updated profile of CALD communities within its service region Conducted research in collaboration or independently to measure the needs of CALD population in its region The service has budgetary policies that allocate resources and fiscal supports to achieve organisational cultural competence While these indicators are useful, they are not detailed enough to measure outcomes. Rather they can lead to broad statements of progress without sufficiently quantifying it. This area has been identified as a gap in the literature by many (National Quality Forum, Brach and Fraser, 2002). A search of the literature did not reveal any benchmarks, which is not surprising given the diversity of health care delivery contexts. Kumas Tan et al (2007) identified 54 different instruments designed to measure cultural competence, (a list of some of the key ones is provided in Appendix 5). The authors noted that many of the tools were related to cultural competence linked with individual awareness, knowledge or individual failing. They concluded that measurement tools are highly problematic due to definitions of what constitutes cultural competence, difficulties with assessing power relations and structural inequality and the assumption that developing awareness and knowledge around cultural competence are sufficient to change behaviour. The success of any indicator is based on a number of factors including: 52 Data and information collected Systems of data collection established Specificity of measures used Time frames in which the monitoring takes place Involvement of stakeholders in the evaluation process Reliability and rigour of processes Reporting systems (Beneforti and Cunningham, 2002; OECD, 1976) Planning or project establishment (at the outset) linkages to the program reporting (after or during implementation) The Third National Conference on Quality Health Care for Culturally Diverse Populations: Advancing Effective Health Care through Systems Development, Data, and Measurement (2002) noted that assessment, measurement, and data collection was an important but under-developed area of work. They pointed out that funders and consumers want more detailed information about the quality and impact of cultural competence programs, yet the task remains difficult due to the scarcity of appropriate tools and resources as well as reluctance on the part of some providers and health care organisations to participate in evaluation and data collection activities. The challenges identified in developing appropriate measurement indicators were identifies as: Finding the balance between the fluid and dynamic nature of culture and cultural competence and the concrete demands of measurement: Managing the complexity that stems from multiple levels of analysis. Balancing short-term versus longitudinal measurement. Compensating for the frequent lack of baseline data, and minimizing the burden of subsequent data collection. Accurately weighing the impact of cultural competence interventions against other factors. Impressing on organisations the value of measurement, and securing the tools, resources and expertise to conduct it. (http://www.diversityrx.org/CCCONF/02/PROCEEDINGS_0401.htm - 03a) It was also noted that a tension often arises between the goals of program evaluation and the desire to produce outcomes data. Programs implementing cultural competence interventions are often under pressure to demonstrate the impact of interventions on different health measures when they are still struggling to understand how best to run their programs and collect basic data on outputs. Given the difficulty of performance measurement, cultural audits have also been put forward as a way to measure progress. Inglehart and Quiney (1997) document an attempt to conduct cultural audits within a school of dentistry. They conclude that: …Conducting a cultural audit is difficult work, often discouraging and frustrating, but always interesting and personally challenging. It must become an ongoing effort for every organisational unit that prepares providers for their professional lives in the next century of this country. Finally, the value of indicators has been questioned and a model of organisational transformation has been put forward as an alternative by Dreachslin (1999:427). He states: 53 '...Diversity leadership entails re-visioning differences…consequently, no checklist of concrete behaviorally-based performance indicators can ever fully capture the essence of diversity leadership.' The notion of organisational change management is noted above in the models of cultural competence. 54 10. TOWARDS A FRAMEWORK OF CULTURAL COMPETENCE ASSESSMENT This literature review indicates there is ample work on models of cultural competence and tools of assessment. Models of cultural competence need to be adopted, implemented in a way that is integrally embedded in the other processes of the organisation. Cultural competence needs to be viewed at different levels on the continuum of individual to systemic. Cultural competence is both a process (means) and an end. Often the measurement is about looking at outcomes at the end, which often misses the process. Therefore some indicators of the process can be less fixed or more qualitative in nature. The domains of assessment and reporting are important. The key headings emerging from the literature that are very important are: Access to services; Attitudinal change and non-discrimination; Equitable utilisation of health services; Removal of disparities in health outcomes; Leadership; Corporate Systems: policies, strategic plans, quality assurance, risk management; Processes: Streamlined processes, cultural competence embedded; Communication: language services, multilingual material, use of interpreters, bilingual staff, clinical communication competence with CALD consumers; Clinical processes and procedures: reviewed through cultural diversity lens; Care delivery and patient support: patient-centred care; Workforce diversity and training: for example, cultural competence training, formal certificates in cultural competence, bilingual staff; Consumer participation: in a range of committees, not just cultural diversity committee; Partnerships and community engagement- with relevant stakeholders Cultural resources and expertise; Integrated data collection systems which can provide cultural data as a sub-set of the whole for example, CALD patient satisfaction; Appropriate research which feeds into quality improvement, service delivery, consumer engagement; and Accountability public reporting of cultural diversity issues in reports, consumer participation in quality assurance processes and reporting. GOOD PRACTICE EXAMPLE The European project ‘Migrant-friendly hospitals’ (MFH), sponsored by the European Commission, DG Health and Consumer Protection (SANCO) brought together hospitals from 12 member states of the European Union, a scientific institution as coordinator, experts, international organisations and networks. These partners agreed to put migrant-friendly, culturally competent health care and health promotion higher on the European health policy agenda and to support other 55 hospitals by compiling practical knowledge and instruments. To test the feasibility of becoming a migrant-friendly and culturally competent organisation the project implemented and evaluated three selected subprojects in European hospitals. Local implementation was financed out of hospital funds, and the European benchmarking process was resourced by the project. In 2004 recommendations were launched as the ‘Amsterdam Declaration towards Migrant Friendly Hospitals in an ethno-culturally diverse Europe. The declaration identified a number of areas which hospitals needed to focus on in making their organisations ‘migrant friendly’ which included: Developing a migrant-friendly hospital is an investment in more individualised and more person-oriented services for all patients and clients as well as their families. Building awareness of migrant population experiences and existing health disparities and inequities, including those that are gender-related, leading to changes in communication, organisational routines and resource allocations. Focusing on ethno-cultural diversity implies the risk of stereotyping—but migrant status, ethnic descent; cultural background and religious affiliation are just a few of the many dimensions of the complexity of human beings. Developing partnerships with local community organisations and advocacy groups who are knowledgeable about migrant and minority ethnic group issues is an important step that can facilitate the development of a more culturally and linguistically appropriate service delivery system. Ensuring that hospital owners and management put quality of services for migrants and ethnic minorities on the organisational agenda. Ensuring that users (actual and potential patients, relatives), representatives of community groups, patient organisations and community groups put diversity and health and health care on their respective agendas. Getting staff in health professions, hospitals and professional organisations to acknowledge that the issues are relevant and being prepared to invest in achieving competence. Health policy and administration to provide a framework to make migrant-friendly quality development relevant and feasible for each hospital (legal, financial, and organisational regulations). Health sciences through moving diversity issues in health and health care higher up on their agendas, by including them in their theory-building and the development of systematic evidence, health science disciplines can make important contributions. Ethnic and migrant background information should be included as a relevant category in epidemiological, socio-behavioural, clinical, health service and health system research. (http://www.mfh-eu.net) An important recommendation from this Declaration is the need to define what cultural competence means. However, rather than generic criteria they note that, as a first step, each service needs ‘to find consensus on criteria for migrantfriendliness/cultural competence/ diversity competence adapted to their specific situation and to integrate them into professional standards and enforce that they are realised in everyday practice’ (Amsterdam Declaration, http://www.mfh-eu.net). There was a pilot program undertaken with 12 hospitals across Europe which began in 2002. A Migrant Friendly Quality Questionnaire (MFQQ) tool was developed and implemented across the 12 hospitals to assess how friendly hospitals were to immigrants. The MFQQ proved useful in systematically assessing migrant-friendly 56 structures such as interpreting services, information material for migrant patients, culturally sensitive services (religion, food), as well as components of a (quality) management system to enable and assure the migrant-friendliness of services. The six problem areas were identified as: language and communication, culturally appropriate patient information and education, cultural barriers/lack of cultural competencies, family visits, lack of culturally appropriate food and spirituality and social support. Three project areas were selected to be worked upon: Improving interpreting services Migrant-friendly information and training for mother and child care Staff training towards cultural competence. A major strategy to test the feasibility of becoming a migrant-friendly and culturally competent organisation was the implementation and evaluation of evidence and experience-based interventions in these three specific areas. An initial assessment in 2003 showed a heterogeneous European hospital group, with some hospitals listing, many existing migrant-friendly services and a well-established management structure in place, but with other hospitals showing considerable areas for further development. The results after one year of work within the European project showed that the majority of hospitals could use the project for considerable improvements both on the level of services as well as for developing their quality management systems (http://www.mfh-eu.net/public/files/mfh-summary.pdf). While the project summary states that experiences and results were presented at the Final Conference ‘Hospitals in a Culturally Diverse Europe’ in Amsterdam, Dec 9-11, 2004, a search of the conference proceedings did not yield sufficient detail of the evaluation of the project. 57 11. CONCLUSION It is evident from this review that in Australia much has been achieved at the Commonwealth and state levels in terms of recognition of the challenges faced by culturally and linguistically diverse populations and health services. However cultural competence practice in health settings is problematic and implementation and reporting are fragmented. It has been noted in this document that addressing discrimination at the personal level is not straight forward as it often reflects broader community and organisational norms. Strategies therefore targeted to individuals are more likely to be effective when they are implemented alongside those aimed at building community, organisational and societal environments that promote and respect diversity. This can be further supported by developing culturally sensitive practice such as that being undertaken in the Migrant Friendly Hospital project or in the United States to measure CLAS outcomes. From this literature review it is noted that there are significant challenges in the implementation and reporting of cultural competence. These include: Precise definitions of what is meant by cultural competence; Integration of cultural competence initiatives with allied health practices such as quality improvement, standards and accreditation, quality of care, risk management and safety systems; Leadership for organisational change to implement cultural competence; Streamlining reporting processes; Appropriate consumer participation; Context specific benchmarks and indicators; and Appropriate resources for cultural competence initiatives. Creating cultural competence requires a shift in thinking as well as practice. NHMRC (2005) points out mandatory measures need to be supported by initiatives that promote good governance and reward change. An approach that combines mandatory measures with incentives for improvement includes: Strong accountability mechanisms; Ensuring performance against these mechanisms; Persuasive leadership for change at senior levels across the sector; Applying existing tools and initiatives to create cultural competence for example, risk assessment/management, continuous improvement cycles, triple bottom line reporting, safety and quality initiatives; Systematic change management strategies; An evidence base built on culturally competent research that can inform policy, planning, education and capacity building, and evaluation; and Measures to build a culturally competent workforce. Health organisations, policy makers and planners need to seek data, develop infrastructure, set achievable short, medium and long-term goals and use business best-practice tools to achieve sustained cultural responsiveness. Future directions in the work relating to cultural competence must pay attention to the lack of consistent 58 definition and framework, strategies to making it integral to the operation of the agency and appropriate measurement indicators of progress. 59 REFERENCES Aged and Community Services Australia (2006) Strength through diverse aged and community care: National Policy Position: Canberra: Author. Anderson, L., Scrimshaw, S. Fullilove, M., Fielding, J., Normand, J., and the Task Force on Community Preventive Services (2003) Culturally competent healthcare systems: A systematic review. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 24 (3s) 6877. Elsevier. Andrews, D., Neville, L., and Wynne, R. Cultural Diversity Plan (2007–08) Department of Human Services Victoria: Author. Andrulis, D.P. (2005) Moving Beyond the Status Quo in Reducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Children’s Health, Public Health Reports / July–August 2005 / Volume 120, pp 370 – 377. Andrulis, D.P. (2003) Reducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Disease Management to Improve Health Outcomes, Disease Management and Health Outcomes. 11(12):789-800. Armstrong A, Francis R., Bourne M. and Dussuyer, I. (2002) Difficulties of Developing and Using Social Indicators and Using Social Indicators to Evaluate Government Programs: A Critical Review, 2002 Australasian Evaluation Society International Conference, http://eprints.vu.edu.au/859/1/Difficulties_of_Developing_and_Using_Social_Indicat ors_.pdf Australian Council on Health Care Standards EQuIP 4 Guide. Accreditation Standards and Guidelines Part 1. Commonwealth Government Canberra: Author. AIHW (2004) Australia’s Health 2004. The ninth biennial report of the Australian Institute for Health and Welfare. AIHW Cat No AUS44. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, Canberra. AIHW (2002) Australia’s Children: Their Health and Wellbeing 2002. AIHW Cat. No. PHE 36. Australian Institute of Health and Welfare, Canberra. Bamlett, M. (2007) Translating What We Know Into What We Do. Creating Culturally Competent Early Childhood Services for Indigenous Children, Victorian Aboriginal Child Care Agency, Melbourne. http://ccyp.scu.edu.au/download.php?doc_id=2068andsite_id=27 Retrieved 26/10/2008. Beach, C., Saha, S., and Cooper, L. (2006) The role of cultural competence and patient-centredness in health quality. Committee on Quality Health Care in America. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A new Health System for the 21st Century, National Academy Press, Washington, DC. Beneforti, M. and Cunningham, J. (2002) Investigating indicators for measuring the health 60 and social impact of sport and recreation programs in Indigenous communities, Australian Sports Commission and Cooperative Research Centre for Aboriginal and Tropical Health,Darwin. Betancourt, J. Green, A and Carrillo, J. (2002) Cultural competence in health care: Emerging frameworks and practical approaches. Field Report, 1-27 www.cmwf.org. Retrieved 26/9/2008. Betancourt J.R. (2006a) Improving Quality and Achieving Equity: The Role of Cultural Competence in Reducing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. The Commonwealth Fund. Betancourt, J.R. (2006) Cultural competency: Providing quality care to diverse populations. Consultant Pharmacist, December, 21 (12), 988-985. Bischoff, A. (2003). Caring for migrant and minority patients in European hospitals A review of effective interventions: A study commissioned by the Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for the Sociology of Health and Medicine, Vienna; ‘MFH – Migrant Friendly Hospitals, a European initiative to promote health and health literacy for migrants and ethnic minorities' Neuchâtel and Basel. Brach, C and Fraserirector, I. (2000) Can cultural competency reduce racial and ethnic health disparities: A review and current conceptual model. Medical Care Research and Review , 57 Supplement 1 181-217: Sage Publications. Campesino, M. (2008). Beyond transculturalism: Critiques of cultural education in nursing. Journal of Nurse Education 47 (7), 298-304. Campinha-Bacote J. (2002) The Process of Cultural Competency in the Delivery of Health Care Services: A Model of Care, Journal of Transcultural Nursing, Vol. 13 (3), pp 181-201. Campinha-Bacote, J. (1999) A model of instrument for addressing cultural competence in health care. Journal of Nursing Education.38 (5): 203-7. Centre for Culture Ethnicity and Health (2003) Diversity in Hospitals: Responding to the needs of Patients and Client Groups from Non-English Speaking Backgrounds; Prepared by Acute Diversity Care Collaboration. Chenoweth, M., Jeon, Y., and Burke, C. (2006). Cultural competency in nursing care: An Australian perspective. International Nursing Review 53 34-40. Cioffi, J. (2005). Nurses’ experiences of caring for culturally diverse patients in acute care settings. Contemporary Nurse 20, (1), 78-86 Cross TL, Bazron BJ, Isaacs MR, Dennis KW. (1989) Towards a culturally competent system of care: A monograph on effective services for minority children who are severely emotionally disturbed. Georgetown University Center for Child Health and Mental Health Policy. CASSP Technical Assistance Center, Washington DC. 61 Davis, T. C., R. Michielutte, E. N. Askov, M. V. Williams and Weiss, B. D. (1998) Practical assessment of adult literacy in health care. Health Educ Behav 25(5): 61324. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Minority Health and Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2004). Setting the agenda for research on cultural competence in health care. US Department of Health and Human Services Offices of Minority Health, Washington DC. Author: http://www.ahrq.gov/research/cultural.htm Retrieved 17/11/08. Department of Human Services Victoria (2008a) Present Practice – Future Opportunities: Health Service Cultural Diversity Plan: Report on the State-wide forum May2008. Victorian Government: Author. http://www.health.vic.gov.au/cald/hlth_service.htm Retrieved 29/9/2008. Deparment of Human Services (2008b) Departmental Plan, Victorian Government,http://www.Department of Human Services.vic.gov.au/ Department of Human Servicesplan Deparment of Human Services (2006a) Cultural Diversity Guide, Victorian Government, http://Department of Human Services.vic.gov.au/multicultural Department of Human Services Victoria (2006) Doing it with us not for us, Strategic direction, http://www.health.vic.gov.au/consumer/downloads/do_it_with_us_strategic.pdf Retreived 14/10/2008. Department of Human Services Victoria (2006b) Cultural Diversity Plan for Victoria's Specialist Mental Health Services, Mental Health Branch, Melbourne. http://www.health.vic.gov.au/mentalhealth/cald/cald-strategy.pdf Department of Human Services Victoria (2006c) The Disability Services Cultural and Linguistic Diversity Strategy, Disability Services Division, Melbourne, www.Department of Human Services.vic.gov.au/disability Department of Premier and Cabinet, Victoria (1988) Performance Indicators and the Social Justice Strategy: A Discussion Paper, Victorian Government Printer, Melbourne, as cited in O’Shaughnessy, T. 2001, ‘Developing organisational indicators: choices and issues’, Evaluation Journal of Australasia, vol. 1 (new series), no. 1, pp. 43-52. Dow, B., Betty, H., Bremner, F., and Marcia, F. (2006) Bench Marking Personcentred Care Statewide Survey (2005). National Ageing Research Institute, Victoria, Australia. Dreachslin JL. (1999). Diversity leadership and organisational transformation: Performance indicators for health service organisations. Journal of Healthcare Management 44: 427-439. Dreachslin JL. (1996) Diversity Leadership, Health Administration Press, Chicago, IL. 62 Effa-Ababio, K (2005) The nature and dynamics of culture and its social, moral and religious dimensions. Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 25(2): 91-102. Ethnic Communities Council of Victoria (2006) Cultural Competence Guidelines and Protocols: Carlton Victoria: Author. Epstein, L. (2007) Health and health care implications of cultural and social diversity: The Israel reality. International Workshop Report: The Israel National Institute for Health Policy and Health Services Research. Fiscella, K. (2002) Using existing measures to monitor minority healthcare quality. In: Improving healthcare quality for minority patients. The National Quality Forum: Washington. Flores, G. (2005) The impact of medical interpreter services on quality of health care: A systematic review. Medical Care Research and Review 62 (3), 255-299. Flores, G. (2000) Culture and the patient physician relationship: achieving cultural competence in health care. The Journal of Pediatrics; 136 (31). Gregg J. and Saha S. (2006) Losing Culture on the Way to Competence: The Use and Misuse of Culture in Medical Education, Academic Medicine, Vol. 81 (6), pp 542-547. Gregg J, Bussey-Jones J, Fernandez L, Lemon M, et al. (2005) Cultural Competence Training in Medicine: Should We? http://www.sgim.org/PDF/ResidencyReform/HealthDisparities.pdf Government of South Australia Culturally Linguistically Diverse: Action Plan 20072010 www.rah.sa.gov.au Retrieved 26/9/2008. Government of Western Australia (2005) Cultural competence Standards and SelfAssessment Audit Tool: Manual: Department of Health: Author. Government of Western Australia (2005b) WA Health Aboriginal Cultural Respect Implementation Framework, Office of Aboriginal Health, Perth. Home and Community Care (1991) HACC National Standards Instrument and Guidelines, A Joint Commonwealth and State Territory Program, Department of Health and Ageing, http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/29EC2F462FD49A70 CA256F190010829E/$File/isd_nsig.pdf. Inglehart, M. and C. Quiney (1997) Cultural audits: Introduction, process and results. Journal of Dental Education 61: 283-288. Institute of Medicine (2002) Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. National Academies Press, Washington. Institute of Medicine (2001) Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century, National Academies Press, Washington. 63 Kroeber, A. L. and Kluckhohn, C. (1952) Culture: a critical review of concepts and definitions. Peabody Museum, Cambridge, MA. Jirwe M, Gerrish K, Emami A. (2006) The theoretical framework of cultural competence. Journal of Multicultural Nursing and Healt.12 (3):6-16. Johnstone, M. and Kanitsaki, O. (2006) Culture, language, and patient safety: making the link. International Journal of Quality in Health Care 18 (5), 383-388. Johnstone, M. and Kanitsaki, O. (2007) Health service and consumer understandings of cultural safety and cultural competence in health care: An Australian study. Journal of Cultural Diversity 14, (2), 96-105. Johnstone, M. and Kanitsaki, O. (2007) An exploration of the Notion and nature of the construct of cultural safety and it’s applicability to the Australian Health Care context. Journal of Transcultural Nursing, 18 (3) 247-256. Institute of Medicine of the National Academies (2008) Challenges and successes of reducing disparities in health. Roundtable on health disparities: National Academy Press. Kelly, N., and Bancroft, M. (2007) The critical role of health care interpreting: views from the literature, promising practices and lessons learned in the United States. The Israel National Institute for Health Policy and Health Services: International Workshop Report. L. Epstein (Ed.) Kreps, G. (2007) Health communication at the population level: Methods and results. The Israel National Institute for Health Policy and Health Services: International Workshop Report. L. Epstein (Ed.) King, R., Green, A., Tan-McGrory, E., Donahue, E., Kimbrough-Sugick, J., and Betancourt, J., (2008). A Plan for Action: Key Perspectives from the Racial/Ethnic Disparities Strategy Forum. The Milbank Quarterly 86 (2) 241-272. Kroeber, A.L., and Kluckhohn, C. (1952). ‘Culture: a critical review of concepts and definitions.’ Papers of the Peabody Museum of American Archaeology, 47(1). Kumas-Tan Z, Beagan B, Loppie C, et al (2007) Measures of cultural competence: examining hidden assumptions. Acad Med 2007 Jun; 82(6):548-57. Levin-Zamir, D. (2007). Health literacy, empowerment and cultural competence. The Israel National Institute for Health Policy and Health Services: International Workshop Report. L. Epstein (Ed.) Lewin Report (2002). Indicators of Cultural Competence in Health Care Delivery Organisations: An Organisational Cultural Competence Assessment Profile US Department of Health and Human Services (HRSA). Like, R. (2007) Cultural competence: Implications for clinical practice, and public policy. The Israel National Institute for Health Policy and Health Services: International Workshop Report. L. Epstein (Ed.) 64 Manderson, L., and Allotey, P. (2002) Cultural politics and clinical competence in Australian health services. Anthropology and Medicine 10 (1). -85 Markova, T. and Broome, B. (2007) Cultural diversity issues: Effective communication and delivery of culturally competent health care. Urologic Nursing 27 (3)239-242. Multicultural Forum of Mental Health Practitioners (2005) Cultural competence Standards and Self-Assessment Audit Tool Manual, Perth, WA. National Aboriginal Health Organisation (NAHO), (2008). National Competency and Safety: A Guide for Health Care Administrators, Providers and Educators. Canada: Author. http://www.haho.ca Retrieved 26/9/2008. National Health and Medical Research Council (2006) Cultural competence in Health: A guide for policy, partnerships and participation. http://www.nhmrc.gov.au Retrieved 23/9/2008. National Quality Forum (2002) Improving Healthcare Quality for Minority Patient, Workshop Proceedings, Washington DC, http://www.qualityforum.org/pdf/reports/minority_patients.pdf Retrieved 15/10/2008. NSW Health (2004) The Health of the People of New South Wales: Report of the Chief Health Officer, 2004. Sydney: Population Health Division, NSW Department of Health, Sydney. www.health.nsw.gov.au/public-health/ chorep/choindex.htm Retrieved 30/9/2008. Omeri, A. (2004) Setting the standards. Nursing Review, August 26. Patterson, S. (2006) CALD Training for HACC Services Project: Analysis Review phase 2. University of New South Wales. http://www.dadhc.nsw.gov.au/NR/rdonl/50B41A Retrieved 30/9/2008. Paradies, Y. (2006b) A systematic review of empirical research on self reported racism and health. International Journal of Epidemiology, 35, 888-901. Proctor, N. (2006) Mental health workforce collaboration and partnership: towards a response to World Health Assembly Resolution WHA 57.19. Migration Letters: An International Journal of Migration Studies. 3 (1) 43 - 52 www.migrationletters.com Retrieved 27/9/2008. Reid J. and Tromph P. (1990) The Health of Immigrant Australia: A Social Perspective, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Sydney. Romeo C. (2007) Caring for Culturally Diverse Patients: One Agency's Journey Toward Cultural Competence, Home Health Nurse, 25(3):206-213. Ronsaville, D. and Hakim, R. (2000) Well childcare in the United States: Racial differences in compliance with guidelines. American Journal of Public Health 90, (9), 1436-43. 65 Royal College of General Practitioners (2007) Standards for Health Services in Australian Immigration Detention Centres, South Melbourne, www.racgp.org.au Smith, W. (2002) in ‘Quality and Culture – Joining the Levers’ Advancing effective health care through systems development, data and measurement, Chicago. Smith, W., Betancourt, J., Wynia, M. Bussey-Jones, J. Stone, V. Phillips, C., Fernandez, A. Jacobs, E., and Bowles, J. (2007) Recommendations for teaching about racial and ethnic disparities in health and health care. Annals of Medicine 147, (9), 654-665. http://www.annals.org Retrieved 1/10/2008. Stewart, S. (2006) Culture competence in health care: Diversity Health Institute Position Paper. Spencer, C., MacDonald, R. and Archer, F. (2008) Surveys of cultural competence in health professionals’ education: A literature review. Journal of Emergency Primary Health Care, 6, (20,) 1-13. www.jephc.com/full_article.cfm?content_id=437 Retrieved 30/9/2008. Tirado M. (1998) Monitoring the Managed Care of Culturally and Linguistically Diverse Population, The National Clearinghouse for Primary Care Information, Washington DC. Travaglia, J. (2008) About culture competence. Australian Resource Centre for Healthcare Innovations. http://www.archi.net.au Retrieved 14/10/2008. Tylor, E. B. (1924) [orig. 1871] Primitive Culture. 2 vols. 7th ed. New York: Brentano's. Serizawa, A. (2007) Cultural competence in Japan: The culturally competent organisation. Nursing education perspectives 28, (3), 141-144. Smith, M. (2002) Culture and quality: joining the levers. Advancing effective health care through systems development, data and measurement, Chicago. Smith, W. Betancourt, J, Wynia, K. Bussa-Jones, J. Stone, V. Phillips, C. Fernandez, A. Jacobs, E. and Bowles, J. (2007) Recommendations for teaching about racial and ethnic disparities in health and health care. Annals of Internal Medicine, 147 654665. www.annals.org Retrieved 12/1/2008. Standards Australia (2nd) What is a Standard? http://www.standards.org.au/cat.asp?catid=2) Retrieved 12/11/2008. Taylor, S. and Lurie, N. (2004). The role of culturally competent communication in reducing ethnic and racial healthcare disparities. The American Journal of Managed Care 10 Special Issue. U.S Department of Health and Human Services (2001) OPHS Office of Minority Health: National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services in Health Care: Final Report (March 2001). Rockville MD: Author. 66 VicHealth (2007) More than tolerance: Embracing diversity for health: Discrimination affecting migrant and refugee communities in Victoria, its health consequences, community attitudes and solutions – A summary report: Victoria Health Promotion Foundation: Melbourne. www.vichealth.vic.gov.au Retrieved 9/10/2008. Waxman, M. and Levitt, M. (2000) Are diagnostic testing and admission rates higher in Non-English-speaking versus English-speaking patients in the emergency department? Annals of Emergency Medicine 36, (5), 456-461. Westwood, B. (2008) Recognition of cultural awareness training as a core component of health services. Aboriginal and Islander Health Worker Journal, 32 (1), 27-29. Wu, E and Martinez, M. (2006) Taking cultural competence from theory to action. The Commonwealth Fund and California Pan-Ethnic Health Network. 67 RESOURCES Appendix 1 Minimum Reporting Requirements Under HSCDP The six areas detailed in the HSCDP are: Understanding clients and their needs Data: Accurately gathering a range of information pertinent to the CALD client group will better assist your service to effectively respond to their needs through strategic and targeted planning. Does current data collection adequately map the CALD client profile? Does current data inform the development of policy, strategies and service delivery? Partnerships with multicultural and ethno-specific agencies Knowledge: Working in partnership with ethno-specific and multicultural organisations can assist your health agency to develop a better understanding of the dynamics of the CALD community in your area, and result in better service delivery outcomes for your health service and CALD client group. What initiatives could benefit from a partnership with local CALD communities? Are the community groups and agencies the health service works with reflective of the diverse groups in and around the health organisation? A culturally diverse workforce Skills: Employing staff with a range of culturally appropriate competencies will better equip your service to respond to CALD issues and clients, and result in a more culturally responsive workforce. Do recruitment methods include strategies to reach out to local communities? Does the human resources department have a system to report diversity awareness progress to the board? Using languages to best effect Language: The effective management, provision and reporting of interpreting and translating services is vital to improve access and communication to services for persons with low proficiency in English. Are there organisational policies on when to use language services? Are there organisational procedures on accessing language services? Does the current range of translations reflect community language groups? Is the organisational information available in plain English? Encouraging participation in decision-making Engagement: Encouraging individuals and organisations to formally take part in the health service’s decision-making process will lead to better service and planning outcomes for your health service and CALD clients. Does the organisation consider CALD representation in the formation of its committees and working groups? 68 Promoting the benefits of a Victoria Education: Promoting diversity and its benefits will result in a more responsive workforce and lead to increased health benefits for the community, of which the CALD clients group is an integral part. Is diversity awareness and cultural competence training required for all leadership positions and staff? Is the organisational diversity reflected in the mission and values statement, and visible to staff and the public? Source: http://www.health.vic.gov.au/cald/downloads/cultural_diversity_plans.pdf 69 Appendix 2 Core Strategies of the Cultural diversity plan for Victoria’s specialist mental health services 2006–2010 Culturally competent practice within mental health services and recognition of this as a core skill required of staff. Action by mental health services to understand the needs of local ethnic communities, consumers and carers and to incorporate these perspectives into service and workforce planning. Action to address the barriers to the appropriate use of language services (interpreting and translating) in mental health settings. Action to address the specific mental health needs of refugees. Mental health involvement and representation in government initiatives to improve the wellbeing of culturally and linguistically diverse communities and address barriers to appropriate use of mental health services. Stronger government mechanisms for monitoring mental health services’ accessibility and responsiveness to culturally and linguistically diverse communities. Source: http://www.health.vic.gov.au/mentalhealth/cald/cald-strategy.pdf 70 Appendix 3 Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services and Standards (USA) 1. Health care organisations should ensure that patients/consumers receive from all staff members effective, understandable, and respectful care that is provided in a manner compatible with their cultural health beliefs and practices and preferred language. 2. Health care organisations should implement strategies to recruit, retain, and promote at all levels of the organisation a diverse staff and leadership that are representative of the demographic characteristics of the service area. 3. Health care organisations should ensure that staff at all levels and across all disciplines receive ongoing education and training in culturally and linguistically appropriate service delivery. 4. Health care organisations must offer and provide language assistance services, including bilingual staff and interpreter services, at no cost to each patient/consumer with limited English proficiency (LEP) at all points of contact, in a timely manner during all hours of operation. 5. Health care organisations must provide to patients/consumers in their preferred language both verbal offers and written notices informing them of their right to receive language assistance services. 6. Health care organisations must assure the competence of language assistance provided to limited English proficient patients/consumers by interpreters and bilingual staff. Family and friends should not be used to provide interpreting services (except on request by the patient/ consumer). 7. Health care organisations must make available easily understood patient related materials and signposting in the languages of the commonly encountered groups and/or groups represented in the service area. 8. Health care organisations should develop, implement, and promote a written strategic plan that outlines clear goals, policies, operational plans, and management accountability/oversight mechanisms to provide culturally and linguistically appropriate services. 9. Health care organisations should conduct initial and ongoing organisational selfassessments of CLAS-related activities and are encouraged to integrate cultural and linguistic competence-related measures into their internal audits, performance improvement programs, patient satisfaction assessments, and outcomes-based evaluations. 10. Health care organisations should ensure that data on the individual patient's/consumer's race, ethnicity, and spoken and written language are collected in health records, integrated into the organisation's management information systems, and periodically updated. 11. Health care organisations should maintain a current demographic, cultural, and epidemiological profile of the community as well as a needs assessment to accurately plan for and implement services that respond to the cultural and linguistic characteristics of the service area. 12. Health care organisations should develop participatory, collaborative partnerships with communities and utilise a variety of formal and informal mechanisms to facilitate community and patient/ consumer involvement in designing and implementing CLAS-related activities. 13. Health care organisations should ensure that conflict and grievance resolution processes are culturally and linguistically sensitive and capable of identifying, 71 preventing, and resolving cross-cultural conflicts or complaints by patients/consumers. 14. Health care organisations are encouraged to regularly make available to the public information about their progress and successful innovations in implementing the CLAS standards and to provide public notice in their communities about the availability of this information 72 Appendix 4 Lewin Group Cultural Competence Domains (2002) Organisational Values: An organisation’s perspective and attitudes regarding the worth and importance of cultural competence, and its commitment to providing culturally competent care pertaining to: Leadership, Investment and Documentation Information/Data Relevant to Cultural Competence Organisational Flexibility. Governance: The goal setting, policy-making, and other organisational vehicles to help ensure the delivery of culturally competent care: Community Involvement and Accountability Board Development Policies. Planning Monitoring and Evaluation: The mechanisms and processes used for: Long and Short-term Policy, Programmatic, and Operational Cultural Competence Planning Informed by External and Internal consumers The Systems and Activities Required to Proactively Track and Assess Organisational Cultural Competence Client, Community and Staff Input Plans and Implementation Collection and Use of Cultural Competence-Related Information/Data. Communication: The exchange of information between the organisation/providers and the clients/population, and internally among staff, in ways that promote cultural competence. Understanding of Different Communication Needs and Styles of Client Population Culturally Competent Oral Communication Culturally Competent Written/Other Communication Communication with Community Intra-Organisational Communication. Staff Development: An organisation’s efforts to ensure staff and other service providers have the requisite attitudes, knowledge and skills for delivering culturally competent services: Training Commitment Training Content Staff Performance indicators. Organisational Infrastructure: The organisational resources required to deliver or facilitate delivery of culturally competent services: Financial/Budgetary Staffing Technology Physical Facility/Environment Linkages. 73 Services and Interventions: An organisation’s delivery or facilitation of clinical, public health, and health related services in a culturally competent manner: Client/Family/Community Input Screening/Assessment/Care Planning Treatment/Follow-up. 74 Appendix 5 Cultural Competence Assessment Tools Source: http://www.transculturalcare.net/assessment-tools.htm ■ Inventory for Assessing the Process of Cultural Competence Among Healthcare Professionals-Revised (IAPCC-R©) – Developed by Campinha-Bacote (2002), the IAPCC-R is based on her model of cultural competence, The Process of Cultural Competence in the Delivery of Healthcare Services (1998) and measures the five constructs of this model (cultural desire, cultural awareness, cultural knowledge, cultural skill and cultural encounters). Studies were conducted with a variety of healthcare professionals and reliability scores ranged from a Cronbach's alpha of 0.72-0.90. This tool has also been translated into several languages and used internationally. Click onto the following link for more details of studies using this tool. ■ Inventory for Assessing the Process of Cultural Competence Among Healthcare Professionals-Student Version (IAPCC-SV©) – Developed by Campinha-Bacote (2007), the IAPCC-SV© is based on the Inventory for Assessing the Process of Cultural Competence Among Healthcare Professionals-Revised (IAPCC-R©). Vito, Roszkowski, and Wieland (2005) noted in a study of 695 student nurses that the IAPCC-SV© could be further revised resulting in a higher reliability of this tool. The IAPCC-SV© is a result of modifying the response format of the IAPCC-R© to reflect only responses of strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree and modifying and deleting selected questions on the IAPCC-R©. Fitzgerald, Cronin and CampinhaBacote (2007) conducted a study entitled, Psychometric Testing of a Proposed Student Version of the Tool, ‘Inventory for Assessing the Process of Cultural Competence Among Healthcare Professionals-Revised’ in which they administered the IAPCC-SV© to 91undergraduate nursing students at Bellarmine University Lansing School of Nursing and Health Sciences to establish reliability of this tool. Reliability testing revealed a Cronbach's alpha of .783. Click onto the following link for more details of this tool. ■ Cultural Diversity Questionnaire For Nurse Educators – Developed by Lorinda Sealey (2003), this fifty-five item tool includes statements developed by this researcher, as well as items adapted from Campinha-Bacote's tool (IAPCC-R). This tool also consists of items adapted from research conducted by Goode, Mason and Ward. The Cultural Diversity Questionnaire For Nurse Educators is based on Campinha-Bacote's model of cultural competence and includes items related to cultural awareness, cultural knowledge, cultural skill, cultural encounters, and cultural desire. Research on the tool is published in the following citation: Sealey, L., Burnett, M. and Johnson, G. (2006). Cultural Competence of Baccalaureate Nursing Faculty: Are We Up to the Task? Journal of Cultural Diversity, 13(1), 131-140. Contact: lsealey@selu.edu http://etd.lsu.edu/docs/available/etd-1112103-133929/unrestricted/Sealey_dis.pdf ■ Blueprint for Integration of Cultural Competence in the Curriculum Questionnaire (BICCCQ) –The 31-item BICCCQ was developed at the University of Pennsylvania, School of Nursing, to measure student reports of components of content on cultural competence taught in undergraduate and graduate nursing programs. BICCCQ items 75 were derived from the Tool for Assessing Cultural Competence Training, which was developed to measure faculty report of components of content on cultural competence in medical school curricula. Cronbach's alpha ranged from .73 to .94 across factors and was .96 overall. Citation: Tulman, L. and Watts, R. (2008). Development and testing of the Blueprint for Integration of Cultural Competence in the Curriculum Questionnaire. Journal of Professional Nursing, 24(3), 161-166. ■ Cultural competence Organisational Assessment – 360 (COA360) – The COA360 is an instrument designed to appraise a healthcare organisation's cultural competence. The Office of Minority Health and the Joint Commission have each developed standards for measuring the cultural competence of organisations. The COA360 is designed to assess adherence to both of these sets of standards. Citation: LaVeist, T., Relosa, R. and Sawaya, N. (2008). The COA360: A Tool for Assessing the Cultural competence of Healthcare Organisations. Journal of Healthcare Management, 53(4):257-66; discussion 266-267. ■ Transcultural and International Nursing Knowledge Inventory (TINKI) – Baldonado et al (1998) developed the TINKI, which is a questionnaire that includes closed and open-ended questions related to participant's experiences in providing cultural care. Citation: Baldonado, A., Ludwig Beymer, P., Barnes, K., Starsiak, D., Nemivant, E. and Anonas-Ternate A. Transcultural Nursing Practice Described by Registered Nurses and Baccalaureate Nursing Students. Journal of Transcultural Nursing, 9: 1525. ■ Cross-Cultural Evaluation Tool – The Cross-Cultural Evaluation Tool was developed by Freeman. It is a five-point likert-type scale which measures a student's ability to make culturally sensitive choices. Hughes and Hood (2007) published an article which presents the psychometric properties of the Cross-Cultural Evaluation Tool that yields a cross-cultural interaction score. Citation: Hughes, K. and Hood, L. (2007). Teaching Methods and an Outcome Tool For Measuring Cultural Sensitivity in Undergraduate Nursing Students. Journal of Transcultural Nursing, 18:57-62. ■ Cultural Competence Assessment (CCA) – Schim and colleagues developed the CCA instrument, which is designed to measure cultural diversity experience, awareness and sensitivity, and competence behaviors among health services and staff. Research on the tool is published in the following citation: Schim, S., Doorenbos, A., Miller, J. and Benkert, R. (2003). Development of a Cultural Competence Assessment instrument. Journal of Nursing Measurement 11(1):29-40. ■ Infant/Toddler Caregiver Cultural Rating Scale (ITCCRS) - Based on Sue's (1981) tri-dimensional model, the ITCCRS was created to assess 109 child care providers' cultural competence and the demographic correlates of that competence. Subjects were from 30 randomly selected infant/toddler centers that were licensed to provide child care. The ITCCRS consists of 40-items; 10 items assessing awareness; 19 measuring knowledge, and 11 measuring skills. Obegi, A. and Ritblat, S. (2005). Cultural Competence in Infant/Toddler Caregivers: Application of a Tri-Dimensional Model. Journal of Research in Childhood Education, 19(3), 199-213. 76 ■ Miville-Guzman Universality-Diversity Scale (M-GUDS) – This is a 45-item questionnaire rated on a 6-point Likert-type scale ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree. This scale is based on the theoretical model called the UniversalDiverse Orientation (Fuertes, Miville, Mohr, Sedlaki, and Gretchen, 2000), which emphasizes an ability to tolerate similarities and differences between one's self and another. The scale's three subscales are diversity of contact, relativistic appreciation, and comfort with differences. This scale makes the theoretical leap that tolerance of difference is key to intercultural work and cultural competence. Citation: Fuertes, J. N., Miville, M. L., Mohr, J. J., Sedlacek, W. E., and Gretchen, D. (2000). Factor structure and short form of the Miville-Guzman Universality-Diversity Scale. Measurement and Evaluation in Counselling and Development, 33, 157-169. ■ Tailoring Initiatives to Meet the Needs of Diverse Populations: A Self-Assessment Tool – A self-assessment tool is provided in Chapter 8 of One Size Does Not Fit All: Meeting the Health Care Needs of Diverse Populations to help organisations evaluate the way they currently provide care and services to diverse patient populations. The questions are designed to promote discussion around the need to improve or expand current initiatives to meet patients’ cultural and language (CandL) needs. ■ Cultural Awareness Scale (CAS) – Developed by Rew, Becker, Cookston, Khosropour, and Martinez (2003) to measure the multidimensional nature of cultural awareness in nursing students. The authors identified five key categories of cultural awareness, based on a review of the literature, and developed scale items in each of these categories: (1) general educational experience; (2) cognitive awareness; (3) research issues; (4) behaviours/comfort with interactions; and (5) patient care/clinical issues. Rew, L., Becker, H., Cookston, J., Khosropour, S., and Martinez, S. (2003). Measuring Cultural Awareness in Nursing Students. Journal of Nursing Education, 42 (6), 249-257. ■ Sociocultural Attitudes in Medicine Inventory (SAMI) - Developed by Tang et al, this 26-item 5-point Likert scale tool measures attitudes toward sociocultural issues in medicine and patient care. Tang, T., Fantone, J., Bozynski, M. and Adams, B. (2002). Implementation and Evaluation of an Undergraduate Sociocultural Medicine Program. Academic Medicine, 77(6),578-585. ■ Transcultural Self-Efficacy Tool (TSET) – Developed by Jeffreys (2000), this tool is designed to measure the degree of cultural self-efficacy among nursing students. According to the tool’s authors, transcultural self-efficacy refers to perceived confidence in performing or learning transcultural skills. The TSET consists of 83 items, conceptually based on the literature of transcultural nursing, ordered into three subscales: (1) Cognitive (knowledge, consisting of 25 items); (2) Practical (interview, consisting of 28 items); and (3) Affective (Values, attitudes and beliefs, consisting of 30 items). ■ Tucker-Culturally Sensitive Health Care Inventories (T-CSHCI) – Tucker has developed three race/ethnicity-specific forms of the T-CSHCI (one each for African Americans, Hispanics and non-Hispanic whites) to be used by patients at communitybased primary care centers to evaluate the level of patient-centered cultural sensitivity perceived in the health care that they experience. The T-CSHCI Patient Form: a) are for patient use by patients; b) assess specific provider and office staff behaviours and attitudes and healthcare center policies and physical characteristics; 77 c) emphasize assessment of cultural-specific interpersonal behaviours; and d) consist of items generated by low-income racial/ethnic minority and majority patients. Citation: Tucker, C., Mirsu-Paun, A., van der Berg, J., Ferdinand, L., Jones, J., Curry, R., Rooks, L., Walker, T., Beato. (2007). Assessments for Measuring PatientCentered Cultural Sensitivity in Community-Based Primary Care Clinics. Journal of the National Medical Association, 99(6), 609-619. http://www.nmanet.org/images/uploads/Publications/OC609.pdf. Based on Tucker's Patient-Center Culturally Sensitive (PC-CS) Health Care Model, she has also developed the T-CSHCI Provider Form and the T-CSHCI Staff Form. Please visit Dr. Carolyn Tucker's home page at: http://www.psych.ufl.edu/~tucker/BMED/BMED%20about.htm ■ Competence Continuum (CCC) – Based on Cross's (1989) Cultural Competence Continuum Model of the 6 stages of cultural competence along a continuum, Wong converted this conceptual model (CCC) to an ordinal scale to assess behavior in cultural interactions revealed in reflective student writing. This tool s based on the premise that students' reflective writing can be analysed using the CCC to reliably and objectively assess the degree of cultural competence revealed in specific cultural interactions. This behavioural assessment of cultural competence may provide a method for providing feedback aimed at professional development in the area of cultural competence for students, clinicians, faculty, and programs. Christopher Wong is director of physical therapy programs at Touro College, 27 West 23rd Street, New York, NY 10010 (ckwong@touro.edu). ■ Intercultural Development Inventory (IDI) – The IDI was designed by Bennett and Hammer and measures how a person or a group of people tend to think and feel about cultural difference. The IDI is based on Bennett’s Developmental Model of Intercultural Sensitivity. Citation: Hammer, M. R., Bennett, M. J., and Wiseman, R. (2003). Measuring intercultural competence: The Intercultural Development Inventory. International Journal of Intercultural Relations. 27(4), ppp.421-443. ■ Cross-Cultural Adaptability Inventory (CCAI) – Developed by Kelly and Meyers (1993) to help participants understand the qualities that enhance cross-cultural effectiveness, become self-aware, decide whether to work in a culturally diverse company and whether to live abroad, and to prepare to enter another culture. The CCAI measures the 4 variables of emotional resistance, flexibility and openness, perceptual acuity, and personal autonomy. (Intercultural Press - 1-800-370-2665). ■ Cultural Bases of Health Survey (CBHS) – The CBHS instrument consists of three close-ended and one open-ended demographic questions; 35 close-ended, Likertscale cultural competence questions; and one open-ended clinical case vignette question. This instrument is a result of the’ Seeing the Body Elsewise: Connecting the Pre-Health Sciences and the Humanities grant project of the University of Michigan's Program in Culture, Health, and Medicine. The aim of this grant was to rethink ways cultural diversity is taught in pre-health education. The project included an interdisciplinary model for teaching pre-health undergraduate students (premedicine, pre-nursing, pre-life sciences) about the intersections of race, gender, health, and ethnicity. The CBHS is one of the project’s evaluation activities. For more information contact Dr. Piontek at mpiontek@umich.edu or visit http://c2003.evaluationcanada.ca/download files/Piontek_Mary_203.B.doc 78 ■ Beliefs, Events, and Values Inventory (BEVI) – The BEVI is a 494-item instrument that is designed to evaluate basic openness, receptivity to different cultures, tendency to stereotype, and self / emotional awareness. The BEVI asks ‘extensive background and demographic items along with validity and process scales in order to assess variables that may influence or shape both the processes and outcomes of international or multicultural learning.’ ■ Personal Intercultural Change Orientation (PICO) – Based on the Deep Culture model of intercultural learning by Shaules, The Personal Intercultural Change Orientation (PICO) instrument was developed. It measures two orientations related to the psychological stresses associated with dealing with new cultural environments: 1) an individual ‘s orientation towards change vs. stability, and 2) whether an individual references decisions internally based on existing knowledge and values or externally, based on the knowledge and values of others. These two measurements are combined to produce four dimensions that represent different intercultural learning orientations: proactive, protective, attentive, and adaptive. http://www.pico-global.com/Default.aspx?l=2 ■ Cultural Competence Self Assessment Protocol for Health Care Organisations and Systems – Developed by Dennis Andrulis, Thomas Delbanco, Laura Avakian and Yoku Shaw-Taylor, this tool can be used by health services, including hospitals and clinics, to conduct organisational assessments of their cultural competence. The protocol’s questions are organized according to the following four cornerstones of cultural competence:1) health care organisation's relationship with its community; 2) the administration and management's relationship with staff; 3) inter-staff relationships at all levels; and 4) the patient/enrollee-provider encounter. http://erc.msh.org/provider/andrulis.pdf ■ Measures of Cultural Competence - The American Institutes of Research prepared a report for the Office of Minority Heath US Department of Health and Human Resources entitled, Cultural competence and Nursing: A Review of Current Concepts, Policies and Practices. I n Appendix C-1 there is a chart entitled Measures of Cultural Competence (page 83 ) that lists cultural assessment tools for healthcare professionals. http://thinkculturalhealth.org/ccnm/documents/CCNMEnvironmentalScanFINAL2004. pdf ■ Tools for Assessing Cultural Competence - Program For Multicultural Health has a website that contains a web page entitled, Tools for Assessing Cultural Competence. This webpage can be accessed at: http://www.med.umich.edu/multicultural/ccp/Assessments.doc. This website also has a section devoted to other tools that assess institutional and organisational cultural competence. This webpage can be accessed at: http://www.med.umich.edu/multicultural/ccp/iia.htm#HPA ■ Resources in Cultural Competence Education For Health Care Professionals – In this California Endowment publication (pages 38-46), Dr. Gilbert (2003) provides a list of organisational and healthcare professional cultural assessment tools. This report can be accessed at: 79 http://www.calendow.org/reference/publications/pdf/cultural/TCE02182003_Resources_in_C.pdf ■ Summary Report Cultural Competence in Primary Health Care: Perspectives, Tools and Resources – Janet Rhymes and Darren Brown published a report entitled, Summary Report Cultural Competence in Primary Health Care: Perspectives, Tools and Resources. This report provides a brief overview of the concept of cultural competence with an emphasis on useful tools and resources. This report can be accessed at: http://www.cdha.nshealth.ca/programsandservices/diversityandinclusion/culturalCo mpetence.pdf ■ Tool for Assessing Cultural Competence Training (TACCT) – Developed by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC ) to help medical schools assess cultural competence training, the Tool for Assessing Cultural Competence Training (TACCT) is a self-administered assessment tool with broad applicability to other health professions disciplines. It is designed to examine all components of a curriculum, including the following areas: where culturally competent care is currently taught, educational elements that have been previously unrecognised, where gaps in the curriculum exist, and planned and unplanned redundancies. It includes specific domains and components and can be viewed at: http://www.aamc.org/meded/tacct/culturalcomped.pdf; http://www.aamc.org/meded/tacct/tacct.xls. The article, ‘Cultural Competence Education for Medical Students: Assessing and Revising Curriculum,’ describes the tool and its use. This article can be accessed at http://www.aamc.org/meded/tacct/culturalcomped.pdf. For more information about the tool contact Dr. Ella Cleveland at ecleveland@aamc.org or (202) 828-0531. ■ Patient Report Measure of Provider Cultural competence – Authors Lucas, Michalopoulou, Falzarano, Menon and Cunningham developed a theoretically grounded and patient report measure of provider cultural competence. This tool is based on a study of predominantly African American patients (N = 310) who were recruited from three urban medical clinics to complete a survey about their relationship with their physician. Psychometric analyses supported a tripartite model of cultural competence that was comprised of patient judgments of their physician's cultural knowledge, awareness, and skill. Citation: Lucas, T., Michalopoulou, G., Falzarano, P., Menon, S., and Cunningham, W. (2008). Healthcare Provider Cultural competence: Development and Initial Validation of a Patient Report Measure. Health Psychology, 27(2), 185-193. ■ Cultural Competence Tools - Hogg Foundation For Mental Health has complied a resource list entitled Cultural Competence Tools. This resource list includes some examples of the following types of cultural competence tools: o Organisational Tools to assess their organisation’s level of cultural competence at an administrative level. o Provider Tools to assess clinicians' cultural competence in working with clients. o Client Tools to assess clients' experience of the organisation and/or clinician’s cultural competence. http://www.hogg.utexas.edu/programs_cai_tools.html 80 ■ Cultural Competence Assessment Tool (CCAT) - Sponsored by Blue Cross Blue Shield of Massachusetts Foundation, the Cultural Competence Assessment Tool (CCAT) guides healthcare organisations through an examination of the administrative structures and practices described in the CLAS standards. Denise Dodd, PhD, developed this tool with input from staff at the Boston Public Health Commission. http://www.bphc.org/director/pdfs/disparities_assess-tool.pdf ■ Organisational Cultural Competence Assessment Profile – The Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) sponsored a project to develop indicators of cultural competence in healthcare delivery organisations. This project is aimed to contribute to the methodology and state-of-the-art of cultural competence assessment. The product - An Organisational Cultural Competence Assessment Profile - builds upon previous work in the field, such as the National Standards for Culturally and Linguistically Appropriate Services (CLAS), and serves as a future building block that advances the conceptualization and practical understanding of how to assess cultural competence at the organisational level. The project was implemented through a contract with The Lewin Group, Inc. HRSA's Office of Minority Health and Office of Planning and Evaluation provided both oversight and substantive input to the project. http://www.hrsa.gov/culturalcompetence/indicators/default.htm#Assessing ■ Cultural Self-Assessment Resources and Tools for Self-Assessment of Cultural and Linguistic Competence – The National Center For Cultural Competence in Health Care (NCCC) has developed the webpage Curricula Enhancement Module Series, that contains ‘Cultural Self-Assessment Resources’ and ‘Tools for Self-Assessment of Cultural and Linguistic Competence.’ http://www.nccccurricula.info/resources_mod2.html#appendixa ■ Cultural Sensitivity Personal Reflection Self-Assessment – This tool was developed to heighten awareness of how one views clients from culturally and linguistically diverse populations (Goode, T. D.1989, revised 2002). http://www.asha.org/NR/rdonlyres/E7805A1A-CCD2-4A35-B84AED889318EFA0/0/personal_reflections.pdf ■ Cultural Sensitivity Service Directory Self-Assessment – This tool was developed to heighten awareness of how one views clients from culturally and linguistically diverse populations (Goode, T. D.1989, revised 2002). http://www.asha.org/NR/rdonlyres/07693109-C4F6-48EA-BFC358874C8998F9/0/service_delivery.pdf ■ Cultural competence Challenge – The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) has developed the Cultural competence Challenge to assist in learning or reinforcing one’s individual knowledge of cultural care issues, without the pressure of an actual patient encounter. It is stated to be particularly useful in a residency setting to teach the next generation of orthopaedists. The CD-ROM program was showcased at their 2005 AAOS Annual Meeting and is offered via the AAOS Diversity in Orthopaedics Web site: http://www.aaos.org/diversity. Contact Dr. Ramon at ramon@jimenez.net. ■ Colour-Blind Racial Attitude Scale (CoBRAS) – The CoBRAS is a 20-item self-report measure. Participants respond utilizing a 6-point Likert-type scale, the scale ranges 81 from 1 (strongly disagree) to 6 (strongly agree). The three subscales which comprise the CoBRAS are Unawareness of Racial Privilege, Unawareness of Institutional Discrimination, and Unawareness of Blatant Racial Issues. Total score which encompasses all three subscales can range from 20 to 120 with higher scores representing more colour-blind racial attitudes. Citation: Neville, H. A., Lilly, R. L., Duran, G., Lee, R. M., and Browne, L. (2000). Construction and initial validation of the Color-Blind Racial Attitudes Scale (CoBRAS). Journal of Counselling Psychology, 47, 59-70. ■ Eastern State University's Office of Cultural Affair – Eastern State University's Office of Cultural Affair has a comprehensive website on cultural resources that contains a section on ‘Evaluation.’ This section provides information on over 10 cultural assessment tools. http://www.etsu.edu/oca/Resources.asp. ■ Clinical Cultural competence Questionnaire (CCCQ) – The Center for Healthy Families and Cultural Diversity, Department of Family Medicine, UMDNJ-Robert Wood Johnson Medical School has developed the Clinical Cultural competence Questionnaire (CCCQ) for assessing physicians' knowledge, skills, and attitudes relating to the provision of culturally competent health care to diverse patient populations. http://www2.umdnj.edu/fmedweb/chfcd/aetna_foundation.htm. ■ Organisational Cultural Competence: Self-Assessment Tools For Community Health and Social Service Organisations – The Centre for Research on Community Services of Centretown Community Health Center at the University of Ottawa produced a report entitled, Organisational Cultural Competence: Self-Assessment Tools For Community Health and Social Service Organisations. The purpose of this report was to identify and review the most relevant assessment tools for the set of organisational cultural competence standards and to make recommendations regarding the future evaluation of organisational cultural competence http://www.socialsciences.uottawa.ca/crcs/pdf/organisational_cultural_competence_ 21-12-2005.pdf ■ Clinical Cultural competence Training Questionnaire (CCCTQ) – Developed by Krajic, Like, Schulze, Strabmayer, Trummer, and Pelikan, the Clinical Cultural competence Training Questionnaire (CCCTQ) is an adapted version of the CCCQ for a hospital setting. This European Union Migrant Friendly Hospitals initiative tool is translated into seven languages. http://www.mfh-eu.net/public/experiences_results_tools/cct_eval_instruments.htm ■ The Client Cultural competence Inventory (CCCI) – The CCCI was developed through a process that incorporated information from focus groups with providers and families, interviews, and a review of relevant research literature. The CCCI is administered via a structured interview. In the field test family members were asked to rate service coordinators by responding to items grouped into four subscales: respect for cultural differences, community and family involvement, appropriateness of assessment and treatment options, and agency services and structure. Results gave evidence of the tool’s usefulness both in assessing cultural competence directly and in providing valuable informational input into a larger process of planning for continuous quality improvement. The research team continues gathering data and refining the CCCI. They are seeking collaborations with communities or organisations that are interested in using the instrument and that are willing to share data so psychometric properties of the scale can be further investigated. For more 82 information, contact Sara Hudson Scholle, Ph.D., Assistant Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Pittsburgh at (412) 624-1703 or scholles@pitt.edu. ■ SIETAR-Europa – The website, SIETAR-Europa, lists an annotated bibliography of over 50 intercultural assessments and instruments. These tools can be found at http://www.sietar.de/SIETARproject/Assessmentsandinstruments.html ■ Assessment Tools of Intercultural Communicative Competence – Fantini (2006) developed a list of 87 Assessment Tools of Intercultural Communicative Competence. http://www.experiment.org/gsi/Appendix%20F.%20ICC%20Assessment%20Tools_8 7-94_.pdf. ■ Cross-Cultural Diversity Experiences and Attitudes Questionnaire – Developed by Guiton et al. 2007, is a 55-item questionnaire measuring medical students' background, experiences, and attitudes related to cross-cultural diversity. ■ The Slope Index of Inequality (SII) – A spreadsheet tool designed to help the user calculate socioeconomic inequalities in health within an area using small area health measures. Based on Low. A. and Low, A. (2004). Measuring the Gap: Quantifying and Comparing Local Health Inequalities. Journal of Public Health Medicine, 26(4):388-396. ■ Communication, Curriculum and Culture (C3) Instrument – Developed by Haidet, Adam, and Chou, the purpose of this instrument is to help educators characterize and understand the hidden curriculum at their own institutions. The authors developed survey items to measure three content areas of the hidden curriculum with respect to patient-centered care. These content areas include role modelling, students' patient-care experiences, and perceived support for students' own patientcentered behaviors. The survey was distributed to third- and fourth-year students at ten medical schools in the United States. Using factor analysis, the authors selected items for the final version of the C3 Instrument. Citation: Haidet, P., Adam, K. and Chou, C. (2005). Characterizing the Patient-Centeredness of Hidden Curricula in Medical Schools: Development and Validation of a New Measure. Academic Medicine, 80(1), 44-50. ■ Self-Administered Instruments to Measure Cultural Competence of Health Professionals: A Systematic Review - Gozu (2007) and colleagues systematically reviewed articles published from 1980 through June 2003 that evaluated the effectiveness of cultural competence curricula targeted at health professionals by using at least one self-administered tool. They included 45 articles in their review comprising a total of 45 unique instruments (32 learner self-assessments, 13 written exams) that were used in the 45 articles. They concluded that most studies of cultural competence training used self-administered tools that have not been validated. Citation: Gozu, A., Bass, E., Powe, N., Cooper, L., Beach, M., Price, E., Gary, T., Robinson, K., Palacio, A., Smarth, C., Jenckes, M. and Feuerstein, C. (2007). Self-Administered Instruments to Measure Cultural Competence of Health Professionals: A Systematic Review. Teaching and Learning in Medicine, 19(2), 180190. 83 ■ Review of Multidisciplinary Measures of Cultural Competence for Use in Social Work Education – Krentzman, A. and Townsend, A. (2008) sought measures of cultural competence from as many sources as possible and found a total of 19 measures/instruments that met the inclusion criteria for this analysis. The tools were developed between 1986 and 2005. They come from various disciplines including social work, counselling psychology, college student affairs, pharmacy, nursing, medicine, applied health, allied health sciences, and education. All were written in the United States except for one developed in the United Kingdom. This article provides an excellent review of these tools. Citation: Krentzman, A. and Townsend, A. (2008). Review of Multidisciplinary Measures of Cultural Competence for Use in Social Work Education. Journal of Social Work Education at: http://www.accessmylibrary.com/coms2/summary_0286-34684777_ITM Mental Health Assessment Tools ■ Making Children’s Mental Health Successful: Organisational Cultural Competence: A Review of Assessment Protocols –This monograph presents the findings from a review of cultural competence assessment tools designed for the use at the organisational level that focused on health or mental health. The search for assessment tools meeting criteria yielded 45 instruments. A final selection of 17 organisational assessment instruments was examined in this report. Citation: Harper, M., Hernandez, M., Nesman, T., Mowery, D., Worthington, J., and Isaacs, M. (2006). Organisational cultural competence: A review of assessment protocols, FMHI pub. no. 240-2). Tampa, FL: University of South Florida, Louis de la Parte Florida Mental Health Institute, Research and Training Center for Children’s Mental Health. http://www.iffcmh.org/Assessment%20Protocols.pdf ■ Cultural Competence Self-Assessment Questionnaire (CCSAQ) – Developed by James Mason (1995), the CCSAQ is designed to assist service agencies working with children with disabilities and their families in self-evaluation of their cross-cultural competence. The measure is based on the Child and Adolescent Service System Program Cultural Competence Model. This model describes cultural competence in terms of four dimensions: attitude, practice, policy, and structure. This instrument is intended to help service providers and staff at child and family serving agencies to assess their cross-cultural strengths and weaknesses in order to design specific training activities or interventions that promote greater competence across cultures. The Cultural Competence Self-Assessment Questionnaire (CCSAQ) was designed for use in child and adolescent mental health systems. ■ CAMHS CCATool – The Children and Adolescent Mental Health Services (CAMHS) Cultural Competence in Action Tool (CCATool) is a tool that measures the cultural competence of individuals working with children and adolescent mental health services. It is based on the Papadopoulos, Tilki and Taylor's model of cultural competence. Citation. Papadopoulos, R., Tilki, M. and Ayling, S. (2008). Cultural Competence in Action for CAMHS: Development of a Cultural Assessment Tool and Training. Contemporary Nurse, 28(2), 129-140. Advances in Contemporary Transcultural Nursing 2nd edition. ■ Organisational Cultural Competence: A Review of Assessment Protocols – Authored by Harper, M., Mernandez, M., Nesman, T., Mowery, D., Worthington, J., and Isaacs, 84 M. (2006), is a publication that contributes to understanding how cultural competence is currently operationalised and measured at the organisational level. This monograph compares organisational assessment instruments through the following questions: For what type of organisation was the instrument developed? How were the instruments developed? How do the authors define cultural competence? What domains do the authors use as categories of analysis? http://rtckids.fmhi.usf.edu/rtcpubs/CulturalCompetence/protocol/CultCompProtocol.p df ■ Build the Field and They Will Come: Multicultural Organisational Development for Mental Health Agencies - Authored by Zetzer and Shockley (2005), this 123-page document is a Multicultural Access and Treatment Demonstration Project at Antioch University funded by the California Endowment. It contains an excellent compilation of strategies to enhance cultural competence in mental health agencies. Pages 8-14 of this document provides readers with an annotated bibliography of several organisational cultural assessment tools. In addition, pages 31-33 consists of an annotated bibliography of several individual cultural assessment tools. http://www.calendow.org/reference/publications/pdf/mental/MHAntioch.pdf ■ Consolidated Culturalogical Assessment Tool (C-CAT) Tool Kit – The Ohio Department of Mental Health, released the C-CAT, which is a set of dynamic measurement instruments that allow systems and organisations to assess their cultural competence from the perspective of an array of raters. The C-CAT Tool Kit includes the C-CAT instruments, a stand-alone database, and training and promotional materials. The C-CAT Tool Kit was developed in conjunction with mental health consumers, family members, service planners and providers, and the Outcomes Management Group, a Columbus-based management consulting firm. http://www.ccattoolkit.org/ ■ A Practical Guide for the Assessment of Cultural Competence in Children’s Mental Health Organisations – With support from a federal grant from Child Mental Health Services of the Department of Health and Human Services, the Technical Assistance Center of Judge Baker Children’s Center developed a manual with a list of cultural assessment tools. This manual, A Practical Guide for the Assessment of Cultural Competence in Children’s Mental Health Organisations, authored by Dr. Monica Roizner, is a guide to planning and implementing cultural competence assessments, with brief reviews of 14 assessment tools, resources for post-assessment cultural competence, and contact information. It is useful to agency and program administrators, providers, and human resource personnel, cultural competence trainers, and family members. http://www.jbcc.harvard.edu/publications.htm ■ The California Brief Multicultural competence Scale (CBMCS) – The CBMCS can be used by an agency to identify the training needs of the agency staff. It has its own training program that ‘flows’ from the scale. The CBMCS is a likert scale consisting of 21 items representing 4 factors: Multicultural Knowledge: Issues of acculturation, racial/ethnic identity, language, etc.; Awareness of Cultural Barriers: Challenges people of color experience accessing mental health services; Sensitivity to Consumers: What does it mean to be a person of color AND a mental health consumer of services; and Sociocultural Diversities: formerly (Nonethnic Ability) 85 Issues of gender, sexuality, aging, social class, and disability. Cronbach’s Alpha of internal consistency ranges from .90 to .75. Citation: Gamst, G., Dana, R., DerKarabetian, A., Aragon, M., Arellano, L., Morrow, G. and Martenson, L. (2004). Cultural competence Revised: The California Brief Multicultural competence Scale. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 37(3),163-187. http://www.cbmcs.org ■ Compendium of Culturally-Sensitive Assessment Tools and Inventories – The West Australian Transcultural Mental Health Centre took part in a project that developed the Compendium of Culturally-Sensitive Assessment Tools and Inventories. This project aims to assist clinicians in assessing the mental health of people from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds. Contact: Valza.Thomas@health.wa.gov.au ■ Consumer Based Cultural competence Inventory – Cornelius and colleagues developed a 52-item consumer assessment instrument of the cultural competence of mental health providers. Following a 2-year, community-driven instrument development process, this consumer assessment tool was administered to 238 African American, Latino, and Vietnamese American mental health consumers across the state of Maryland. The overall instrument had a Cronbach’s alpha of .92. Research on the tool is published in the following citation: Cornelius, L., Booker, N., Arthur, T., Reeves, I. and Morgan, O. (2004). The validity and reliability testing of a consumer-based cultural competence inventory. Research on Social Work Practice, 14(3):201-9. ■ Developing Cultural Competence in Disaster Mental Health Programs: Guiding Principles and Recommendations - This document is written by Drs. Athey and Moody-Williams. This guide includes two sections and six appendices. Section One explores the nature of culture and disaster and discusses cultural competence in the context of disaster mental health services. Section One also presents the Cultural Competence Continuum and a list of questions to address in a disaster mental health plan. Section Two sets forth nine guiding principles for culturally competent disaster mental health services and related recommendations for developing these services. The appendices provide an annotated bibliography of cultural competence resources and tools as well as a Cultural Competence Checklist for Disaster Crisis Counselling Programs. http://www.mentalhealth.samhsa.gov/publications/allpubs/SMA033828/default.asp ■ State Mental Health Agency Cultural Competence Activities Assessment – This assessment was developed by the National Association of State Mental Health Program Directors and the National Technical Assistance Center for State Mental Health Planning based on discussion at two expert meetings. The assessment consists of questions appropriate for state mental health agencies in ten areas of cultural competence. The categories include the Commissioner's Personal Leadership, Staff and Stakeholder Commitment, Responsibility for Cultural Competence, Cultural Competence Advisory Committee, Organisational Self-Assessment, Data Analysis, Cultural Competence Plan, Linguistic Competence, Standards and Contractual Requirements, and Resources. http://www.nasmhpd.org/general_files/publications/cult comp.pdf 86 ■ Cross-cultural Counselling Inventory – Revised (CCCI-R) - CCCI-R was originally created as an 18-item scale used by learners to rate the behaviour of a counsellor in a short video of a counselling session. The developers of the instrument suggest that it is best used for providing feedback during training – by faculty, peers, and clients – during simulated or actual counselling sessions, and as a self-assessment tool. This instrument has been cited in more than 75 scientific articles. Citation: LaFromboise, T. D., Coleman, H. L. K., and Hernandez, A. (1991). Development and factor structure of the Cross-cultural Counseling Inventory – Revised. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 22(5): 380-88. ■ Multicultural Counselling Awareness Scale (MCAS) – The MCAS, a revision of the MCAS: B, is a 32-item self-report measure that assesses respondents' knowledge and awareness of multicultural competence. The instrument was developed for use by counsellors and has been tested on both professional and trainee populations. Citation: Ponterotto, J. G., Gretchen D., Utsey, S. O., Rieger, B. P., and Austin, R. (2002). Revision of the Multicultural Counselling Awareness Scale. Journal of Multicultural Counselling and Development, 30: 153-80. ■ Multicultural Awareness-Knowledge-and Skills Survey – Counsellor Edition- Revised (MAKSS-CE-R) – The MAKSS-CE-R is a self-assessment instrument that is based on the MAKSS instrument, developed in 1990 which consisted of 60 self-report items on three subscales of knowledge, skills and awareness. The MAKSS-CE-R was revised in 2003 to assess the impact of training on learners' multicultural counselling competence. The MAKSS-CE-R now consists 33 items (10 items each for the Awareness and Skills subscales and 13 items for the Knowledge subscale) Citation: Kim, B. S. K., Cartwright, B. Y., Asay, P. A., and D’Andrea, M. J. (2003). A revision of the Multicultural Awareness, Knowledge, and Skills Survey-Counsellor Edition. Measurement and Evaluation in Counselling and Development, 36: 161-80. ■ Multicultural Counselling Competence and Training Survey (MCCTS) – Developed by authors Holcomb-McCoy and Myers in 1999, the MCCTS is a self-report instrument containing 32 behaviourally stated items and 29 items that require participants to provide information regarding their entry-level counselling training experiences and demographics such as gender, age, race, and year of graduation. These authors assert that there were five factors underlying the multicultural counselling competence items of the MCCTS: Multicultural Knowledge, Multicultural Awareness, Multicultural Terminology, Knowledge of Racial Identity Development Theories, and Multicultural Skills. In the calculation of internal consistency reliability coefficients (Cronbach's alpha) for the instrument, alphas of .92, .92, .79, .66, and .91 were derived for the Multicultural Knowledge, Multicultural Awareness, Multicultural Terminology, Racial Identity, and Multicultural Skills subscales, respectively (the somewhat lower reliability coefficient for the Racial Identity subscale. ■ MHA/MHP/CCAG – The Mental Hygiene Administration/Maryland Health Partners (MHA/MHP) Cultural competence Advisory Group (CCAG) developed a 52-item scale (still in progress) to assess clients' perceptions of the Public Mental Health System. Statistical analysis identified four core domains assessed by the instrument: as 1) the ability to tune into psycho-social, medical, and spiritual needs; 2) the accessibility of services and the willingness to negotiate on priorities for care; 3) 87 efforts to reach out to racially diverse communities; and 4) the willingness to listen to and respect people in recovery from various cultures. Citation: T. E., Reeves, I., Morgan, et al. (2005). Developing a Cultural Competence Assessment Tool for People in Recovery From Racial, Ethnic and Cultural Backgrounds: The Journey, Challenges, and Lessons Learned. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 28(3):pp.243-50. ■ The Cultural competence Standards and Audit Tool (the Tool) – the Tool was developed and produced by the Multicultural Forum for Mental Health Practitioners. This Western Australia based group of mental health clinicians was a policy and advisory group to the state’s mental health directorate on issues concerning service development and provisions for Western Australia’s Culturally and Linguistically Diverse (CALD) mental health consumers. The central objective of the Tool is to ensure that the organisational culture and practice of mental health services effectively accommodates Western Australia’s growing multicultural population. The Performance Measures in the Tool were designed to have three functions: to measure the extent to which services can achieve the Cultural competence Standards; to guide services in how to strive for best practice and quality-assured service provisions to CALD communities; and to assist services in implementing cultural competence initiatives at all levels. Copies of the Cultural competence Standards and Self-Assessment Audit Tool may be obtained from the Mental Health Division, Department of Health, Western Australia - 08 9222 4222. To learn more about this tool, please visit: http://www.mmha.org.au/mmha-products/synergy/edition-1-2007/using-201cthetool201d-to-test-yourself ■ Multicultural Counselling Inventory (MCI) – The MCI consists of 43 self-report items that assesses multicultural competencies on a 4-point Likert scale (1 = very inaccurate; 4 = very accurate) asking the respondent to indicate the degree to which the scale items describe their work as counselors/trainers. The MCI is based on a conceptual framework from Sue et al. (1982) on multicultural counseling competencies on the following four subscales: Awareness (ten items measure multicultural sensitivity, interactions, and advocacy in general life experiences and professional activities); Knowledge (eleven items measure treatment planning, case conceptualization, and multicultural research); Skills (fourteen items measure general and specific multicultural skills); and Relationship (eight items measure the interaction process with the minority patient for example, comfort level, world view, and trustworthiness). Citation: Sodowsky, G., Taffe, C., Gutkin, T. and Wise, S. (1994). Development of the Multicultural Counselling Inventory (MCI): A self-report measure of multicultural competencies. Journal of Counselling Psychology, 41,pp. 137-148. ■ Measures of Cultural Competence: Examining Hidden Assumption – This article, authored by Kumas-Tan et. al (2007), critically examines the quantitative measures of cultural competence most commonly used in medicine and in the health professions and identifies underlying assumptions about what constitutes competent practice across social and cultural diversity. Citation: Kumas-Tan, Z., Beagan, B., Loppie, C., MacLeod, A. and Frank, B. (2007). Measures of Cultural Competence: Examining Hidden Assumptions. Academic Medicine. 82(6), 548-557. http://www.healthsystem.virginia.edu/internet/surgery-clerkship/Measures-ofCultural-Competency-June-2007.pdf 88