File
advertisement

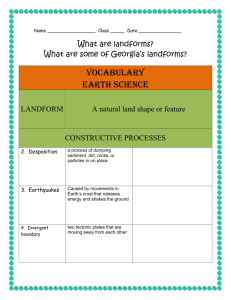
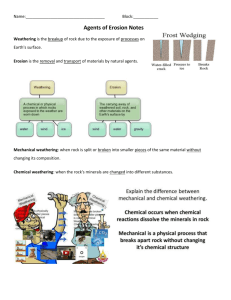
World Geography Chapter 2 List of facts Denudation- the laying bare of underlying rocks through weathering and erosion. Transportation – The moving of weathered material away from its source to another location. Deposition – The material drops away from the agent and settles on the surface. Physical weather – Wearing down of rocks caused by physical forces. Chemical weathering – Wearing down of rocks caused by chemical forces. Frost Fracture – Water seeps into the cracks of the rock and as ice forms they split apart. Exfoliation – The peeling of rock layers. Solution – weathering caused when carbon dioxide mixes with rain water, forms a weak acid and falls to the ground. Hydrolysis – Chemical reaction of a compound containing a silicate, with water. Oxidation – involves the reaction of metallic minerals in rocks to the oxygen in the water. Drainage basin – The area of land drained by a river. Divides – a line of separation between water flowing to different rivers, basins or seas. Youthful River – Rivers or streams are typically found in high lands or mountain areas. They are characterized by steep slopes a relatively small volume of water with a rapid flow. Youthful rivers tend to have narrow V shaped valleys that are relatively straight. Mature River – A river characterized by well developed tributaries a broad flat valley with a well developed flood plan and relatively broad channel with meanders. Water moves efficiently in mature rivers. Since erosion and deposition are almost balanced. Old River – A river characterized by extremely flat relief with little or no slope, very little force and elaborate meanders, because of their slow flow and lack of slope, old rivers tend to be muddy with swampy areas. Old rives have a U shaped valley. Tributaries – A river which flows into another, usually a larger one. Vertical erosion – When a river erodes the bottom of a channel. Lateral erosion – When a river erodes the sides of a channel. Hydraulic pressure – The force a river exerts on lose rock and material. Corrosion – River water flowing over rocks containing substances such as lime stone and calcium which dissolves minerals. Abrasion – Rock fragments in the river scrape, grind and gouge out other material. Meanders – Sweeping curves created in river channels. Arcuate Delta – Shaped like a bow or fan. Digitate Delta – Shaped like a finger. Estuarine Delta – Formed by tidal mud flats .. looks like a bay. Glacier – A mass of ice which may be moving or has moved over land. Alpine Glacier – A mass of ice situated on an upland which may be moving or has moved over land. Continental Glacier – A mass of ice situated over most of the continent which may be moving or has moved over land. Cirque – A circular hollow cut in the bed rock during glaciation, the side and back walls are steep but the front opens out downward. Hanging Valley – A high level tributary valley from which the ground falls sharply to the level of the lower main valley. Arete – Steep knife edge ridge between cirques in a mountainous region. Lateral Moraine – A land form deposited by a glacier or ice sheet at the side of the glacier. Medial Moraine – A land form produced for two lateral Moraines to combine. Terminal Moraine – A land form deposited by a glacier or ice sheet which marks the end of a glacier. Fiord – Long, narrow arm of the sea which the result of the drowning of the glaciated valley. Chapter 3 : Facts to know. Deflation – The land surface is slightly lowered or hollowed out. Hamada – A desert landscape made up of exposed bedrock or compacted coarse stones and gravel. Erg – A desert landscape made up of sand dunes. Abrasion – The smoothing out of the surface by blown sand and rock particles. Sand Dune – Crescent or triangle shaped pile of sand in a desert. Barchan – A crescent shaped dune with horns or arms streaming out at either side pointing in the direction of the wind. Loess – Valuable agricultural soil which has been deposited by the wind over many centuries. Wave Refraction – The bending of waves to match the shore line. Note : Energy of waves will be concentrated on headlands. Longshore Drift – Waves moving eroded rock, sand or gravel along a shore line. The order of headland erosion: 1. Sea Cave 2. Sea Arch 3. Sea Stack See diagrams on page 48 and 49.