Motion in the Ocean: currents, waves and tides all
advertisement

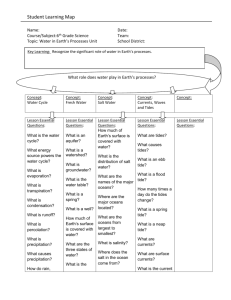
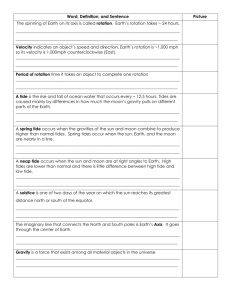
MOTION IN THE OCEAN Motion in the Ocean: currents, waves and tides all move and mix ocean waters 1. Currents http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e8nOowxO5-k a. Coriolis Effect – deflection of winds and water due to the rotation of the Earth i. Toward the right in the northern hemisphere (clockwise) ii. Towards the left in the southern hemisphere (counterclockwise) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BPNLZyBNPTE b. Gyres – large circular system of surface currents produced by global wind patterns and the Coriolis Effect http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x0EqbdSMC8E c. Upwelling – currents and wind push away water from the surface of the ocean, bringing cold, deep water up from the bottom. Rising water is rich in nutrients which attracts marine organisms to the area. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XV90dy0ns1U http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=APMzM-xYlOs d. El Niño – a warming of the surface currents around Christmas time in the eastern Pacific which stops upwelling. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B0D7NY6enIk http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7FVZrw7bk1w e. Biological Effects of Currents i. Allows for migration of marine organisms ii. Food distribution iii. Oxygenation of ocean water iv. Distribution of heat 2. Waves – the undulation of currents that forms a disturbance that moves along the surface of the ocean http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bQrj0DNXjMY a. Crest – Top of the wave b. Trough – Bottom part of the wave c. White Cap – Strong wind pushes on the top of the wave http://farm1.staticflickr.com/168/443753222_036fb4014c_z.jpg?zz=1 d. Wave Height – Calculated by measuring the vertical distance between the crest and the trough e. Wave Length – Distance between two consecutive crests or troughs http://hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca/leal/Wave_Diagram.jpg f. Breaker – Wave that loses it’s shape when it approaches shallow water http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8y1MkFZSwIs&feature=endscreen&NR=1 g. Fetch – The span of water over which wind blows generating the specific size of a wave http://www.vos.noaa.gov/MWL/apr_06/Images/Wave-Fig-2.jpg h. Swells – A wave with a flatter, rounder crest and trough found in deeper waters http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qS0lJaxkFAE i. Tsunami – (Seismic wave) The long, fast waves produced by earthquakes or other seismic disturbances of the sea floor http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P-T00d-0MGQ http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w3AdFjklR50 3. Tides – rhythmic rising and lowering of water caused by the gravitational attraction of the sun and the moon i. High Tide – water is deep ii. Low Tide – water is shallow http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rn_ycVcyxlY There is a six hour average between high and low tides A. Three Types of Tides: a. Diurnal – 1 high tide and 1 low tide per day. i. Occurs in the Gulf of Mexico b. Semi-Diurnal – 2 high tides and 2 low tides per day; the tides are relatively equal in height, easy to predict i. Occurs on the east coast c. Mixed – 2 high tides and 2 low tides per day; height of tides not equal, difficult to predict i. Occurs on the west coast B. Tidal Currents – horizontal water movements caused by tides; water periodically flows in one direction for awhile and then reverses its flow in the opposite direction a. Flood Current – Tide on the way “in” b. Ebb Current – Tide on the way “out” c. Slack Water – The period of no current in between flood and ebb currents d. Tidal Range – Vertical distance between high and low tides http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qfhNjpu_IU4 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EnDJ6_XpGfo e. Spring Tide – Greatest tidal range f. Neap Tide – Least tidal range g. Rip Tide – Caused by 2 converging currents or ebb tides moving over an irregular surface h. Biological Effects of Tides i. Planktonic distribution ii. Feeding and reproductive cycles iii. Food iv. Oxygenation