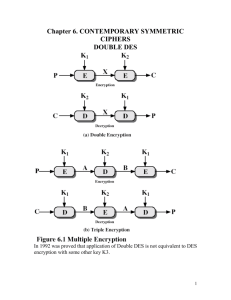
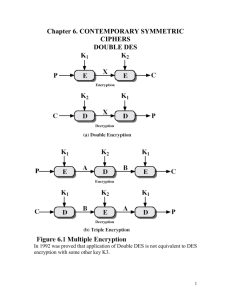
Cryptography falls under the umbrella of cryptology
advertisement

KONERU LAKSHMAIH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING VADDESWARAM BLOWFISH A PIONEER IN SYMMETRIC KEY CRYPTOGRAPHY PRESENTED BY: K.Krishna Chaitanya Azeez Shaik II/1V BTECH C.S.E II/1V BTECH C.S.E Y5cs315 Y5cs211 Chaituy252005@yahoo.co.in azeezshk@yahoo.com ABSTRACT “What makes Blowfish a preferred that DES is vulnerable to other attacks as encryption algorithm for corporations well. and banking algorithms in the literature--Khufu [11, institutions worldwide”? This paper 12], REDOC II [2, 23, 20], and IDEA [7, gives the solution why Blowfish is an 8, 9]--are protected by patents. RC2 and efficient RC4, approved for export with a small and best known algorithm used. key size, are proprietary [18]. GOST [6], Many of the other unbroken Blowfish, a new secret-key a Soviet government algorithm, is block cipher, is proposed. It is a Feistel specified without the S-boxes. From the network, iterating a simple encryption start Blowfish was intended to be a function 16 times. The block size is 64 completely free--unpatented, unlicensed, bits, and the key can be any length up to and uncopyrighted--alternative to DES. 448 bits. Although there is a complex Since then it has been analyzed by some initialization phase required before any people and has started to see use in some encryption can take place, the actual systems, both public and private. In this encryption of data is very efficient on we paper discuss the powerful blowfish large standard microprocessors. cryptographic community The needs to encryption algorithm. Its platforms, characteristics and speed provide the world with a new encryption comparisons standard. DES [16], the workhorse algorithms and its applications. While it encryption algorithm for the past fifteen may not be possible to satisfy all years, is nearing the end of its useful life. requirements with a single algorithm, it Its 56-bit key size is vulnerable to a may be possible to satisfy them with a brute-force attack [22], and recent family of algorithms based on the same advances in differential cryptanalysis [1] cryptographic principles. and linear cryptanalysis [10] indicate with other encryption INTRODUCTION Cryptography falls umbrella of Cryptology, along tography, under the cryptology. with also cryp- vided into two categories: asymmetric key cryptography and symmetric key cryptography. includes Asymmetric cryptanalysis. Cryptanalysis can be cryptography, understood as the techniques for public key cryptography, involves deciphering/ decoding a message the use of two keys, namely, without any encoding knowledge. public key (shared) and private In a layman's language, we can key (specific to a person), in pro- link cryptanalysis with “code breaking”. It can be difficult to transport strictly viding also key known as confidentiality, authentication and key distribution. confidential Symmetric key information to a secure place cryptography, also known as private without persons key cryptography, involves the use of having access to it. For centuries only one key called 'private key' that people have always tried to create is specific to a set of persons. argots that could not be decoded In symmetric key cryptography, there easily. From the ancient Rome to are many ciphers or cryptosystems. the Second World War to until One today, heads of states and other Blowfish is a symmetric key block powerful persons have spread cipher developed by Bruce Schiener orders and other important in- in 1993. It was designed to provide a formation cheat fast, free -alternative to the then enemies or to keep information existing encryption algorithms. Since away from unauthorised persons. then it has been analysed con- Cryptography can be broadly di- siderably, and slowly gained accep- unauthorised encoded to such cipher is Blowfish. tance as a strong encryption some of which include speed, algorithm. Even after more than a compactness, simplicity and security. decade, it is considered as the first We can say that it is a formidable choice because of its characteristics, block cipher. BLOWFISH ALGORITHM DESCRIPTION: The cipher encrypts 64-bit makes use of 32 to 448 bits to generate blocks of plain text into 64-bit blocks 18 P-boxes with 32-bit sub-keys and of cipher text. It uses a variable-size four 5boxes of type '8x32' with entries of key ranging from 32 bits to 448 bits. 32 bits each. The number of entries for The algorithm consists of two parts: P-boxes comes to 576 bits or 72 bytes. Key expansion/generation. The number of entries for S-boxes This includes sub-key (P- comes to 32,768 bits or 4096 bytes. The box) and S-box generation. total is 4168 bytes. Data encryption/decryption. In S-box, we have mentioned This includes the encryption/ the type as '8x32’ I would like to explain decryption operation, that an S-box of type 'nxm' typically whichever is being done, consists of 2n rows of 'm' bits each. So based on the generated P- and each S-box in Blowfish has 28=256 S-boxes. rows of 32 bits each. S-box rows range Key expansion / generation: Blowfish from '0' to '255' in Blowfish. One more uses the cipher itself for key scheduling. significance of 'nxm' (8x32) is that 'n' A slow, complicated key schedule can bits of the input select one of the rows of help protect against attacks but might the S-box and the 'm' bits in that row are make the cipher unsuitable for use in the output. For example, if the input is situations where frequent key change is '00001010' in Blowfish (5-box is of type needed. As mentioned earlier, Blowfish '8x32'), the output consists of 32 bits in tenth row. Key expansion/ generation convert a key of at most 448 bits into several sub-key arrays totaling 4168 bytes (72 bytes for P-box and 4096 bytes for S-box). The fractional part of Pi (n), i.e.,22/7 is used for initialization purpose. The reason is that mathematical constants have good pseudo-random distribution. These are transcendental and hence not predictable. They can generate as many digits as needed. They are known in public, so it can never be a choice for trap doors. Fig 1 Steps in P - and S- box Generation Data encryption/decryption: Blowfish uses two important operations for both encryption and decryption: Key: Assume that the keys are stored in 1. Addition (non-commutative): It is a key-array. Each entry in the array is 32 performed as modulo 232. bits long. 50 if we take the maximum 2. Bit-wise exclusive-XOR (non- key size, which is 448 bits in the case of commutative) Blowfish, we end up with a maximum of 14 entries: One good point of the algorithm is that KEY1, KEY2, KEY3, the decryption process in Blowfish KEY4 ….KEY14 occurs in the same algorithmic direction P-boxes: The sub-keys are stored in P- as array with each entry of 32 bits. So the decryption are used in the reverse order P-array will look like: of encryption. The encryption and PI, P2, P3, P4, P18 S-boxes: As mentioned earlier, there are four 5-boxes with 256 entries of 32 bits each. So S-boxes will look like: s1, 0 s1, 1 s1, 2 ------------- s2, 0 s2, 1 s2, 2 ------------- s3, 0 s3, 1 s3, 2 ------------- s4, 0 s4, 1 s4, 2 ------------- s1, 255 s2, 255 s3, 255 s4, 255 Steps in P-and S-box generation: Total of 521 executions of the Blowfish algorithm are required to produce the final 5- and P-boxes for a single key. encryption. The sub-keys in decryption processes are shown in Figs 2 and 3, respectively. FIG 2 Encryption process Fig 4: The ‘F’ function divides the left half of a ciperblock (a 32bit value) Into four values and encrypts Fig Decryption process 3 them with the S- boxes change with 0.5 probability when any single input 'k' is inverted for all 'k' and 'j.' 3. Bit-independence criterion: When a single 'j' bit is inverted, output bits 'k' and 'p' should change independently for all 'j,' 'k' and 'p.' In Blowfish, 'F' function is denoted as: F [a,b,c,d]= ((Sl,a+S2,b)XOR S3,c)+S4,d Fig 5: In Blowfish, operations are performed on both the halves of the CHARACTERISTICS OF data (i.e. BLOWFISH 32 bits each) in each round. This 1. On a 32-bit microprocessor, Blowfish enhances the cryptographic strength encrypts data at a rate of 18 cycles per byte. It F function: In encryption and can run in less than 5 kB of memory. decryption, 'F' function provides the 2. Sub-key calculation requires all sub- element of confusion in Blowfish. It keys to be calculated in advance of any should be such that it is difficult to data unscramble the substitution performed Encryption. Infact, it is impossible to by 'F' function. Certain criterion to make calculate the last sub-key of the last S- 'F' function difficult and strengthen the box effectiveness of the confusion function is as under: comes before. 1. Non-linearity 3. As seen above, the S-boxes are key- 2. Strict avalanche criterion: Any dependent. Since these are not fixed, it output bit 'j' of an 5-box of Blowfish should without calculating every sub-key that is impossible to analyse the S-boxes ahead of time to look for weakness. Also the Sboxes and the sub-keys are produced by repeated use of Blowfish itself. 4. In Blowfish, operations are performed on both the halves of the data (i.e., 32 bits each) in each round. This enhances the cryptographic strength. (Additional operation is Linear XOR). 5. It is quite invulnerable to Brute-force attack as the key length can go up to 448 bits. To add to this, the sub-key process is very lengthy with 521 executions required for a single key test. 6. Some tests have been done to cryptanalyse the algorithm but till now no practical weakness has been found. 7. Blowfish design is easy to implement and eases the task of determining the strength of the algorithm. common. The algorithm should be efficient on 32-bit microprocessors with 4 kbyte PLATFORMS A standard encryption algorithm must be program and data caches. Medium-size processors: The implementable on a variety of different algorithm should run on platforms, each with their own microcontrollers and requirements. These include: medium-size processors, such as Special hardware: The algorithm should be efficiently other the 68HC11. Small processors. It should be implementable in custom VLSI possible to implement the hardware. algorithm on smart cards, even Large processors: While dedicated hardware will always be used for the fastest applications, software implementations are more inefficiently. The requirements for small processors are the most difficult. RAM and ROM limitations are severe for this platform. Also, efficiency is more important on these small extend it. It exploited the 'F' function. machines. Workstations double One more fact that the addition their capacity almost annually. mod 232and XOR do not commute was Small embedded systems are the also exploited. same year after year, and there is Vikramjit Singh Chhabra's attack: little capacity to spare. If there is This attack implemented a a choice, the extra computation Brute-force key-search machine. burden should be on large Serge Vaudenay's attack: processors rather than small This processors. attack examined a simplified variant of Blowfish, with the S-boxes known and not key-dependent. KNOWN ATTACKS ON For this variant, a differential attack can BLOWFISH recover the P-array with 28r+1chosen The most efficient way to break plain-texts (where 'r' is the number of Blowfish is through exhaustive search rounds). Such an attack is impossible for (lest the key size is small) of the 8-round and higher Blowfish, since more keyspace. The relative strength of the plain-text is required than can possibly encryption algorithm is based on the key be generated with a 64-bit block cipher. length. Bruce Schneier, creator of the Blowfish encryption algorithm, has Weak keys: A weak key is one for calculated that according to what we which two entries for a given S-box are know of quantum mechanics today, the identical. There is no way to check for entire energy output of the sun is weak insufficient to break a 197-bit key. expansion. keys before One doing can do the key the key expansion and check for identical S-box entries only after a Blowfish key is generated. Weak keys generate weak SFew attacks on blowfish are listed below: boxes. (The odds of getting them John Kelsey's attack: randomly are 'I' in '214'.)The same attack This attack could break 3round Blowfish, but was unable to requires only 24r+1chosen plain-texts to recover the P-array (again, assuming the 5. Conversion into a one-way hash S-boxes are known). function With unknown S-boxes, this attack can detect whether a weak key is IT’S HERE TO SAY! being used, but cannot determine what it No one has come close to developing an is (neither the S-boxes, the P-array, nor attack that breaks Blowfish. It is an the key itself).It works only against unpatented algorithm. The algorithm is reduced-round variants; it is completely hereby placed in the public domain, and ineffective against 16-round Blowfish. can be freely used by anyone. An open Differential attacks. Few of such competition attacks have been reported against cryptanalysis of Blowfish supported by certain variants of Blowfish but without Dr Dobb's Journal with a $1000 prize. much success. Vincent Rijmen's Ph.D This thesis However, includes a second-order was contest held ended Blowfish in for the Apri11995. can still be differential attack on 4-round Blowfish considered secure, and Schneier has that cannot be extended to more rounds. invited APPLICATIONS OF investigating BLOWFISH Blowfish will offer substantial security 1. Encrypt a large chunk of data, e.g., a portion of a hard disk 2. Encrypt data files or a continuous data stream, e.g., voice encryption cryptanalysts his to continue cipher. However, for many years to come and will continue to be the preferred encryption algorithm used by many corporations and banking institutions worldwide. . 3. Produce single random bits 4. Encrypt packet-sized data. (An ATM REFERENCES: packet has a 48-byte data field). It http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blowfish_(c should be ipher) implementable in an application where successive packets may be encrypted or decrypted with different keys. www.schneier.com/blowfish.html www.search.cpan.org/~dparis/CryptBlowfish-2.10/Blowfish.pm www.splashdata.com/splashid/blowfish.htm