Plate Tectonics, Volcanoes & Earthquakes
advertisement
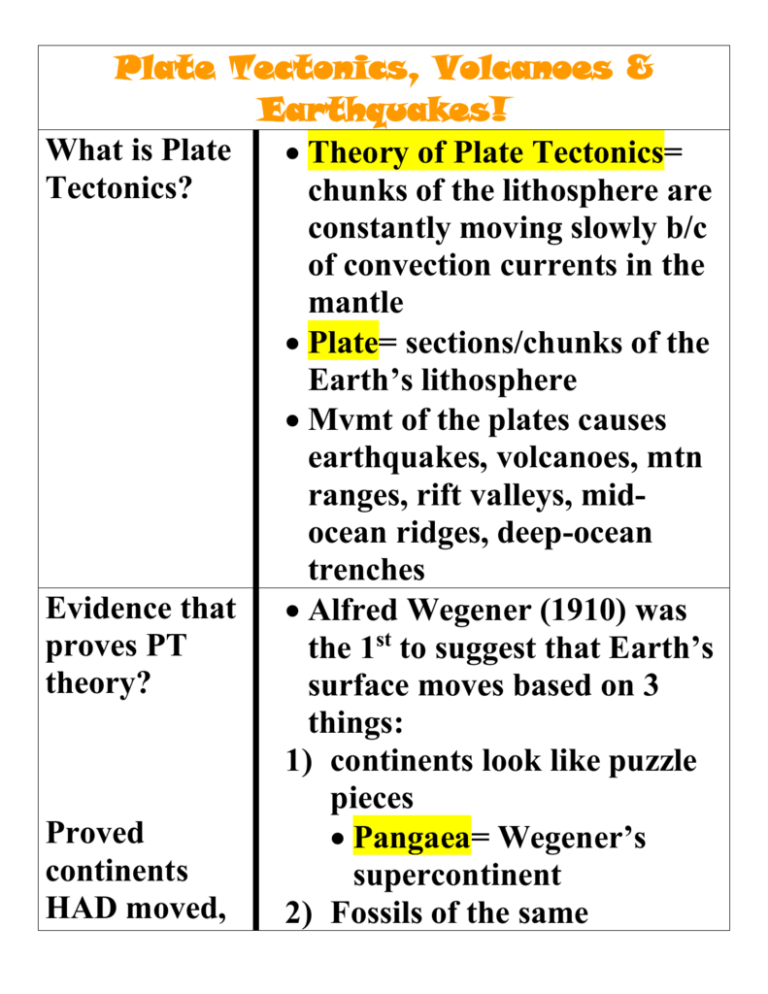
Plate Tectonics, Volcanoes & Earthquakes! What is Plate Theory of Plate Tectonics= Tectonics? chunks of the lithosphere are constantly moving slowly b/c of convection currents in the mantle Plate= sections/chunks of the Earth’s lithosphere Mvmt of the plates causes earthquakes, volcanoes, mtn ranges, rift valleys, midocean ridges, deep-ocean trenches Evidence that Alfred Wegener (1910) was proves PT the 1st to suggest that Earth’s theory? surface moves based on 3 things: 1) continents look like puzzle pieces Proved Pangaea= Wegener’s continents supercontinent HAD moved, 2) Fossils of the same but not HOW. Explained HOW continents moved and proved Wegener’s Theory organism spread across the continents 3) Found warm weather fossils where it is really cold & vice versa Wegener’s idea was rejected b/c he could show continents HAD moved, but not HOW they moved 1960 technological advancements led to: 4) sea floor spreading= magma erupts on the ocean floor, hardens into rock then erupts again pushes the ocean floor apart/makes the ocean bigger creates a mid-ocean ridge= under H2O mtns pushes continents away from e@ other 5) subduction zones= where What are plate boundaries? one plate sinks under another plate b/c it is denser—oceanic plate always sinks creates a deep ocean trench= deep under H2O canyon * continents move SLOWLY! 124 cm/yr * ocean floor renews itself every 200 million yrs (glued in chart) Additional notes: Tectonic plate boundaries= where one plate touches another plate 1a= runs down the middle of the Atlantic Ocean 1b= Great Rift Valley in E. Africa 2a= Cascade Mtns in Oregon & Washington (Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Ranier, Mt. What is a volcano? How does PT cause volcanoes? Olympia), mtns in New Zealand 2b= Indonesian Islands 2c= Himalaya Mtns where India meets Eurasia & The Alps in Europe 3= San Andreas Fault in CA where Pacific Plate & North American Plate slide by e@ other Volcano= a weak spot in the crust that creates & destroys things and looks like a pimple & firework and is extremely beautiful Magma= melted rock INSIDE a volcano Lava= melted rock OUTSIDE a volcano Plates colliding cracks the crust so magma can escape (subduction zones only!) @ rift valleys and sea-floor What is a “hot spot” volcano? What are the parts of a volcano? (structure) spreading b/c the crust is getting pulled apart, getting weaker in the middle and magma can erupt through the thinner crust Hot Spot Volcano= a volcano that forms in the middle of a tectonic plate, NOT near a boundary 1) magma chamber= a pool of magma at the bottom of the volcano 2) pipe= the long tube that magma travels through during an eruption 3) vent= the opening at the top of a volcano where magma becomes lava 4) crater= bowl shape that surrounds the vent 5) side vent= a vent on the side of a volcano; optional! Can have several or none at all! What causes a volcano to erupt? What are the Gases trapped in magma expand and create pressure! Pressure pushes magma up & out Amt of silica in the magma determines the type of eruption: 1) Quiet Eruption: LOW silica magma that is thin & runny! Lava flows easily, like a river 2) Explosive Eruption: HIGH silica magma that is thick & sticky! It plugs the vent and causes great pressure to build up. BOOMER! Pyroclastic flow= mixture of hot, poison gases, ash, cinders & bombs that hurtles down the volcano, killing everything in its path Active= currently erupting or stages of volcanic activity? What landforms are created by volcanoes? will erupt soon Dormant= “asleep” “hibernating” can become active at any time Extinct= will never erupt again…maybe! 1) shield volcano= a wide, gently sloping mtn formed by layer upon layer of thin, runny lava from quiet eruptions; Hawaiian volcanoes & Medicine Lake in CA (most hot spot volcanoes) 2) cinder cone volcano= a steep, cone shaped hill/mtn formed by layers of cinders, bombs & ash from explosive eruptions; Paricutin in Mexico (subduction zone volcano) 3) composite volcano= quiet & explosive eruptions alternate layers of lava & ash create TALL volcanic mtns; Mt. Shasta & Mt. St. Helens & Mt. Fuji (subduction zone volcanoes) 4) lava plateau 5) caldera 6) volcanic soil Intrusion: Igneous rock forced among the bedrock; younger than the surrounding rock 7) volcanic neck 8) dike 9) sill 10) batholith 11) hot springs= hot! H2O that forms in pools around Geothermal activity= “Earth heated” phenomena Video notes: Earth Science: Volcanoes DVD notes: How Earth Was Made: Ring of Fire volcanic areas (stink!) 12) geysers= H2O volcano!eruption of H2O out of the Earth b/c of heat Roman God of Volcanoes is Vulcan 1511 volcanoes, 500 active & 60 eruptions/yr Pelee, Hawaiian goddess of volcanoes, erupts volcanoes when she is angry R of F volcanoes are the most destructive in the world A volcano can threaten Earth for eons, but will eventually “die” ** Why are Ring of Fire volcanoes and earthquakes so destructive?** ¾ of all volcanoes & 90% of EQ’s in the R of F 25,000 miles around the Pacific Ocean 75% of all US volcanoes are in Alaska Strato volcanoes in the R of F Have thick, sticky lava/magma that traps gasses & causes massive eruptions Magma contains hornblende minerals that only forms in the presence of H2O H2O causes the magma to form in the first place Gases coming from the R of F volcanoes have C12 in them C12 is the remains of plankton that make up sediments on the ocean floor Subduction carries H2O & the ocean floor down to a magma chamber-that’s What is an earthquake & why do they happen? where the H2O & the C12 come from! R of F EQ’s are thrust or megathrust quakes-the most pwrful on earth! Thrust EQ’s happen when rock slides under another Thrust EQ’s cause tsunamis 1500 EQ/month in Alaska! 14 plates on the planet NA moving west 3 inches/yr Subduction releases and enormous amt of energy! The Earth is NEVER at rest Earthquake= when the earth shakes & possibly destroys buildings & such Happen b/c stress from plate mvmts adds energy to rock Released energy causes the shake Seismic waves= energy waves that shake the crust during (diagram) What types of seismic waves are there? What types of an EQ Fault line= crack/break in the crust where rocks slip by e@ other & build up stress Focus= the point underground where an EQ begins Epicenter= the point on the surface directly above the focus 1) P waves= primary/first waves of an EQ; move like an accordion 2) S waves= secondary/second waves; move up,down & side to side through rock only 3) Surface wave= P&S waves on the crust; slowest waves, but the most destructive; move in a combo. of P&S wave mvmts 1) Normal Fault= tension faults are there? stress (pulling) fault; hanging slips down (diagram) 2) Reverse Fault= compression (pushing) stress fault; makes mtns!; hanging wall bulges up & over the footwall (diagram) 3) Strike-slip fault= shearing (rubbing) tension; both sides move against e@ other; NO up or down mvmt (diagram) Video notes How do seismologists monitor & measure EQ’s? 1 million EQ/yr! Earth can move 5mm in just a couple of hrs Strongest EQ in US was in Alaska in 1964 San Francisco is VERY prone to EQ’s b/c San Andreas Fault runs across it 20-30 EQ’s daily in S.Cali 4 minutes is a LONG time for an EQ to shake Seismic waves are like ripples in water @ the San Andreas Fault can put one foot on Pacific Plate & one foot on NA plate EQ’s are NOT predictable! TOOLS TO MONITOR 1) tilt meter 2) creep meter 3) laser-ranging device 4) GPS (global positioning system)