Chapter 6 Study Guide
advertisement

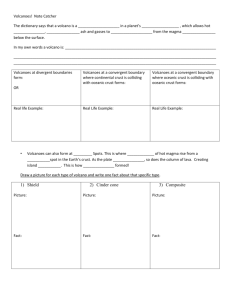
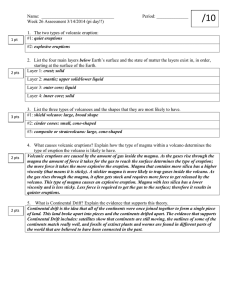
Chapter 6 Study Guide Volcanoes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. The molten mixture of rock – forming substance, gases, and water deep in Earth’s mantle is called ______________________. The belt around the rim of the Pacific Ocean is called ___________. Thicker magma contains more ______________________. What is a wide gently sloping mountain made of hardened layers of low silica lava know as? _____________________. What forms when magma hardens in a volcano’s pipe and is later exposed? ______________. California’s Mount Shasta and Lassen Peak are volcanoes caused by __________ of the Juan de Fuca plate. A(n) _____________ happens when an explosive eruption hurls ash, cinders, bombs, and gases out of a volcano. When plate movement causes the crust to bend downward, what is formed? __________________ A _______ is a weak spot in the crust where magma comes through. Liquid magma flows upward through the crust because it is _______ dense than the solid liquid around it. Pahoehoe and aa are produced during __________ eruptions. A ________________ is hot water and steam that erupts from the ground. _____________________ provided the force that pushed up California’s Sierra Nevada and Coast ranges. A _______ is a mass of rock that formed when a large body of magma cooled inside the Earth’s crust. An are where magma melts through the crust in the middle of a plate is called a(n) ________________. Inside a volcano, magma collects in a pocket called a ________________. Magma from and explosive eruption is ______ and ________, has __________, and is high in ________. Volcanic soils are fertile because they contain _____________________. layers of thin, runny lava that flow over a wide area before they cool and harden can build up a ________________________________. A volcano that is erupting or has shown signs that it may erupt in the future is called ________. Be able to explain why ash, cinders, and bombs are produced only in explosive eruptions, not in quiet eruptions. Be able to explain how the faults, volcanoes, mountain ranges, and basins of California are related.