Cell Structure and Function
advertisement

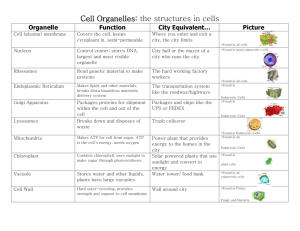
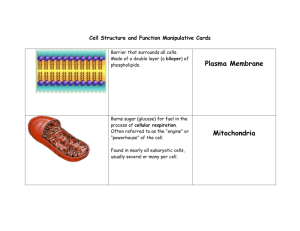
Cell Structure and Function Across 4. Cell structure that provides plants structural support. 5. A membrane-enclosed sac that is part of the endomembrane system of a eukaryotic cell, having diverse functions. It is large in plant cells. 6. An organelle found only in plants and photosynthetic protists; contains chlorophyll, which absorbs the light energy used to drive photosynthesis. 9. Means having "less solute" 11. Comes together to create the cell membranes. (hint: 2 parts) 14. The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane, without any input of energy. 15. The organelle in eukaryotic cells that carry on cellular respiration, release energy from food molecules and storing it in ATP. Singular. 18. dissolved substance within solution (e.g. - salt) 20. Molecules disperse in random directions down their concentration gradient. 22. A membrane-enclosed structure with a specialized function within a cell. 23. An extensive membranous network in a eukaryotic cells, continuous with the outer nuclear membrane and composed of ribosome-studded and ribosome-free regions. 24. A mixture in which particles of one substance are distributed through another substance. Down 1. Means "water fearing" and describes part of a phospholipid. 2. An organelle in eukaryotic cells consisting of stack of membranous sacs that modify, store, and ship products of the endoplasmic reticulum (two words). 3. Means having "more solute" 7. The passive diffusion of water. 8. Diffusion of a substance through a specific transport protein across a biological membrane down its concentration gradient. 9. Means "water loving" and describes part of a phospholipid. 10. The structure separating the interior of a cell from the outside environment. It is a semipermeable lipid bilayer found in all cells. 12. A threadlike, gene-carrying structure found in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. 13. Plural. An organelle in eukaryotic cells where cellular respiration occurs. Enclosed by two concentric membranes, it is where most of the cell's ATP (energy) is harvested from food. 16. An organized structure of DNA and supporting regulatory proteins found in cells. They contain many genes. 17. A cell part constructed in the nucleus. It consists of two subunits and functions as the site of protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. 19. The liquid in which a solute is dissolved (e.g. - water) 21. Means having "equal solute" 25. The genetic control center of a eukaryotic cell.