Chronic Liver Disease
advertisement

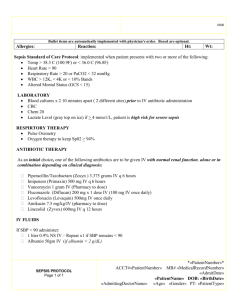
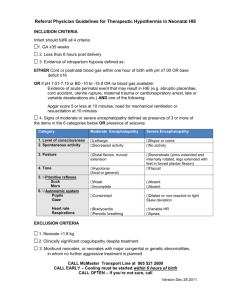
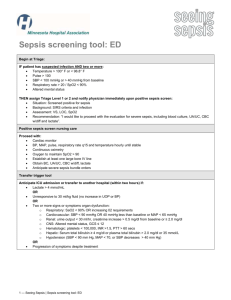
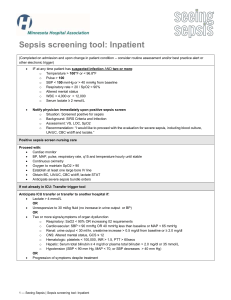
Chronic Liver Disease 10/2/11 Tek OH Oxford Handbook of Critical Care OHOA page 134 JFICIM and FANZCA Examinations Book – pages 178-180 - may come to ICU for many reasons: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) encephalopathy from acute decompensation sepsis renal failure variceal bleeding cardiorespiratory failure ENCEPHALOPATHY FROM ACUTE DECOMPENSATION - find cause: -> -> -> -> -> -> -> -> sepsis (spontaneous bacterial peritonitis) dehydration alcohol drug introduction (opiates, sedatives, diuretics) GI haemorrhage electrolyte imbalances hepatocellular carcinoma portal vein thrombosis HISTORY - weakness & fatigue jaundice abdominal pain or swelling altered mental state pruritis - durations of disease alcohol intake IV drug use blood transfusions tattoos overseas travel drugs (isoniazid) EXAMINATION - general – abdominal distension, jaundice, cachexia, bruises palmar erythema bruising spider naevi yellow sclerae Jeremy Fernando (2011) - fetor - gynaecomastia - abdomen: masses, distension, bruising, scars hepatosplenomegally ascites bruits INVESTIGATIONS - FBC – anaemia U+E – hepatorenal syndrome BSL LFT’s – active damage Albumin – synthetic function Coags – bleeding ABG – lactate acidaemia alpha-feto protein paracentesis: culture and cell count (>250/mm3 = diagnositic for SBP) endoscopy – varices US: hepatic and portal veins, hepatocellular carcinoma CT: hepatocelluar carcinomia liver biopsy MANAGEMENT - resuscitate: intubation to protect airway albumin IV lactulose to decrease ammonia levels monitor glucose vitamin K and FFP for coagulopathy MARS therapy feed enterally and can use protein - find cause and treat: -> antibiotics in SBP: third generation cephalosporin or tazocin + spinrolactone -> steroids in alcoholic hepatitis -> consider for transplantation SURGICAL RISK (Child-Pugh Classification) Mortality < 5% 5-50% >50% Bilirubin (mmol/L) Albumin (g/L) Ascites Nutrition INR Encephalopathy <25 >35 none excellent <1.7 grade 0 25-40 30-35 moderate good 1.7-2.3 1-2 >40 <30 marked poor >2.3 3-4 Jeremy Fernando (2011) COMPLICATIONS Sepsis - immunosuppressed - SBP: gram negative rods, strep pneumoniae, enterococci - other organisms: Listeria, Tb, Fungi, CMV, norcardia -> early source control -> early antibiotics (empiric) Renal Failure - hepatorenal syndrome -> more likely to see rapidly progressive form - also consider abdominal compartment syndrome - investigation: U/S: renal and hepatic -> volume expansion with colloid (albumin) -> vasoconstriction (noradrenaline or glypressin) -> ascitic drainage with albumin loading -> consider TIPs procedure in Budd-Chari syndrome -> consider transplantation Variceal Haemorrhage - decreased production of factors, thrombocytopaenia, platelet dysfunction) -> resuscitate -> correct coagulopathy -> sepsis of precipitant: culture and give antibiotics -> splanchic vasoconstriction: glypressin -> endoscopy: banding and ligation -> TIPS procedure -> transplantation Encephalopathy - causes: sedation, high protein diet, infection, trauma, hypokalaemia, constipation -> accumulation of toxic products - grade 0 = alert and orientated, grade IV = unresponsive to deep pain Others - hypoglycaemia (decreased glycogen stores) ascites (from portal hypertension and fluid retention) cholecystitis pancreastitis Jeremy Fernando (2011)