Musculoskeletal Learning Guide
advertisement

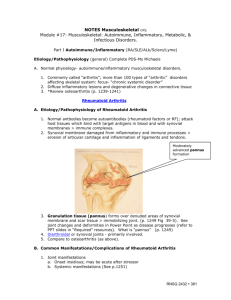
LEARNING GUIDE cmj Autoimmune, Inflammatory, Metabolic & Infectious Disorders Answers to “matching” in Discussion Board Part I 1. Autoimmune/inflammatory Indicate whether each of the following statements are true or false: (p. 1248) Women are affected with RA 3 times more often than men Manifestations of RA usually occur initially in a single joint on one side of the body. Remissions of RA are most likely to occur during the first year Disease progression of RA usually speeds up after the first 6 years. 2. Explain how the clinical manifestations of osteoarthritis defer from those of RA. (p. 1249) 3. What are rheumatoid factors and how do they contribute to the clinical manifestations of RA? (p. 1249) 4. What is pannus and how does it develop? 5. Describe the following deformities associated with RA: a. Swan neck deformity b. Boutonniere deformity c. Hallux valgus 6. What common extra-articular manifestations are common in clients with high levels of circulating rheumatoid factor? (p. 1250) RNSG 2432 399 What are rheumatoid nodules and what problems do they cause? 7. What is the goal of treatment for RA? 8. Complete the following grid for each of the medication types indicated: (p. 1254-1255 & 1263) Medication Side Effects Nursing Implications ASA NSAIDS Corticosteroids Disease modifying Drugs _________________ Gold salts (Cuprimine) Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)_________ Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine)_________ Penicillamine_______ Immunosuppressive drugs ie Methotrexate 400 RNSG 2432 ______________ ____________________________ 9. Describe the following “experimental” therapies for RA and SLE: a. Plasmapheresis (p. 241 & 1255…why does this work?) 10. State 5 recommendations that you would give to a client with RA for preventing pain and deformities? (p. 1255) 11. Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false: (p. 1260) SLE is less common in women of child bearing age. Women with SLE have reduced levels of androgens The number of SLE exacerbations tend to decrease over time. The leading cause of death in clients with SLE is pneumonia. Early manifestations of SLE mimic those of RA. _____ A “butterfly rash” is common is patient’s with SLE (p.1261) 12. What “causes” (pathophysiology) SLE? 13. Describe what you would expect to find for each of the following diagnostic tests for a client with SLE: a. Anti-DNA antibody testing b. ESR c. Serum complement levels d. CBC e. Urinalysis 14. What hematologic problems are associated with SLE? Why do they occur? (1260-1261) 15. Which clients with SLE would require corticosteroid therapy in high doses? (Discoid or systemic form of lupus) (Notes & 1263) 16. Clients with SLE often have impaired skin integrity. What should the nurse teach the client as to how to minimize these effects of the disease? (p. 1263-1264) RNSG 2432 401 17. Case study: a client with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) presents with a BP of188/104. she also complains of esophagitis and shortness of breath. She has a history of Raynauld’s phenomenon. Her laboratory tests return with an elevated serum BUN and creatinine. a. What complication(s) may be occurring with this client? b. What nursing interventions should be implemented as soon as possible? c. What are the medications that will most likely be prescribed for this client? Why/when are these medications needed? (p. 1276-1277) d. What is CREST syndrome? (Notes, p. 1275) 18. Compare and contrast the following the diseases Disease Ankylosing Spondylitis Lyme disease 402 RNSG 2432 Etiology/Initiating Event Manifestations Priority Treatment/Mgt Part II Metabolic 1. Match each of the following risk factors with one of the disorders on the left. The disorder may be used more than once: (p. 1233, 1230, 1224. 1237) Common Pacific Islanders a. Paget’s Disease Women in Northern China b. Gout Nephrotic syndrome c. Osteoporosis Asst. with long term steroid therapy d. Osteomalacia Peak onset in men aged 40 – 50 Post-menopausal women 20-30% with family history (genetic ?) Smoking 2. The bones of clients with Paget’s Disease are larger than normal but break more easily. Explain how and why this occurs. (p. 1230) 3. What is the difference between primary and secondary gout? (p. 1233) 4. Match the following manifestations with the appropriate disorder: Dowager’s hump a. Paget’s Disease Waddeling gait b. Osteoporosis Red, hot, tender joints c. Osteomalacia Loss of height d. Gout Elevated WBC and sed rate Enlarged skull Flushing of skin over the bone Ulceration over the joint Fever, chills, malaise 5. Why do clients with chronic gout often develop kidney disease? (p. 1233) RNSG 2432 403 6. Complete the following table: Medication What Disorder(s) is Side Effects it used for (major) Allopurinol p. 1235-1236 Nursing Implications Probenecid (Benemid) Sulfinapyrazon (Anturane) p. 1235-1236 Colchicine p. 1235-1236 Biphosphates (Fosamax) p. 1231, 1232 Calcitonin (Miacalcin) p. 1226 Raloxifene p. 1226 7. Clients with gout are sometimes instructed to eat a low purine diet. Name several foods that the client should avoid. What else should the client with gout avoid? Why is a high fluid intake very important for the client with gout? Is this needed when the client is taking medications as treatmnt for gout? Why should aspirin NOT be given to client receiving probenecid? (1236) What stressors might trigger an “attack of gout” (p. 1233)? 8. How is a definitive diagnosis of gout determined? ( what lab results, such as uric acid level, etc) (p. 1234) 9. What lab values are typically altered in Paget’s disease? (p. 1231) 404 RNSG 2432 10. What recommendations would you make to a client with Paget’s disease to help reduce pain, promote comfort, and increase physical mobility? What medications are helpful in treating Paget’s disease? (ref table above & p. 1231-1232) Part III 1. Infectious Disorders of the Bone and Joint Explain how an infection of soft tissue can lead to an infection of the bone (describe the pathophysiology.) p. 1267-1268) 2. Complete the chart for management of osteomyelitis (acute/chronic) Osteomyelitis Identify Treatment Length of Teaching Pathogen /management treatment needs/p. (usual) indicated (include 1271 medications/surgery) Osteomyelitis 3. Describe the difference between septic arthritis and osteomyelitis? 4. Which of these statements are true or false about septic arthritis and/or osteomyelitis? a. b. c. d. e. f. 5. Osteomyelitis is usually caused by a bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus Septic arthritis typically has a viral causative agent With septic arthritis multiple joints are effected at the same time Onset of septic arthritis is typically very abrupt and a medical emergency Sequestra is devitalized (dead) bone that has separated from the periosteum due to osteomyelitis Bone and joint immobilization is required to avoid pathological fractures with osteomyelitis What are three (3) priority nursing diagnosis for the patient with acute osteomyelitis? (p. 1270-1271) RNSG 2432 405 406 RNSG 2432