Metabolic Bone Diseases – Learning Guide
advertisement

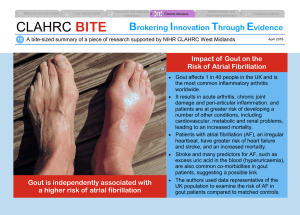
Metabolic Bone Diseases – Learning Guide 1. What is osteomalacia and what factors contribute to it? 2. What are the clinical manifestations of osteomalacia? 3. Describe the laboratory and diagnostic test results associated with osteomalacia. 4. Describe the treatment for osteomalacia. 5. What are the modifiable and non modifiable risk factors for osteoporosis? a. Modifiable b. Non modifiable 6. Describe the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. 7. What are the clinical manifestations and complications of osteoporosis? 8. What diseases and medications can cause osteoporosis? 9. Describe the following diagnostic tests used for osteoporosis: a. Quantitative ultrasound b. Dual-x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) 10. What is the difference between osteoporosis and osteopenia? 11. Describe the following types of treatments for osteoporosis: a. Dietary supplementation and nutritional choices b. Exercise c. Medications: Medication Hormone replacement Side Effects Nursing Implications/Teaching Calcitonin Biphosphates (etidronate, alendronate, pamidronate, resedronate, cldronate, tiludronate, ibandronate.) Selective estrogen receptor modulators (raloxifene) Teriparatide (Forteo) Denosumab (Prolia) 12. What is the pathophysiology for Paget’s Disease? 13. What are the clinical manifestations and complications of Paget’s disease? 14. Describe the treatments used to achieve the following goals for Paget’s disease: a. Decrease bone resorption b. Pain management c. Correction of deformities and treatment of fractures d. Prevention of fractures or other injury e. Maintain adequate intake of nutrients 15. What is the pathophysiology for gout? 16. What are the primary and secondary causes of gout? 17. What are the clinical manifestations of gout? 18. What can trigger an attack of gout? 19. Describe the progression in chronic gout. 20. How can gout cause renal disease? 21. How is gout diagnosed? 22. What is the priority nursing diagnosis for a client with gout? 23. Describe the following interventions for gout: a. Medication therapy b. Positioning and activity c. Dietary 24. What medication should be avoided by the client who is taking uricosurics such as probenecid?