Vocabulary Flip Chart - Effingham County Schools
advertisement

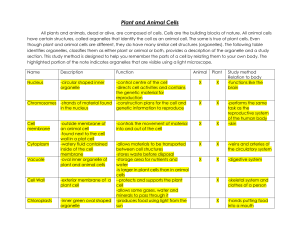
a eukaryote that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. organisms whose cells contain nuclei and other organelles. a close long term relationship between two or more organisms a symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed a structure within a cell that performs a specific function and is surrounded by a membrane an organelle found in plant and protist cells where photosynthesis occurs cell organelles that break down food molecules and releases ATP (cellular energy) organisms that can make their own food by carrying out photosynthesis an organism that eats producers or other organisms for energy an organism that gets energy by breaking down the remains of dead organisms or animal wastes, and consuming and absorbing the nutrients a large membrane -covered structure that serves as a storage container for water and other liquids the cell organelle that modifies, packages, and transports materials out of the cell a phospholipid bilayer that covers a cell's surface and acts as a barrier between the inside and the outside of the cell; regulates what enters and exits the cell. a small organelle in cells where proteins are made from amino acids the organelle found in eukaryotic cells; contains the cell's DNA and serves as the control center for the cell a special vesicle in a cell that digests food particles, wastes and foreign invaders a structure that surrounds the cell membrane of some cells and provides strength and support Protist Eukaryote Symbiosis Unit 2 Vocabulary Flip Chart Mutualism Parasitism Organelle Chloroplast Mitochondria Producer Consumer Decomposer Vacuole Golgi Body Cell Membrane Ribosomes Nucleus Lysosome Cell Wall