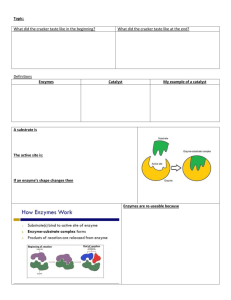
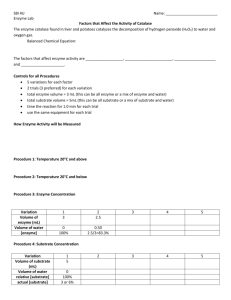
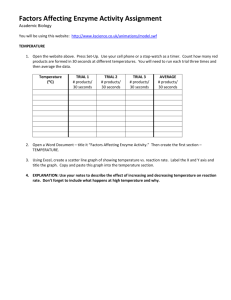
practice midterm answers
advertisement

BIOLOGY 100 UCSC – Kamakaka – Summer 2010 - Sample Midterm Definitions Hydrogen bond Dissociation constant Quarternary structure of proteins Allosteric interactions Multiple Choice 1) The role of an enzyme in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is to A) bind a transition state intermediate, such that it can be converted back to a substrate B) ensure that all substrate is converted to product C) ensure that product is more stable than substrate D) increase the rate at which substrate is converted to product E) make the free energy change for the reaction more favorable 2) The number of substrate molecules converted to product in a given unit of time by a single enzyme molecule at saturation is referred to as the A) dissociation constant B) half-saturation constant C) maximum velocity D) Michaelis-Menten number E) turnover number 3) In competitive inhibition, an inhibitor A) binds at several different sites on an enzyme B) binds covalently to an enzyme C) binds only to the ES complex D) binds reversibly at the active site E) lowers the characteristic Vmax of the enzyme 4) The Lineweaver-Burke plot is used to A) determine equilibrium constant for an enzymatic reaction B) extrapolate for the value of reaction rate at infinite enzyme concentration C) illustrate the effect of temperature on an enzyme reaction D) solve, graphically, for the rate of an enzyme reaction at infinite substrate concentration E) solve graphically for ratio of products to reactants for any starting substrate concentration BIOLOGY 100 UCSC – Kamakaka – Summer 2010 - Sample Midterm 5) PMSF inactivates serine proteases by binding covalently to the catalytic site and this enzymeinhibitor bond cannot be cleaved by the enzyme. This is an example of A) irreversible inhibition B) competitive inhibition C) non-competitive inhibition D) mixed inhibition E) activation 6) Alpha helices are stabilized by A) hydrogen bonds B) hydrophobic interactions C) van der Waals interactions D) none of the above E) all of the above 7) In aqueous solution, protein structures are determined primarily by two factors. One is maximum numbers of hydrogen bonds. The second is A) maximum number of hydrophilic interactions B) maximization of ionic interactions C) minimization of entropy by formation of a water solvent shell around the protein D) placement of hydrophobic residues in the interior of proteins E) placement of polar residues in the interior of the protein 8) Amino acids found in the middle of ß-turns are A) A and G B) P and G C) R and K D) polar E) hydrophobic 9) SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is performed in the presence of reducing agents to A) denature proteins B) disrupt disulfide bonds C) disrupt hydrogen bonds D) disrupt hydrophobic interactions E) disrupt ionic interactions 10) In a mixture of the five proteins listed below, which will elute second in a gel filtration chromatography A) cytochrome C (MW=13,000) B) RNA polymerase (MW=450,000) C) Ribonuclease A (MW=13,700) D) immunoglobulin (MW=145,000) E) albumin (MW= 68,000) BIOLOGY 100 UCSC – Kamakaka – Summer 2010 - Sample Midterm True or False 1) . T . Hemoglobin is composed in part of a heme group. 2) . F . Km is the time for half of the substrate to be converted to product. 3) . T . Individual hydrogen bonds in liquid water exist for many seconds and sometimes for minutes. 4) . F . Peptide bond formation is an isomerization reaction. 5) . T . At the isoelectric point, a tetrapeptide (A-R-K-R) has zero net charge. 6) . F . The average molecular weight of an amino acid in proteins is 128. 7) . F . In proteins, alpha helices are almost always left handed. 8) . F . Van der Waals interactions are too weak to stabilize proteins. 9) . F . HCl is a strong acid. This means it does not dissociate at all. 10) . T . Allosteric proteins are generally composed on multiple subunits. Short Answers 1) What does it mean when Km is unchanged between wildtype and mutant enzyme but Kcat is altered? Km is a simple measure of substrate affinity by an enzyme. Kcat is the number of substrate molecules converted to product in a unit of time. So…… 2) What is the function of BPG? Why do RBCs have large amounts of BPG? BPG is found in RBC and is an allosteric effector of Hb binding to oxygen. BPG binds an allosteric site and reduces affinity of Hb for oxygen leading to its release. 3) What is the pH of a solution that has a H+ concentration of 1.90 x 10–7 mol/lit? What is the H+ concentration of a solution with a pH of 4.40? pH = ‐log[H+] 4) Martian myoglobin has a binding site for nitrogen with a Kd of 10–5M while Saturnian myoglobin has a binding site for nitrogen with a Kd of 10–9M. Which protein has a higher affinity for nitrogen? Explain. What is the Ka of the Martian and Saturnian myoglobin? Saturnian myoglobin has higher affinity. Lower Kd indicates that Saturnian myoglobin will be half saturated with bound nitrogen at a much lower concentration of nitrogen Ka=1/Kd. 5) Use the Michaelis-Menten equation vo = (Vmax[S] o) / (Km + [S] o) to complete the enzyme kinetic data set. The Km is 1mM/lit. [S]o vo mM/lit uM/lit/min 0.5 50 1 75 2 100 3 112.5 10 136.4 Solution using equation and the first entry in the table gives Vmax = 150umol/lit/min. The other entries simply follow by substituting [S] o values into the equation.