key
advertisement

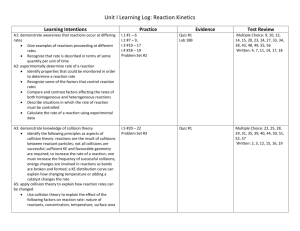
Chemistry 12 1. Which of the following units could be used to express the reaction rate? A. B. C. D. 2. enthalpy. activation energy. the ΔH of the reaction. the activated complex. As an activated complex changes to products, A. B. C D. 5. decreasing the [HCl]. increasing the temperature increasing the volume of H2. decreasing the surface area of Zn. The statement, the minimum energy needed for a successful collision, defines A. B. C. D. 4. mL/s mL/g g/mL mL/mol Consider the reaction: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) The rate of production of ZnCl2, can be increased by A. B. C. D. 3. Kinetics Practice Test # 2 potential energy changes to kinetic energy. kinetic energy changes to potential energy. kinetic energy changes to activation energy. potential energy changes to activation energy. Which of the following is most likely to have the greatest rate at room temperature. A. B. C. D. 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) 2Ag+(aq) + CrO42-(aq) → Ag2CrO4(s) Pb(s) + 2HCl(aq) → PbCl2(aq) + H2(g) CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(g) 6 Consider the following PE diagram for an uncatalyzed and catalyzed reaction PE (kJ) 35kJ 10kJ 15kJ Progress of the Reaction Which of the following describes the forward catalyzed reaction? Activation Energy (kJ) A. B. C. D. 7. -15 15 -15 15 A substance that increases the rate of a reaction without appearing in the equation for the overall reaction is a(an) A. B. C. D. 8. 10 10 25 25 ΔH (kJ) product catalyst reactant intermediate Activation energy can be described as the A. B. C. D. energy of motion energy of the activated complex. energy difference between the reactants and the products. energy difference between the reactants and the activated complex. 9. What effect does a catalyst have on a reaction? It changes the ΔH of a reaction. It increases the kinetic energy of the reactants. It decreases the potential energy of the products. It provides a reaction mechanism with a lower activation energy. A. B. C. D. 10. Consider the following reaction involving 1.0 g of powdered zinc: Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) Trial Temperature (0C) Concentration of HCl 1 2 3 40 20 40 3.0 3.0 6.0 The rates in order of fastest to slowest are A. B. C. D. 11. 1, 2, 3 2, 1, 3 3, 1, 2 3, 2, 1 Consider the following potential energy diagram for a reversible reaction: 140 PE (kJ) 130 110 Progress of the reaction Which of the following describes the system above? A. B. C. D. Reaction Activation Energy (kJ) ΔH (kJ) reverse reverse forward forward 10 10 30 20 -20 -30 +10 +30 12. An activated complex is a chemical species that is A. B. C. D. 13. stable and has low PE. stable and has high PE. unstable and has low PE. unstable and has high PE. Consider the reaction: Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + H2(g) At a certain temperature, 2.05 g Ca reacts completely in 30.0 seconds. The rate of consumption of Ca is A. B. C. D. 14. 15. 0.00208 mol/min 0.0833 mol/min 0.102 mol/min 5.00 mol/min Increasing the temperature of a reaction increases the reaction rate by I. II. III. increasing frequency of collision increasing the kinetic energy of collision decreasing the potential energy of the collision A. B. C. D. I only. I and II only. II and III only. I, II, and III. A certain reaction is able to proceed by various mechanisms. Each mechanism has a different Ea and results in a different overall rate. Which of the following best describes the relationship between the Ea values and the rates? A. B. Ea Ea Rate C. Rate D. Ea Rate Ea Rate 16. For collisions to be successful, reactants must have A. B C. D. 17. favourable geometry. sufficient heat of reaction only. sufficient potential energy only. sufficient kinetic energy and favourable geometry. Consider the following reaction: 1/2 H2(g) + 1/2 I2(g) → HI(g) ΔH = +28 kJ The activation energy for the formation of HI is 167 kJ. The activation energy for the decomposition of HI is A. B. C. D. 18. 28 kJ 139 kJ 167 kJ 195 kJ Which of the following factors affects the rate of heterogeneous reactions only? A. B. C. D. nature of the reactant temperature surface area of reactants concentration of reactants 19. A 25.0 mL sample of hydrogen peroxide decomposes producing 50.0 mL of oxygen gas in 137 s. The rate of formation of O2 in mL/min is A. B. C. D. 20. 0.182 mL/min 0.365 mL/min 10.9 mL/min 21.9 mL/min Consider the following reaction mechanism: step 1 step 2 In this reaction H2 is a A. B. C. D. product catalyst reactant reaction intermediate 2NO + H2 → N2 + H2O2 H2O2 + H2 → 2H2O 21. Which of the following properties could be used to measure the rate of the following reaction taking place in an open container? Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g) A. B. C. D. 22. mass of Zn solubility of HCl concentration of Clcolour of the solution Consider the following reaction: N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3 The rate of formation of NH3 is 3.0 mole/min. The rate of consumption of H2 is: A. B. C. D. 23. 1.5 mole/min 2.0 mole/min 4.5 mole/min 9.0 mole/min Consider the following reaction mechanism: NO2 + NO2 → N2O4 N2O4 + CO → CO2 + NO + NO2 Step 1 Step 2 In the overall reaction, N2O4 is a A. B. C. D. 24. product catalyst reactant reaction intermediate Consider the following mechanism: NO + O3 → NO2 + O2 O + NO2 → NO + O2 Step 1 Step 2 The catalyst is A. B. C. D. O2 O3 NO NO2 25. Consider the following reaction: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) The rate of this reaction increases when more Mg is added. This change is caused by the A. B. C. D. 26. addition of a catalyst increase in surface area change in the nature of the reactants increase in concentration of reactants Consider the following PE diagram 100 PE (kJ) 40 20 Progress of the reaction The forward reaction can be described as A. B. C. D. 27. H Ea Type +20 +20 -20 -20 80 60 80 100 endothermic exothermic exothermic endothermic Consider the following reaction: HgO(s) → Hg(l) + 1/2O2(g) The rate of this reaction can be expressed as A. B. C. D. rate = [O2}1/2 rate = Δ[O2]/Δt rate = Δ[Hg]/Δt rate = Δ[HgO]/Δt 28. Which of the following would react most rapidly? A. B. C. D. 29. Powdered Zn in 1.0 M HCl at 25 0C Powdered Zn in 20 M HCl at 40 0C A lump of Zn in 2.0 M HCl at 25 0C A lump of Zn in 1.0 M HCl at 40 0C Addition of a catalyst to a reaction increases the rate because it A. B. C. D. increases the value of ΔH decreases the value of ΔH provides an alternate mechanism with a lower Ea provides an alternate mechanism with a higher Ea 30. When a collision occurs between two reactant species which possess between them the minimum kinetic energy a product does not always form. This may be a result of A. B. C. D. low temperature small surface area low concentrations unfavourable geometry Subjective Answers 1. An experiment is done to determine the rate of the following reaction: 2Al(s) + 6HCl(aq) → 3H2(g) + 2AlCl3(aq) The following data are collected Time (s) Mass of Flask + Contents (g) 0.0 30.0 60.0 270.230 270.200 270.170 60.0 s 0.060 g H2 270.170 Calculate the rate of consumption of Al in mol/min. 0.060 g H2 x 60.0 s 60 s x 1 min 1mole H2 2.0 g (3 marks) x 2 mol Al 3 mol H2 = 0.020 mol Al/min 2. Define the term activation energy. The minimum energy required for a successful collision. 3. Define the word Activated complex. Unstable reaction intermediate with high potential energy and low kinetic energy. 4. Define the word mechanism. A sequence of steps that determines the overall reaction. 5. Consider the following reaction mechanism Step 1 ? Step 2 H2 + Cl → HCl + H Step 3 H + Cl2 → HCl + Cl Step 4 Cl + Cl → Cl2 Overall H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl a) Write the equation for step 1 Cl2 b) 2Cl Identify the reaction intermediate(s) Cl 6. → H Consider the overall reaction: 4HBr + O2 → 2H2O + 2Br2 A proposed three-step mechanism is: Step 1 HBr + O2 → HOOBr Step 2 ? Step 3 HBr + HOBr → H2O + Br2 Write the equation for step 2. 2HBr + HOOBr → HOBr + H2O + Br2 7. A student wishes to monitor the rate of the following reaction: CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Identify two properties that could be used to monitor the rate of the reaction. Describe and explain the changes that would occur. Property 1 Mass of CaCO3(s) Change and explanation Decreases, as reactants are converted into products. Property 2 Concentration of HCl Change and explanation Decreases, as reactants are converted into products. Any two in this list! Concentration of CaCl2(aq) Increases, as reactants are converted into products. Volume of CO2 Increases, as reactants are converted into products. Mass of an open beaker Decreases as CO2 escapes Pressure of a closed system Increases as CO2 is produced 8. Carbon burns in air according to the following equation: C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) List four ways the rate of the above reaction could be increased. Increase temperature Increase the pressure Increase O2 concentration Add a catalyst Increase C surface area 9. Sketch the potential energy diagram for an endothermic reaction in the space below. On your diagram clearly label: i) ii) iii) the energy of the activated complex the activation energy ΔH PE Ea ∆H Progress of the Reaction