Biochemistry
advertisement

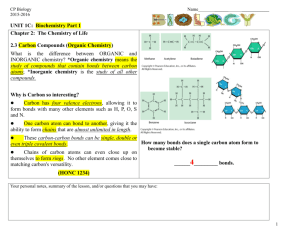
all compounds are classified into 2 broad categories: organic and inorganic compounds Organic compounds are made primarily of carbon atoms Inorganic compounds with a few exceptions, do not contain carbon. CO2 is inorganic and has C A carbon atom has 4 valence electrons and readily forms 4 covalent bonds to achieve stability It can bond with other elements or can bond with itself Monomers – building blocks of larger carbon (they are small and simple) Polymers – two (dimer) or more monomers that bond together Macromolecules -Large polymers Carbohydrates proteins Lipids nucleic acids DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS Removal of water to join two building blocks Forms dimers, polymers Glucose + Fructose Sucrose + H2O HYDROLYSIS Large molecules can’t pass thru membrane Must be broken down to monomer units to be absorbed into blood Water is ADDED to bonds, breaking them into smaller pieces Glucose + Fructose Sucrose + H2O Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) - molecule that can store large amounts of energy in its structure consists of a five carbon sugar (ribose) adenine, and three phosphate groups. The energy is stored in the bonds between the phosphate groups When a bond between the phosphate groups is broken, energy is released The hydrolysis of ATP is used by our cells to provide the energy necessary to perform chemical reactions that enable an organism to function