Obstretrics
advertisement

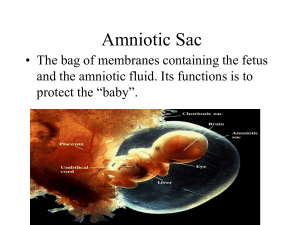
Obstetrics Definition of Obstetrics Branch of medicine dealing with the pregnant woman during pregnancy, child birth and period following birth Word Parts Word Combining root form Obstetric Obstetr/ic Meaning midwife Semen Mixture of sperm & secretions in seminal vesicles Insemination – deposit of semen in the female reproductive tract Artificial Insemination Semen is inserted into uterus via a cannula instead of coitus AI (AIH) by husband AI (AID) by donor Word parts Word root Semin Combinin Meaning g form semin/ i liquid secretion of the testicles and glands Sperm sperm/o, sperm cells or spermatozoa, spermat/o, ejaculated from the male sprem/i Act 1 Fertilisation Is the union of sperm and ovum Fertilised ovum is called zygote Zygote travels down fallopian tube to endometrium where it implants itself Foetus development Embryo – developing human during first 2 months - embryonic membranes form which protect & nourish the embryo Foetus – developing human after the second month - amniotic membrane forms surrounds foetus and is filled with amniotic fluid - amniotic fluid is a shock absorber for the foetus Placenta Develops between the embryo and endometrium Exchanges nutrients and waste between mother and foetus Also secretes hormones to maintain pregnancy Word parts Word root Foet Combining form Foet/o Meaning Placent Placent/o flat cake an unborn baby Terms related to placenta Adherent placenta – placenta is fused to uterine wall Retained placenta – placenta is not expelled Placenta praevia – placenta forms abnormally in lower part of uterus over the internal opening of the cervix Act 3 Umbilical cord Connects foetus to placenta Transports blood and nutrients to the foetus Gestation Period of time embryo and foetus is carried in uterus Usually 280 days Word parts Word root Combining Meaning form Gravida -gravida relates to pregnancies Para -para Toc toc/o, -tocia number of previous pregnancies resulting in a live infant birth, labour Nat nat/o birth Antenatal Period from conception to birth 3 trimesters – 3 months each Labour and Delivery Parturition refers to birth Labour is period preceding birth Uterine contractions are called eutocia Syntoconon is a drug to induce uterine contractions Stages of labour 1. Dilation – onset of labour to full dilation of 10 cm 2. Expulsion – full dilation to delivery 3. Placental – delivery of placenta and occurs a few minutes after birth Foetus during labour Lies in a lateral position in uterus Engagement – when head moves down into cervix Presentation – part of foetus that is touched by examining finger through the cervix Puerperium Period 6 – 8 weeks following birth Reproductive system reverts to pre pregnant state Definitions Post partum haemorrhage – excessive bleeding from birth canal Eclampsia – sudden convulsion due to toxaemia of pregnancy Stillbirth – foetus is born dead Congenital – present at time of birth Caesarian section – delivery by surgical excision into abdominal wall Forceps – surgical instruments used to help delivery Act 4 Mammary Glands Function is milk secretion i.e. lactation Ducts convey milk from lobes to the exterior The circular pigmented area surrounding the nipple is known as the areola Word parts Word root Mast Combining form mast/o Meaning Mamm mamm/o breast Lact lact/o, lact/i milk Galact galact/o milk breast Abbreviations ARM CTG DOB EDC/D EDD EP FDIU FECG Artificial Rupture of Membranes cardiotocograph date of birth estimated date of confinement / delivery estimated date of delivery ectopic pregnancy foetal distress in utero foetal electrocardiograph Abbreviations FHR HDN IUD LSCS NB PET PPH PROM PV foetal heart rate haemolytic disease of the newborn intrauterine device lower section caesarian section newborn pre- eclamptic toxaemia postpartum haemorrhage premature rupture of membranes per vagina Abbreviations Apgar score method of assessing general state of baby at birth.Appearance (colour); Pulse(heart rate); Grimace( response to slap); Respiration (breathing) epesi/o gravida multigravida multipara pubic region,vulvo a pregnant woman at least 2 pregnancies given birth to 2 or more children nulligravida para having never been pregnant to bear primigravida first pregnancy primipara first delivery Miscarriage Expulsion of products of conception before 20 weeks Conditions and Terms cervical incompetence abnormal weakness of the cervix; can lead to recurrent miscarriages ectopic pregnancy pregnancy outside of uterus usually in fallopian tubes placenta praevia placenta situated near the cervix pre - eclampsia condition in which hypertension, oedema, and proteinuria developing during 2nd half of pregnancy