Dominant and Recessive:
advertisement

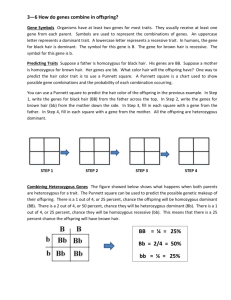
Name ______________________ Class _____HW Packet #3 Week of 12/6-12/11 Monday (Alleles) You inherit characteristics from your parents through their chromosomes. A chromosome has small parts called genes all the way along it. The genes are made of a chemical called DNA. Genes control the development of inherited characteristics. For example, there are genes which control eye color, hair color and skin color. What happens to genes during fertilization: A sperm has 23 chromosomes with genes from a man. An ovum (egg) has 23 chromosomes with genes from a woman. During fertilization the sperm and ovum join together. Each chromosome from the sperm then pairs up with a matching chromosome from the ovum. This brings the two sets of genes together. The genes for hair color pair up, the genes for skin color pair up, and so on. Genes always work in pairs. The genes in a pair may be identical. For example, they may both produce black hair. But if one is a gene for black hair and the other a gene for blond hair they are in competition. Dominant and recessive genes: The child has black hair because the gene for black hair is more powerful than the gene for blond hair. It dominates the gene for blond hair and produces the final hair color. Genes which dominate other genes are called dominant genes. Genes which are dominated are called recessive genes. When a dominant gene pairs up with a recessive gene, the dominant one produces the final effect. However, it is still part of the genotype and can be passed on to the next generation. Homozygous and heterozygous: A person with two identical genes for a characteristic is pure bred or homozygous for that characteristic. (HH is a pure bred gene.) A person with two different genes (one dominant and one recessive) for a characteristic is hybrid or heterozygous for that characteristic. Answer the Questions! 1. Which parts of chromosomes control inherited characteristics? 2. What are genes made of? 3. In the gene pair Hh (for black and blond hair) which gene is dominant? 4. If E is the gene for brown eyes, and e is the gene for blue eyes, what eye color will the following gene pairs give? a) EE _____________ b) Ee _________________ c) ee ______________ 5. Look at question 4 and pick out a gene pair which is heterozygous, and a gene pair which is homozygous. Tuesday (Vocabulary) ___Homozygous ___Allele ___Gene ___Genetics ___Punnet Square ___Recessive ___Genetics ___Genotype ___Heterozygous ___Heredity ___Dominant ___Trait ___Phenotype a. A gene for a particular trait (Y, y) b. A tool used to predict the probable breeding outcomes c. An inherited trait that is present even when inherited from one parent d. Characteristic e. The form of the gene that shows up only when inherited from both of the parents f. The letter combination that makes up a trait (Ee, EE, YY, yy) g. The likelihood of an occurrence h. The passing of traits from parent to offspring i. The physical characteristics of a trait. What it looks like. j. The segment of DNA that determines a particular trait k. The study of heredity l. Two different genes for the same trait (Yy) m. Two identical genes for the same trait (YY) Wednesday (Punnet Squares) Part A: Getting Started with Punnet Squares Circle the choices that are examples of each of those words. 1. Homozygous dominant AA Gg KK mm uu Rr TT 2. Homozygous recessive ee Ff HH Oo qq Uu ww 3. Genotypes in which dominant gene must show AA Dd EE ff Jj RR Ss 4. Genotypes in which recessive gene must show aa Gg Ff KK rr Oo Tt Part B: Punnett Squares 5. Examine the following Punnett squares and circle those that are correct. 6. What do the letters on the outside of the Punnett square stand for? 7. What do the letters on the inside of the Punnett square stand for? Thursday (Making Your Own Punnet Squares) 1. B= Brown eyes b= blue eyes Mom= Bb to have children? Genotypes Dad= BB What are the eye color possibilities if they chose Phenotypes 2. Curly hair is recessive, and straight hair is dominant. A woman with curly hair marries a man who is homozygous dominant for straight hair. Predict the outcomes for their children. Genotypes Phenotypes 3. Black hair is homozygous dominant. Brown hair is heterozygous. Blonde hair is homozygous recessive. (This is an example of incomplete dominance.) A woman with brown hair marries a man with brown hair. What are the possible outcomes for their kids? Genotypes Phenotypes 4. Attached earlobes are dominant over free hanging earlobes. Complete the Punnett Square for the following individuals: Mom=BB and Dad=bb Genotypes ***Review your notes for Friday’s Quiz on Punnet Squares!




![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)

