Genetics & Heredity Vocabulary: Key Terms Defined
advertisement
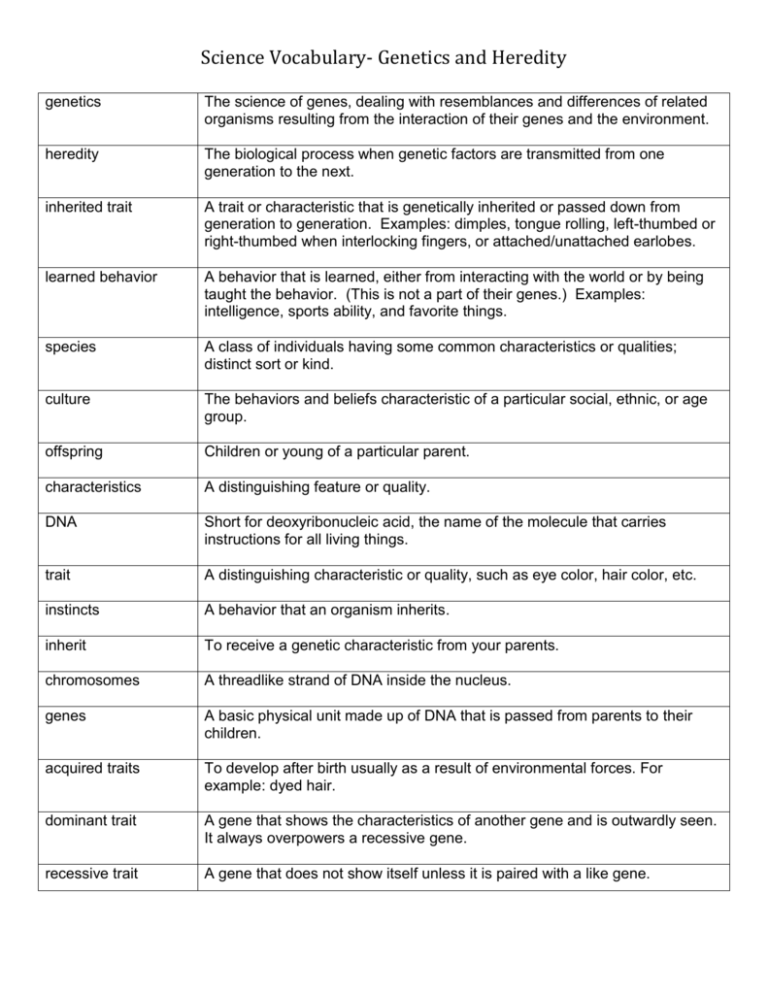
Science Vocabulary- Genetics and Heredity genetics The science of genes, dealing with resemblances and differences of related organisms resulting from the interaction of their genes and the environment. heredity The biological process when genetic factors are transmitted from one generation to the next. inherited trait A trait or characteristic that is genetically inherited or passed down from generation to generation. Examples: dimples, tongue rolling, left-thumbed or right-thumbed when interlocking fingers, or attached/unattached earlobes. learned behavior A behavior that is learned, either from interacting with the world or by being taught the behavior. (This is not a part of their genes.) Examples: intelligence, sports ability, and favorite things. species A class of individuals having some common characteristics or qualities; distinct sort or kind. culture The behaviors and beliefs characteristic of a particular social, ethnic, or age group. offspring Children or young of a particular parent. characteristics A distinguishing feature or quality. DNA Short for deoxyribonucleic acid, the name of the molecule that carries instructions for all living things. trait A distinguishing characteristic or quality, such as eye color, hair color, etc. instincts A behavior that an organism inherits. inherit To receive a genetic characteristic from your parents. chromosomes A threadlike strand of DNA inside the nucleus. genes A basic physical unit made up of DNA that is passed from parents to their children. acquired traits To develop after birth usually as a result of environmental forces. For example: dyed hair. dominant trait A gene that shows the characteristics of another gene and is outwardly seen. It always overpowers a recessive gene. recessive trait A gene that does not show itself unless it is paired with a like gene.











