Unit 7 Vocab Log KEY
advertisement

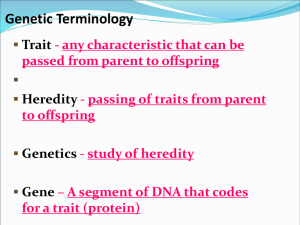
Unit 7 Vocab Log – Genetics Term Inherit Chromosomes Definition To derive a quality, characteristic, or predisposition genetically from one's parents or ancestors. Thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Genes A gene is the molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. Genes, which are made up of DNA, act as instructions to make molecules called proteins. Allele A number of alternative forms of the same gene. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. Genetics The study of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. Traits A distinguishing quality or characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring. Illustration Dominant Trait/Gene One allele is expressed over a second allele at the same locus; the first allele is dominant and the second allele is recessive. Term Definition Recessive Trait/Gene A trait that must be contributed by both parents in order to appear in the offspring; a genetic trait that results from the expression of the two recessive alleles. 1. Heterozygous (Hybrid) When the alleles of a pair are heterozygous, one is dominant and the other is recessive. Homozygous (Pure) Having identical pairs of genes for any given pair of hereditary characteristics. Punnett Square A simple graphical way of discovering all of the potential 1. combinations of genotypes that can occur in children, given the genotypes of their parents. It also shows us the odds of each of the offspring genotypes occurring. Offspring The product of reproduction of a new organism produced by one or more parents. Gregor Mendel The founder of the modern science of genetics; Mendel coined the terms “recessive” and “dominant” in reference to certain traits. (In the preceding example, green peas are recessive and yellow peas are dominant.) He published his work in 1866, Illustration demonstrating the actions of invisible “factors”—now called genes—in providing for visible traits in predictable ways.