Fluvial Landforms oht intro - ASGeography
advertisement

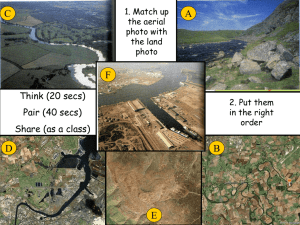
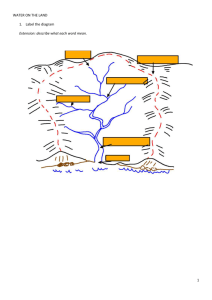
Fluvial Landforms The cross profile shows the view of the valley from one side to another and as the river moves from its source to the mouth changes take place that result in distinctive features. Some of these features result from erosion, some from deposition and some are a consequence of both processes. They include; Waterfalls and rapids Knick points Interlocking spurs potholes Braided channels Fluvial features Meanders (incised and entrenched) Ox-bow lakes Deltas Floodplains and river terraces Levees V-shaped valleys Hydraulic action causes intensive vertical erosion which results in a steep sided valley. The exact shape of the valley depends on Geology – e.g. Limestone results in a steep sided valley such as The Winnats Pass near Castleton. Clays result in a more gently sloping valley side. Climate – Higher precipitation levels are needed for the increased discharge levels needed to give vertical erosion and to move material from the valley sides. Vegetation – vegetation will bind the soil together leading to more stable valley sides – removal will lead to increased soil erosion. Interlocking Spurs How do they form? They form when the river winds its way round hills or protruding ridges of land. In the upper course of the river this may obstruct the view of the river channel. Lower down the course, in the middle stage, lateral erosion results in a wider valley bottom and river bluffs may be found (slopes at the edge of the floodplain) So how does a v-shaped valley form? 1. ________ erosion (in the form of abrasion, hydraulic action and solution) in the river channel results in the formation of a s_____ s______ valley 2. Over time the sides of this valley are weakened by w________ processes and continued v_______ e_______ at the base of the valley 3. Gradually mass movement of materials occurs down the valley sides, gradually creating the distinctive ___ shape. 4. This material is then gradually transported away by the river when there is enough energy to do so. As the river flows through the valley it is forced to swing from side to side around more r______ rock outcrops (spurs). As there is little energy for lateral erosion, the river continues to cut down v_______flowing between spurs of higher land creating _______ ________. Task Use the following link to find a photograph of an interlocking spur – draw an annotated fieldsketch of the photo. You can paste the photo onto this sheet. http://www.geograph.org.uk/search.php?i=9036702