Rivers - WordPress.com
advertisement

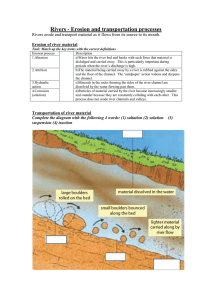
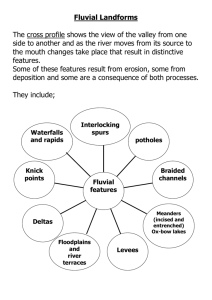
1E Geography Ms Cummins Revision 1. Name and explain the different parts to a river. 2. Name and explain the 3 different stages of a river. 3. Name and explain the work of rivers. Start on high, Flow down low, Creating features As they flow! River System Youth Stage = Upper Course Mature Stage = Middle Course Old age Stage = Lower Course The Work of Rivers • The Work of Rivers includes: 1. River Erosion (wearing away the landscape). 2. River Transportation (removing the material that it erodes). 3. River Deposition (Laying down or dropping the material along the way or in the sea). River Erosion • Hydraulic Action • Abrasion • Attrition • Solution Transportation Deposition • The River drops or deposits its material when: • • • • It loses speed and has less energy. The river’s volume decreases. It enters a flat or gently sloping plain. When it flows into a lake or sea. Learning outcomes • You will know about the features that form at a rivers Youthful Stage! 1. V-Shaped Valley 2. Interlocking Spurs 3. Waterfall and Plunge Pool. The Youthful Stage • The River has a steep gradient (slope). • The Valley has a narrow floor and steep sides. The Youthful Stage • At the youthful stage rivers tend to be fast flowing with lots of energy! • Erosion is the dominating process at the youthful stage Features at a rivers Youthful Stage • A number of features are created at a rivers youthful stage! • These are: 1. V Shaped Valley. 2. Interlocking Spurs. 3. Waterfall and Plunge Pool. V Shaped Valley, example: River Liffey. V Shaped Valley • Description: A river valley with steep valley sides and a narrow floor. • Formation: In the youthful stage the steep gradient results in a fast flowing river with lots of energy. The river uses this energy to erode the river bed. Vertical erosion dominates here. Through abrasion and hydraulic action the river erodes its bed to produce a valley with steep sides and a narrow floor i.e. A V Shaped Valley. • Leave space for diagram page 38 of book. Interlocking Spurs, example: River Liffey Interlocking Spurs • Description: are series of ridges that jut out from both sides of a young river valley and lock into one another like the teeth of a zip. • Formation: when the river meets hard or resistant rocks, it is unable to erode them. Instead, it winds and bends to avoid them. The rock land where the river has to make its way around are called interlocking spurs. • Leave space for diagram page 38 of book. Waterfall and Plunge Pool e.g Torc Waterfall, Kilarney, Co. Kerry Waterfall • Description: A sudden/sharp fall in the river bed. • Formation: water falls from where there is hard and soft rock side by side on the river bed. The hard rock resists river erosion but the soft rock is eroded by the river through abrasion and hydraulic action. The river erodes the soft rock, lowers the river bed and in time produces a waterfall. Plunge Pool • Description: a pool at the bottom of a waterfall. • Formation: when the river plunges over a waterfall it “crashes” onto the river bed directly beneath the waterfall. The impact of this on the river bed cause hydraulic action to take place. This causes erosion of the river bed which results in a plunge pool directly beneath the waterfall. • Leave space for diagram page 39 of book. Can you put the labels below into the correct place on he diagram? Features at a rivers Mature Stage 1. Meanders 2. U Shaped Valley Meander example: River Strule, Omagh Meanders Meanders Description: Meanders are curves/bends that develop along the mature (and old) course of a river. Formation: Meanders are formed by a combination of erosion and deposition. Erosion by abrasion and hydraulic action on the outer bank is balanced by deposition on the inner bank. It is erosion of the outer bank and deposition on the inner bank which results in a meander being formed. The Old Age Stage • The river flows much slower here. • The river has an almost flat gradient. • The valley has a wide flat floor and gentle side. Features at a rivers Old Age Stage • Oxbow lake • Levees • Deltas • Flood plains Floodplain- Irish example- The River Shannon, Shannon Bridge, Co. Offaly • Description: level of land on either side of a mature (or old) river that floods when a river overflows and is covered with alluvium. • Formation: rivers are sometimes not able to carry all of the water in the river system. This might be the result of heavy and persistent rain or winter snow and ice melting. When the river can’t carry all of its water it overflows. The flood waters carry sand, silt and sediment with them this material is known as alluvium material. When the floods are gone the alluvial material left on the land make up a flood-plain. Floodplain example, The River Tay, Scotland. Oxbow lake, example, River Liffey and Mississippi • Description : a meander which has been cut off from the main river. • Formation: erosion continues to take place on the outer bank of the river and the neck of land between the 2 meanders, as it gets narrower (diagram page 41 of book). • During a flood when the river has more energy, the neck of land is finally cut through. When this happens, a new straighter river channel is created. • Both ends of the meander are cut off from the river channel to form an oxbow lake. Levees • Description : raised banks of alluvium that are found along the banks of some rivers in their old age stage. • Formation: after many periods of flooding over the floodplain deposits build up to form levees. • Example: River Moy and Liffey. • Diagram page 41 of book. Delta • Description: lots of sand, silt and sediment built up at the mouth of a river. • Formation: Deltas are formed at the mouth of the river. When a river flows into the sea it loses its speed and deposits its material. If the material is a large amount the tides and currents may not be strong enough to take it out to sea. The deposits build up gradually and eventually rise above sea level to form a delta. • Example, Po Delta- Northern Italy. Stage Slope Main processes Valley shape Main features Upper Course Middle Course Lower Course