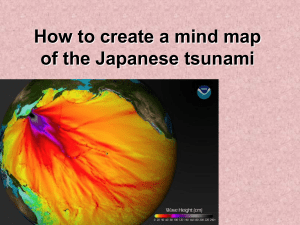
6thGrade_Geology_LP_ Earthquake
advertisement
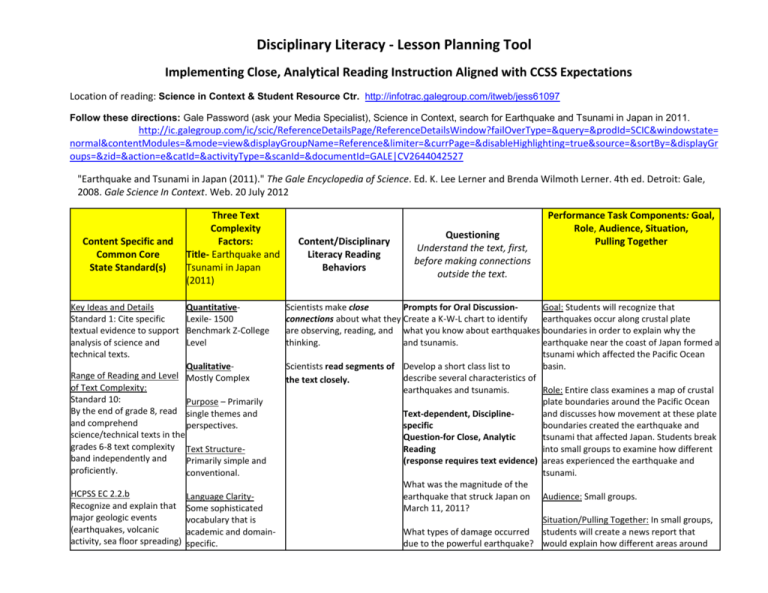
Disciplinary Literacy - Lesson Planning Tool Implementing Close, Analytical Reading Instruction Aligned with CCSS Expectations Location of reading: Science in Context & Student Resource Ctr. http://infotrac.galegroup.com/itweb/jess61097 Follow these directions: Gale Password (ask your Media Specialist), Science in Context, search for Earthquake and Tsunami in Japan in 2011. http://ic.galegroup.com/ic/scic/ReferenceDetailsPage/ReferenceDetailsWindow?failOverType=&query=&prodId=SCIC&windowstate= normal&contentModules=&mode=view&displayGroupName=Reference&limiter=&currPage=&disableHighlighting=true&source=&sortBy=&displayGr oups=&zid=&action=e&catId=&activityType=&scanId=&documentId=GALE|CV2644042527 "Earthquake and Tsunami in Japan (2011)." The Gale Encyclopedia of Science. Ed. K. Lee Lerner and Brenda Wilmoth Lerner. 4th ed. Detroit: Gale, 2008. Gale Science In Context. Web. 20 July 2012 Content Specific and Common Core State Standard(s) Key Ideas and Details Standard 1: Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts. Three Text Complexity Factors: Title- Earthquake and Tsunami in Japan (2011) QuantitativeLexile- 1500 Benchmark Z-College Level QualitativeRange of Reading and Level Mostly Complex of Text Complexity: Standard 10: Purpose – Primarily By the end of grade 8, read single themes and and comprehend perspectives. science/technical texts in the grades 6-8 text complexity Text Structureband independently and Primarily simple and proficiently. conventional. HCPSS EC 2.2.b Recognize and explain that major geologic events (earthquakes, volcanic activity, sea floor spreading) Language ClaritySome sophisticated vocabulary that is academic and domainspecific. Content/Disciplinary Literacy Reading Behaviors Questioning Understand the text, first, before making connections outside the text. Performance Task Components: Goal, Role, Audience, Situation, Pulling Together Scientists make close Prompts for Oral DiscussionGoal: Students will recognize that connections about what they Create a K-W-L chart to identify earthquakes occur along crustal plate are observing, reading, and what you know about earthquakes boundaries in order to explain why the thinking. and tsunamis. earthquake near the coast of Japan formed a tsunami which affected the Pacific Ocean Scientists read segments of Develop a short class list to basin. describe several characteristics of the text closely. earthquakes and tsunamis. Role: Entire class examines a map of crustal plate boundaries around the Pacific Ocean Text-dependent, Disciplineand discusses how movement at these plate specific boundaries created the earthquake and Question-for Close, Analytic tsunami that affected Japan. Students break Reading into small groups to examine how different (response requires text evidence) areas experienced the earthquake and tsunami. What was the magnitude of the earthquake that struck Japan on Audience: Small groups. March 11, 2011? Situation/Pulling Together: In small groups, What types of damage occurred students will create a news report that due to the powerful earthquake? would explain how different areas around occur along crustal plate boundaries. the Pacific Ocean experienced the tsunami after the earthquake in Japan. Knowledge DemandsRequires some discipline-specific content knowledge. Requires knowledge of the map of the Pacific Ocean. According to the text, thrust faulting happens as the Pacific Groups may include costal Japan, China, plate moves west towards Japan at Indonesia, Australia, Hawaii, Alaska, and a velocity of 3.2 inches per year. California. After the earthquake, how far eastward did some parts of Japan move? Reader & TaskReaders will be able to make connections between the content of the text and their prior knowledge of earthquakes and tsunamis. Why were tsunami waves created from this earthquake? Explain why coral atolls were safer and volcanic islands were in more danger from the tsunami. Some waves were as high as 33 feet on the Japanese coastline. What types of damage occurred in Japan due to the tsumani? Compare the damage from a Tsunami to damage from a hurricane. How are they similar and different? CCSS Literacy - Standard 2. Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; provide an accurate summary of the text distinct from prior knowledge or opinions.