100-2日本311地震
advertisement

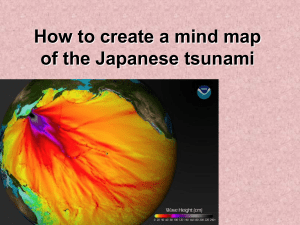
日本311地震、海嘯滿週年 談現今全球的環境與資源問題 臺北市立建國中學 李文禮 wllee@ck.tp.edu.tw 2012.03.20 Outline of Talk Earthquake Tsunami Environment and Resource 美國官方機構對地球環境的調查 USGS(U.S. Geological Survey) NOAA(National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) NASA(National Aeronautics and Space Administration) NOAA(National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) A 3D view of our Planet Earth Global Distribution of Earthquakes (Real-time Earthquake Information) The distribution of some of the Earth's 500 active volcanoes Plate Tectonics Plate Boundaries seismogram Body and surface waves Seismic Waves(motion) 車籠埔斷層錯動引發集集地震 Kobe,Japan 1995 Bigger Faults Make Bigger Earthquakes Bigger Earthquakes Last a Longer Time Great Tohoku Earthquake (northeast Honshu, Japan) Magnitude :9.0 Date-Time:2011 March 11 05:46:24 UTC Location:38.297°N, 142.372°E (horizontal +/- 13.5 km) Depth:30 km 近百年世界十大地震(圓圈) 及十大災害地震(菱形) 全世界規模大於 8.0 的地震 (after 1900 ) Plate World earthquakes 2011 Visualization map Depth Profile Magnitude type rangeDistance Comments • Richter and Gutenberg for local earthquakes in 1935. Local 0-400 2-6 • maximum amplitude of a seismogram (ML) km recorded • Wood-Anderson torsion seismograph • A magnitude for distant earthquakes Surface 20-180 • based on the amplitude of Rayleigh wave 5-8 degrees surface waves measured (Ms) • at a period near 20 sec. • the moment of the earthquake • the rigidity of the earth times the Moment > 3.5 all average amount of slip on the fault (Mw) times the amount of fault area that slipped. 海嘯發生原因 海底發生規模7.5 以上的淺源地 震,鼓起海水 海底火山爆發 大規模的海底山崩 隕石撞擊 Generation of a tsunami by fault movements Velocity of Tsunami 海嘯是一種長波及長週期的淺水波 深水波與淺水波的不同 淺水波 波浪的往返運動受水底摩 擦力影響,水分子往返運 動路線為橢圓形。 深水波 深水波的速率 與波長的平方根成正比,不隨水深改變 ※ C為波速,g為重力加速度,L為波長 淺水波的速率 與水深的平方根成正比,水深愈淺,速率愈慢 ※ C為波速,g為重力加速度,h為水深 斯里蘭卡Kalutara 海岸在南亞 海嘯發生前後的變化 (a)2004 年1 月海嘯發生前 (b)2004 年12月26 日海嘯發生時, 波谷先到達,海水後退約400 公 尺。 南亞海嘯襲擊印尼亞齊市 (a)破壞前 (b)破壞後 Propagation of tsunami of the Japan earthquake 利用全球定位系統GPS 觀察電離層海嘯現象 GPS 衛星 電離層海嘯之 現象示意圖 電離層海嘯 在海嘯發生後,太空之電離層亦有明顯的波動,並一同傳至 四方。 NOAA海潮計分布 GPS地面接收測站 日本(1211)及台灣(131) COMCOT模擬海嘯變化與地震當 天與前一天之TEC變化 total electr on conte nt (TEC u) 3/10 TEC 3/11 TEC 0 -0.3 time after earthquake (hr) tsunami height (m) 0.3 電離層海嘯與COMCOT模擬海嘯之 動畫比較[Liu et al.,2011] TEC波動速度與其對震央距離之關係圖。在距離震央1000公里的 範圍內,距離越遠則速度越快,這是因為本次地震所造成之海嘯 波源範圍極大,故造成1000公里範圍內幾乎同時產生波動現象, 而1000公里範圍外則無此現象,故我們取1000公里外的其中46筆 TEC資料。 智利大海嘯(2010)之TEC變化 基隆海嘯(1867) 石垣島海嘯(1771) 歐亞板塊 台 灣 淺 海 ** * 花蓮海底火山噴發(1853) 琉 球 海 溝 高屏海嘯(1781) 深 海 馬 尼 拉 海 溝 菲律賓海板塊 Japan Tsunami Debris Tracked Across Pacific Ocean “The Great Pacific Trash Vortex,” “… Trash Island,” “… Garbage Patch” 他(她)需要什麼樣的環境?多少資源 Environment and Resource ? 1,925 磅的銅 1.8 盎司的金 23,048 磅的黏土 589,974 磅的煤 30,415 磅的鹽 27,797 磅磷酸鹽 1,001 磅的鋅 5,929 磅的鋁 83,890 加侖石油 1,078 磅的鉛 68,915 磅的水泥 42,581 磅的鐵砂 170萬磅的石頭、砂、礫石 600萬立方英尺的天然氣 69,088磅的其他礦物和金屬 Population & Energy Consumption (1820-2010) 石油的重要性 没有石油的一天怎麼過? 很難過,因為我們都上癮了! 石油在空間上的有限性 石油產生於大的沈積盆地,在變質岩或火成岩中均不生成,太老(大於 幾億年)會化為瀝青,太熱(高於300度)會分解。石油生成要有生油 岩(浮游生物)、儲油岩(砂岩)、及蓋層(頁岩),發生不易。 石油在時間上的有限性 中東紛爭 Katrina 颶風 第2次石油危機 反恐戰爭 第1次石油危機 伊拉克入侵 科威特 911 金融風暴 Data source: (*) Crude oil prices 1970-1987 - IEA, crude oil prices 1988-2010 - Platt’s; (**) Deflator - IMF; (***) Deflator - Bureau of Labor Statistics. The redistribution or reproduction of data whose source is Platt’s is strictly prohibited without prior authorization from Platt’s. 石油世紀 1859年:第一口油井在美國賓州開採,此 時因石油的用途不多,故需求不大。 1908年至1970年代:因福特T型車量產,大 規模的公路建設及城市擴張,使得石油需 求大增;而期間兩次的世界大戰及戰後嬰 兒潮,石油需求越形殷切。 Percentages of energy types used in the US Estimated world reserves of crude oil Annual electricity net generation in the world Hubbert curve Liebig's law of the minimum growth is controlled not by the total amount of resources available, but by the scarcest resource (limiting factor) originally applied to plant or crop growth Liebig's barrel 没有石油的明天 我的老爸騎著駱駝 我開勞斯萊斯轎車 我兒子搭噴射客機 而我的孫子又回到騎駱駝的日子 謝謝聆聽 敬請指教