THE AIR AROUND YOU - Delran Middle School
advertisement

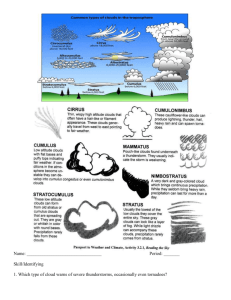
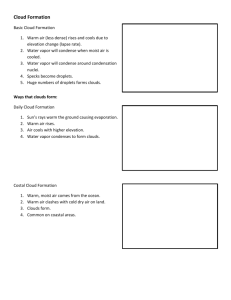
THE AIR AROUND YOU CHAPTER 2; SECTION 1 WEATHER Weather – the state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place 4 WEATHER FACTORS 1. temperature 2. moisture 3. wind 4. air pressure The SUN has a strong influence on the weather. Temperature- a measure of molecule movement - when molecules move faster the temperature is warmer - when molecules move slower the temperature is cooler WIND Wind – when air moves from high pressure areas (cold) to low pressure areas (warm) Wind vane- an instrument used to show the direction the wind comes from Wind sock- blows in the direction of the wind Anemometer- an instrument used to measure the wind speed HUMIDITY Humidity- the amount of water vapor in the air **warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air Relative humidity- the amount of water vapor in the air compared to the amount of water vapor the air can hold Dew point- the temperature at which air is saturated and condensation form CLOUDS Formation of clouds- Warm, moist air rises and cools and the air can no longer hold as much water vapor, so some of the water vapor turns into tiny droplets of liquid (which are clouds). Condensation nuclei- small particles that water droplets form on Luke Howard developed the first system of classifying clouds by shape and height. WAYS TO CLASSIFY CLOUDS 1. SHAPE a. stratus clouds- sheets or layers of clouds located close to the earth b. cumulus clouds- big, white, fluffy clouds (look like cotton) with a flat base c. cirrus- thin, feathery clouds made of ice crystals found high in the atmosphere 2. HEIGHT a. cirro – refers to clouds found high up in the atmosphere b. alto- refers to clouds found in the middle of the atmosphere c. strato- refers to clouds found low in the atmosphere 3. PRODUCES RAIN OR SNOW a. nimbus- a dark cloud that does not let light through and produces rain or snow example: cumulonimbus cloud is a big, dark rain cloud PRECIPITATION Precipitation- water that falls from a cloud - the type of precipitation depends on the air temperature Rain- occurs anytime water falls from clouds and the temperature is above freezing Snow- when the temperature near the cloud and near the ground is below freezing Sleet- the temperature near the cloud is warm, but the temperature near the ground is cold. Sleet occurs when water droplets fall from a cloud and freeze when they get closer to the ground. Hail- The top of the cloud is cold while the bottom of the cloud is warmer. Ice crystals fall from higher in the atmosphere, then begin to melt as they fall. Wind (an updraft) pushes the melted ice crystal back up causing it to freeze again. As the ice crystal is tossed up and down it grows larger. THE AIR AROUND YOU Chapter 2; Section 2 AIR MASSES Air mass- a large body of air that has properties like the earth’s surface that is formed above -When looking at air masses we look for temperature and moisture -There are 6 major air masses in the United States. 1. Low pressure system L -winds move counterclockwise -brings stormy weather -move northeast across U.S. 2. High pressure system H -winds move clockwise -brings fair weather -move southeast across U.S. FRONTS Front - A boundary between two different air masses -clouds and precipitation usually form at a front Cold Front- occurs when colder air advances pushing up warmer air up Warm front- occurs when warm air advances and goes over cold air Occluded front- involves 3 different air masses; when two colder masses of air force the warm air up Stationary front- occurs when warm air and cold air masses collide but neither air mass moves THE AIR AROUND YOU CHAPTER 2; Section 3 FORCASTING WEATHER Meteorologist- a person who studies and predicts the weather To predict weather, the atmosphere and earth’s surface are looked at. Station model- a point on a map that shows the weather conditions for a specific area STATION MODEL Cloud cover Temperature barometric pressure (air pressure) Dew point change in air pressure Wind direction (SE) Isotherm- a line drawn on a map that connects areas with the same temperature Isobar- a line drawn to connect points of equal atmospheric pressure; when isobars are close together the air pressure changes rapidly, which makes stronger winds 2 instruments used to measure humidity (water vapor) 1. hygrometer 2. psychromoter