Meteorology Unit Test Review Sheet
advertisement

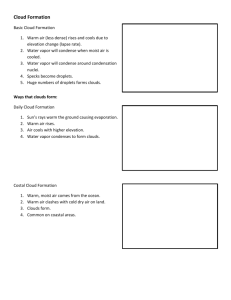
Meteorology Unit Test Review Sheet Mr. Mumpower General Knowledge you should know: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Cold air comes from the north and warm air comes from the south. High pressure spins clockwise and low pressure spins counterclockwise. High pressure brings good weather and low pressure brings stormy weather. Warm air is less dense than cold air. Cold air is more dense than warm air. Weather moves west to east across the United States due to the prevailing westerlies. Wind blows from high pressure to low pressure. Wind direction is measured from were it comes from. Chapter 17 – The atmosphere 1. The ozone layer is in the stratosphere and it protects us from ultraviolet radiation. 2. Nitrogen is the major gas in our atmosphere. 3. Earth is the only planet to have oxygen – from photosynthesis. 4. Troposphere is the closest layer to the Earth – contains clouds and rain. 5. The ionosphere is located in the thermosphere – made of electrically charged particles. 6. Know the three types of convection with examples: radiation, convection, and conduction. 7. The greenhouse effect traps carbon dioxide and water vapor for heating of the Earth’s atmosphere. Burning of fossil fuels and deforestation has increased carbon levels to increase carbon dioxide, which increase temperatures known as global warming. 8. Trees reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the air. 9. Smog, an air pollutant, is caused by automobiles. Chapter 18 – Water in the atmosphere 1. Clouds form by condensation; moist air from warm land rises,cools, and condenses into clouds. 2. Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. 3. Relative Humidity is the % of water vapor in the air, 100% relative humidity = totally saturated = raining/snowing. 4. Cumulus clouds are white, puffy clouds with sharp outlines. 5. Equator – direct radiation from sun – hot temperatures, Poles – indirect radiation – cool temperatures. Chapter 19 – Air Pressure and Wind 1. Coriolis Effect turn objects to the right in the northern hemisphere. 2. Jet stream moves west to east, slows down westward flying airplanes. 3. Difference between a sea breeze and a land breeze? Continued on other side >>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>> Chapter 20 – Severe Weather and Weather Maps 1. What is the difference between a storm watch and a storm warning? 2. Station model – used for wind speed, wind direction, and cloud coverage. 3. A wind vane determines wind direction, anemometer determines wind speed. 4. A hurricane is large enough to be seen from outer space. 5. Know the conditions of a warm front, cold front, and stationary front. 6. Know the symbols on a weather map: warm front, cold front, and stationary fronts. 7. What is an air mass? What is the relationship between air masses and fronts? 8. Meteorologist use satellites and radar to help them predict the weather. 9. Why do you see lightning before you hear thunder? 10. Lightning forms by opposite charged particles in a cloud creating an electrical charge that makes light in the form of lightning. Lightning can be cloud to cloud or cloud to ground. Notes: