Animal Habitats
advertisement

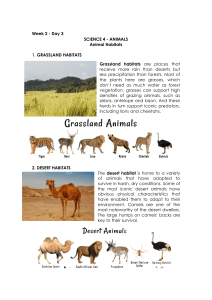
Animal Habitats Study Guide Vocabulary population - a specific group of plant or animal organisms. Examples would be a flock of geese near a pond or a herd of elephants in the grassland. community - a collection of different populations interacting with each other and their environment. An example of a dry-land community would be a forest made up of trees, squirrels, worms, rabbits, and hawks. An example of a water-related community would be an ocean made up of fish, crabs, and seaweed. habitat - the natural environment of a plant or animal. Examples include grasslands, desert, tundra, forest, and ocean. Key Concepts Water-related environments include those with fresh water or salt water. Examples include ponds, marshes, swamps, streams, rivers, and oceans. Dry-land environments include deserts, grasslands, rain forests, and forests. Students should be able to describe each habitat and give examples of plants and animals that live in each one. Students should be able to compare and contrast land habitats and water habitats. There are distinct differences among pond, marshland, swamp, stream, river, ocean, desert, grassland, rainforest, and forest environments. Organisms compete for the limited resources in their specific environment. Students should be able to predict what would happen if a population in a specific habitat would die.