Animal Habitats Worksheet: Grassland, Desert, Arctic, Forest, Ocean
advertisement
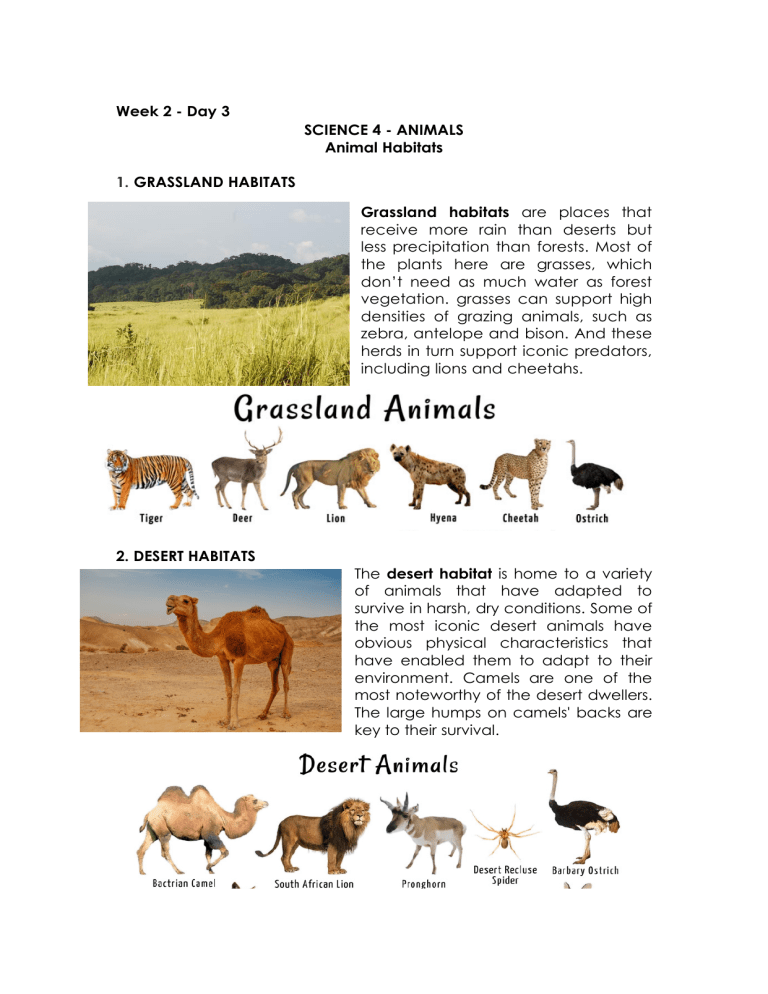
Week 2 - Day 3 SCIENCE 4 - ANIMALS Animal Habitats 1. GRASSLAND HABITATS Grassland habitats are places that receive more rain than deserts but less precipitation than forests. Most of the plants here are grasses, which don’t need as much water as forest vegetation. grasses can support high densities of grazing animals, such as zebra, antelope and bison. And these herds in turn support iconic predators, including lions and cheetahs. 2. DESERT HABITATS The desert habitat is home to a variety of animals that have adapted to survive in harsh, dry conditions. Some of the most iconic desert animals have obvious physical characteristics that have enabled them to adapt to their environment. Camels are one of the most noteworthy of the desert dwellers. The large humps on camels' backs are key to their survival. 3. ARCTIC HABITATS The Arctic habitat is a freezing cold area at the top of the Earth, above the Arctic Circle. It's made up of the Arctic Oceans, as well as areas of the U.S., Canada, Russia, Iceland, Sweden, Finland, Norway and Greenland. It's a diverse habitat, meaning that lots of different plants and animals live there. 4. FOREST HABITATS Forest is a habitat for many plants and animals because it provides a suitable environment for them. For example, neem, Sheesham, Palash, tiger, porcupine, elephants, jackal etc. The ground beneath the tree of the forest is the forest floor. It consists of a root, soil, decomposers and decomposing organic matter. Long, woody trees in the forest also provide shelter creepers and also the climbers. Animals in the forest are very particular regarding their habitats. They need everything the forest provides in order to survive. 5. OCEAN/SEA HABITATS Some habitats are shallow, sunny and warm. Others are deep, dark and cold. Plant and animal species are able to adapt to certain habitat conditions, including movement of water, amount of light, temperature, water pressure, nutrients, availability of food, and saltiness of water. Ocean habitats can be divided into two: coastal and open ocean habitats. Most of the open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. References: https://www.desertusa.com/animals.html#ixzz6s5sqIRHU https://kids.nationalgeographic.com/nature/habitats https://www.twinkl.com.ph/teaching-wiki/arctichabitat#:~:text=The%20Arctic%20habitat%20is%20a,plants%20and%20a nimals%20live%20there. https://eslforums.com/arctic-animals/ https://loveenglish.org/forest-animals/ https://www.toppr.com/guides/science/forest-our-lifeline/forest-as-ahabitat/ https://www.nps.gov/subjects/oceans/oceanhabitats.htm#:~:text=Ocean%20habitats%20can%20be%20divided,edg e%20of%20the%20continental%20shelf.