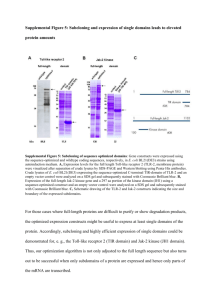
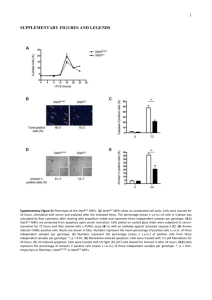
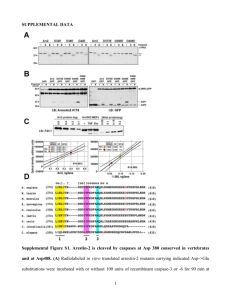
Supplementary Methods - Word file (25 KB )
advertisement

Supplementary Methods GST-pull down, immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation (IP) and in vitro kinase assays. Bacterial GST fusion proteins were purified via glutathione agarose beads. When used as substrates for in vitro kinase assays, GST fusion proteins were eluted from the beads via glutathione, and the eluate was dialyzed against PBS. For GST-pull down kinase assays, 293T cells were lysed by homogenization in hypotonic buffer containing 50mM Tris, pH8.0 with 10mM NaF, 1mM Na3VO4, 0.5mM DTT and protease inhibitors. The lysates were cleared by centrifugation at 10,000xg and incubated at 4C for 6hrs with GST or GST-LRP6C bound to glutathione beads. Beads were afterwards washed 5 times in PBS and once in the kinase buffer (20mM Hepes, pH8.0 and 20mM MgCl2). Kinase reactions were carried out at RT for 6hrs in the kinase buffer supplemented with 100M ATP. For the Axin IP kinase assay, hypotonic cell lysates prepared from 293T cell expressing Flag-Axin were incubated with Flag-M2 antibody conjugated agarose beads (Sigma) to IP Axin. Purified GST-LRP6C (2g) was added as the substrate to the Axin precipitates in the subsequent kinase reaction as above. For in vitro GST-LRP6C and Axin binding assay, GST-LRP6C bound to beads were phosphorylated in vitro by purified GSK3 and/or CK1 (kinase domain) (New England Biolabs, 100 units per reaction) for 4hrs at RT and washed several times before incubation with lysates from 293T cells expressing Flag-Axin. Cell lysates were prepared in 50 mM Hepes, pH7.4, 1.5mM EDTA, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1% Triton X-100, 10mM NaF, 1mM Na3VO4, 0.5mM DTT and a cocktail of protease inhibitors. Binding was carried out at 4C for 6hrs and the beads were washed 5 times in 1% Triton buffer before SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting, which were done as described7. Co-IPs using cell extracts were done as described5. Membrane and cytoplasmic fractionations. 293T cells were washed with cold PBS and lysed in 0.5ml hypotonic buffer as above via a Dounce Homogeniser. The lysate was 1 centrifuged at 3,000 rpm at 4ºC for 5 min. The supernatant was collected and centrifuged at 100,000xg at 4ºC for 1hr. The resulting supernatant was collected as the cytoplasmic fraction. The pellet was resuspended in 0.1ml hypotonic buffer plus 1% TritonX-100 and rotated on a nutator at 4ºC for 15-30 min, and then centrifuged for 14,000 rpm for 15 min at 4ºC. The resulting supernatant was collected as the membrane fraction. Gsk3Gsk3(flox/flox) MEFs. E14K ES cells that harbour LoxP-recombination sites flanking exon 2 of Gsk3both alleles) were made null for Gsk3 through conventional gene targeting by first replacing exon 2 with a neo cassette for positive selection with G418 and then rendering the locus homozygous through selection in 2.5 mg/ml G418. These Gsk3Gsk3(flox/flox) ES cells were injected into blastocysts derived from B6 mice to generate chimeric embryos. 14 embryos from 3 pregnant recipient mothers were harvested at day 16.5 dpc to generate separate cultures of MEFs from each embryo. To select MEFs derived from the injected ES cells, cultures were placed under selection with 1 mg/ml G418. 1 of the 14 pups gave rise to a large number of G418-resistant MEFs, which were passaged 10 times under the selection in G418 and using a split ratio of 1:3. These cells entered crisis after 10 passages, and one of the 3 flasks of fibroblasts escaped crisis and provided the spontaneously immortalized Gsk3Gsk3(flox/flox) MEFs used in this study. CKI (-/-) MEFs. These cells were derived from E14 mouse embryos harbouring homozygous null alleles of CKI gene (H. O., T. Prolla, A. Bradley, A. Rao, unpublished results). Immortalized stable cells were selected for puromycin resistance after infection 2 with a retrovirus encoding SV40 T antigen in the pBabe puro vector. Control wild type MEFs were selected similarly. 3