PRO_408_sm_suppfig5
advertisement
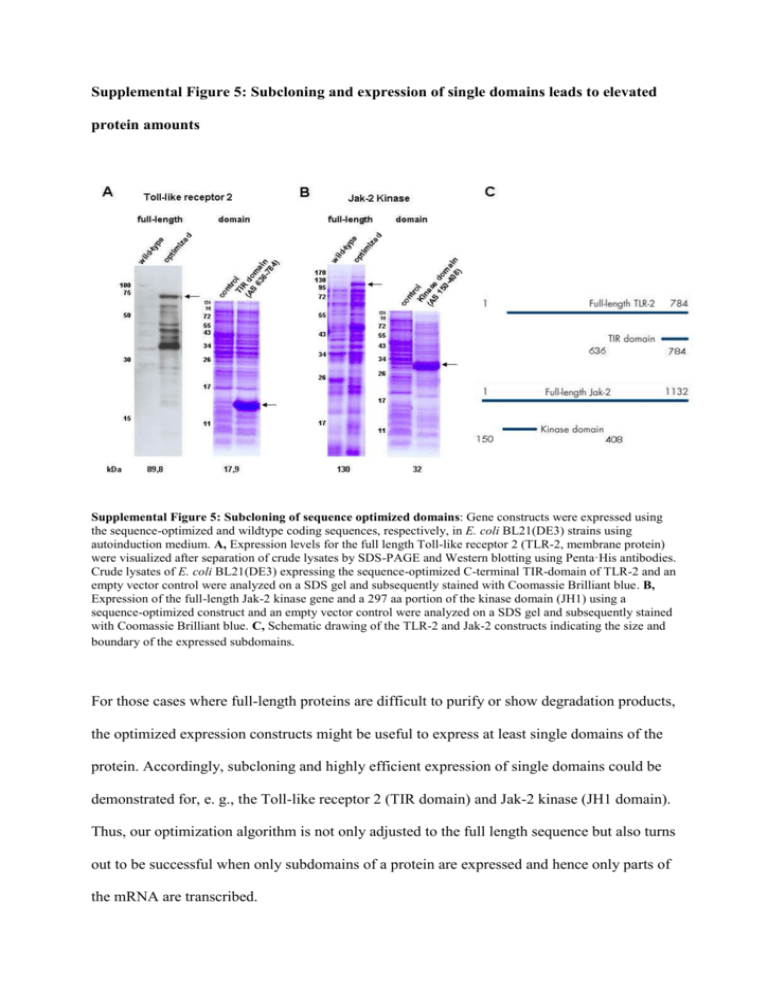
Supplemental Figure 5: Subcloning and expression of single domains leads to elevated protein amounts Supplemental Figure 5: Subcloning of sequence optimized domains: Gene constructs were expressed using the sequence-optimized and wildtype coding sequences, respectively, in E. coli BL21(DE3) strains using autoinduction medium. A, Expression levels for the full length Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2, membrane protein) were visualized after separation of crude lysates by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting using Penta·His antibodies. Crude lysates of E. coli BL21(DE3) expressing the sequence-optimized C-terminal TIR-domain of TLR-2 and an empty vector control were analyzed on a SDS gel and subsequently stained with Coomassie Brilliant blue. B, Expression of the full-length Jak-2 kinase gene and a 297 aa portion of the kinase domain (JH1) using a sequence-optimized construct and an empty vector control were analyzed on a SDS gel and subsequently stained with Coomassie Brilliant blue. C, Schematic drawing of the TLR-2 and Jak-2 constructs indicating the size and boundary of the expressed subdomains. For those cases where full-length proteins are difficult to purify or show degradation products, the optimized expression constructs might be useful to express at least single domains of the protein. Accordingly, subcloning and highly efficient expression of single domains could be demonstrated for, e. g., the Toll-like receptor 2 (TIR domain) and Jak-2 kinase (JH1 domain). Thus, our optimization algorithm is not only adjusted to the full length sequence but also turns out to be successful when only subdomains of a protein are expressed and hence only parts of the mRNA are transcribed.