last lecture - Lectures For UG-5
advertisement

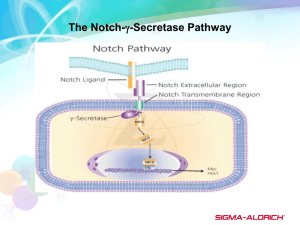
Cell Signaling Lecture 13 and 14 Ligand-activated Notch undergoes 2 cleavages before releasing the transcription factor ADAM10: A disintegrin and Metalloprote ase 1. Notch is cleaved by the matrix metalloprotease ADAM10, which is bound to the membrane releasing the extracellular Notch segment 2. Y-secretase, a complex of four membrane proteins including the protease presenilin 1 (PS1) then associates with the remaining portion of Notch 3. and catalyzes an intramembrane cleavage that releases the cytosolic segment of Notch. Wnt Signals trigger release of a transcription from cytosolic protein complex 1. In the absence of Wnt (protooncogene: a normal cellular gene whose inappropriate expression promotesthe onset of cancer), Bcatenin is found in a complex with Axin, APC and the kinase GSK3. 2. The kinase GSK3 phosphorylates Bcatenin leading to its degradation. 3. The TCF transcription factor in the nucleus acts as a repressor of target genes unless altered by Wnt signaling. 1. Binding of Wnt to its receptor Frizzled (Fz) triggers phosphorylation of the LRP coreceptor by GSK3 and another and another kinase, and thus allows subsequent binding of Axin. 2. This disrupts the Axin-APC-GSK3B-catenin complex, preventing phosphorylation of B-catenin by GSK3 which leads accumulation of B-catenin in the cell. 3. After translocation to the nucleus, B-catenin may act with TCF to activate target genes or, alternately cause the export of TCF from the nucleus and possibly its activation in the cytosol Processing of Hh Hedgehog Signaling