Ecology Study Guide
advertisement

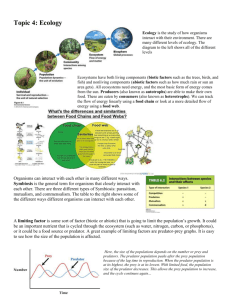
Ecology Study Guide - The living parts of the environment are called the _biotic_ factors. - _abiotic____ factors are the non-living things that impact the living organisms. - Give three examples of abiotic factors: soil, water, sun, rocks, air - Organism _population____ __community____ _ecosystem_ Biosphere - A _habitat____ is the specific part of the environment that provides all the things an organism needs. - Does the population increase or decrease when: _increase___ more move into a population than die _decrease________ more leave a population than move into a population _decrease_______ more die than are born - A __limiting factor______________ factor causes a population to go down (disease, introduction of predators, lack of food, water shelter) - The __carrying capacity__________ __________ is the largest population an area can sustain over a long period of time. - What is the carrying capacity of the deer on Wallawalla Island? approximately 80 - Name three resources that organisms compete for: food, shelter, water__________. - Competition occurs between _organisms____ of the same species and different _populations__________________. - A _predator_________ is the organism doing the eating. - A _prey__________ is the organism eaten. - As a predator population increases, does the prey population decrease or increase? ___decrease___________ Why?_Initially the prey population will decrease until the carrying capacity is met. - What happens if the predator population gets too high? . It will begin to decrease as the number of prey become more scarce limiting the amount of the predator population - Prey Adaptations _c__ Camouflage _e__ Mimicry _b__ Defensive Chemicals _a__ Warning coloration _d__ Protective covering - a. bright coloring to keep a prey away b. a skunk spraying a potential predator c. coloring to blend in with the surroundings d. a coat of armor (needles, a shell, etc) e. A viceroy butterfly looks like a monarch butterfly which tastes bitter to birds. List two adaptations of a predator stealth, camouflage, speed, ambush, patience Symbiosis: __mutualism_______________ both benefit __commensalism_________________ one benefits the other is neither helped or harmed - A(n) _herbivore___________ eats only plants - A(n) _carnivore___________ eats only animals - A(n) ___scavenger__________ eats the leftover remains of a dead animal - How does energy first enter the food web? __through the sun____________________ - Draw a food chain from the food web below. Be sure to include the sun. A(n) omnivore___________ eats plants and animal Sun > grass > mouse > snake > fox - Name the producer in the above food web: _grass_____________ - Name a primary consumers in the above food web: __mouse, rabbit, or deer__________ - Write the food chain in which the wolf is the secondary consumer: ____grass, deer, wolf_ - Name a tertiary consumer in the above food web: __wolf______________ - Explain the job of a decomposer _To break down dead plants and animals and return them to the soil __ - How is a decomposer different from a scavenger _The decomposer breaks down the organism and returns the nutrients to the soil. A scavenger eat dead animals and consumes nutrients______________________ - _10____ % energy moves from one level to the next in an ecosystem Populate the energy pyramid using the food chain below: Tertiary Consumer Level/ includes omnivores and carnivores/heterotrophic/contain least amount of biomass - - Which organism in the above pyramid has the least available energy___wolf______ Secondary Consumer Level/ includes omnivores and carnivores/heterotrophic Primary consumers/includes herbivores/ heterotrophic - Label the trophic levels in the above energy pyramid and explain each level. - Explain the idea of trophic levels. Label each level and be prepared to explain the amount Producer level/ most biomass/contains autotrophs of biomass available. As you move up the energy pyramid there is less biomass available. There needs to be enough organisms to allow for reproduction and sustained support for the levels above. - Which way do the arrows point in a food web? In the direction the energy flows from the prey to the predator. Example: grass > rabbit > snake - Was removing the wolves from Yellowstone beneficial explain: Removing the wolves from Yellowstone was NOT beneficial because the elk population overpopulated and overgrazed. The overgrazing left too little grass for the populations that depended upon it. - Organisms can be divided into three groups based on how they get their energy. Describe each of these. o Producers_ - _Make their own food/Plants/Autotrophs____ o Consumers - Get their food from somewhere else/heterotrophic o Decomposers - Gets energy by breaking down organisms and absorbing their nutrients - What are the different types of consumers? Describe each one. o herbivore - eats only plants o carnivore - eats only meat o o omnivore- eats plants and animals scavenger- omnivores that eat dead plants and animals - What do ecologists study? the study of interactions of living organisms with each other and their environment - Study a diagram of the water cycle. Explain the processes. Be able to label these on the diagram. o Condensation- _change from gas to a liquid_______ o Precipitation – a form of water that falls to the earth (rain, sleet, snow, hail) o Transpiration - _plants release water vapor into the air_______ o Evaporation - _change from liquid to gas_____________ - Study a diagram of the carbon cycle. o Explain the processes of respiration - takes in oxygen and glucose and gives off carbon dioxide and water when making energy. photosynthesis – takes in carbon dioxide and water to make food. Gives off oxygen and glucose. o o o o o o Which process releases carbon into the soil? decomposition Which processes release it into the atmosphere? Respiration and combustion Which process removes carbon from the atmosphere? photosynthesis How do animals obtain their carbon? When they eat. Through which process do plants get their carbon? photosynthesis How might carbon stored in fossil fuels be released? combustion - Study a diagram of the nitrogen cycle. o Explain the process of nitrogen fixation. Atmospheric nitrogen which is a gas cannot be used by producers or consumers. It has to be fixed first. Lightning and bacteria fix nitrogen, so plants can absorb or assimilate the nitrogen. Animal then eat plants or other animals to get their nitrogen. Decomposition returns nitrogen to the nitrogen cycle as well. List two ways nitrogen fixation occurs _bacteria______________________________ _lightning______________________________ How do animals get the nitrogen they need? _by eating plants or animals that eat plants_____________________________ How do plants get the nitrogen they need? __by absorbing or assimilating fixed nitrogen from the soil.