StudyQuestionsforUnit9Testanswers
advertisement

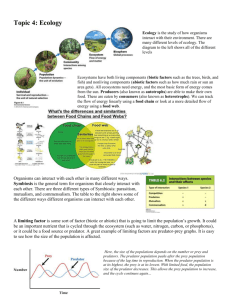
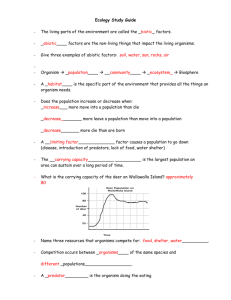
Study Questions for Unit 9 Test Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration ● What do producers need to carry on photosynthesis? Energy from the sun, carbon dioxide, and water ● What do organisms need to carry on cellular respiration? Glucose (sugar), oxygen ● What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? Identify the reactants and products. Reactants: energy from the sun, carbon dioxide, water/Products: oxygen, water, sugar ● What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration? Identify the reactants and products. Reactants: glucose, oxygen/Products: carbon dioxide, water, energy Chemistry ● What is a physical property? What is a chemical property? A physical property is a characteristic of a substance that is observed as long as the substance DOES NOT change into another substance. A chemical property is a characteristic of a substance that is observed ONLY when the substance changes into another substance. ● How do you know the difference between a physical property and chemical property? Physical—substance does not change identity. Chemical—substance changes its identity. ● What is a physical change? List a few examples of physical changes. It is a change in appearance of the substance WITHOUT changing the identity of a substance. Examples—state changes, change in size, shape, or color. ● What is a chemical change? List a few examples of chemical changes. It is a change in the identity of a substance. Examples—burning, rotting, rusting, corrosion by acid. ● How do you know the difference between a physical change and chemical change? A chemical change alters the identity of substance. Evolution ● What is evolution? It is the process by which life on Earth slowly and gradually changes over time. ● What are used as evidence that two different species may have had a common ancestor? Anatomical features (body structures) Organization of Ecosystems and Relationships ● What are some abiotic factors that organisms need to survive? Water, temperature, air, rocks, soil, wind. ● What are some biotic factors that organisms need to survive? Other organisms (as food). ● What may happen if a population’s living space increases? Decreases? If a population’s living space increases, the population may increase. If the living space decreases, the population may decrease. ● What may happen if a population’s water source increases? Decreases? If the water source increases, the population may increase. If the water source decreases, the population may decrease. ● What may happen to a population of prey if the predator population increases? Decreases? If the predator population increases, the population of prey may decrease. If the predator population decreases, the population of prey may increase. ● What may happen to a population of predators if the prey population increases? Decreases? If the prey population increases, the predator population may increase. If the prey population decreases, the predator population may decrease. Food Chains and Food Webs ● What is a producer? How does a producer get its energy? A producer is an organism that, through the process of photosynthesis, creates sugar from oxygen, water, and the sun’s energy. A producer then uses the sugar it has created to get energy from it (cellular respiration). ● What is a consumer? How does a consumer get its energy? A consumer gets its energy from eating another organism. ● What is the difference between a primary consumer and a secondary consumer? A primary consumer eats a producer, while a secondary consumer eats a primary consumer. ● What is a decomposer? How does a decomposer get its energy? A decomposer is an organism that feeds on and breaks down organic matter ● What are some examples of decomposers? Fungi, bacteria ● What may happen if something happens to one of the organisms in a food chain? The organisms of a food chain are interdependent, and a change in an organism at one of the trophic levels will affect all other trophic levels. ● About _______% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next. 10% Biogeochemical Cycles ● What is the carbon cycle? Be able to identify key parts of the carbon cycle. The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon moves from the atmosphere into the earth and its organisms and then back again. ● How does burning fossil fuels contribute to the carbon cycle? The combustion of fossil fuels returns carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. ● What is the role of photosynthesis in the carbon cycle? Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the atmosphere into a plant’s leaf during photosynthesis. ● What is the role of cellular respiration in the carbon cycle? Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere during cellular respiration ● What are some examples of storage reservoirs for carbon? the atmosphere, plant cells, consumer cells, the soil (dead organisms’ remains, fossil fuels) ● What is the nitrogen cycle? Be able to identify key parts of the nitrogen cycle. The nitrogen cycle is the process by which nitrogen in the atmosphere is converted into forms that can be used by organisms and then converted back into atmospheric nitrogen ● What is the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nitrogen cycle? They are able to convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that organisms can use ● What is the role of lightening in the nitrogen cycle? Lightning is able to convert atmospheric nitrogen into forms that organisms can use