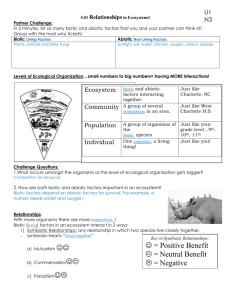
Ch. 12 Study Guide
advertisement
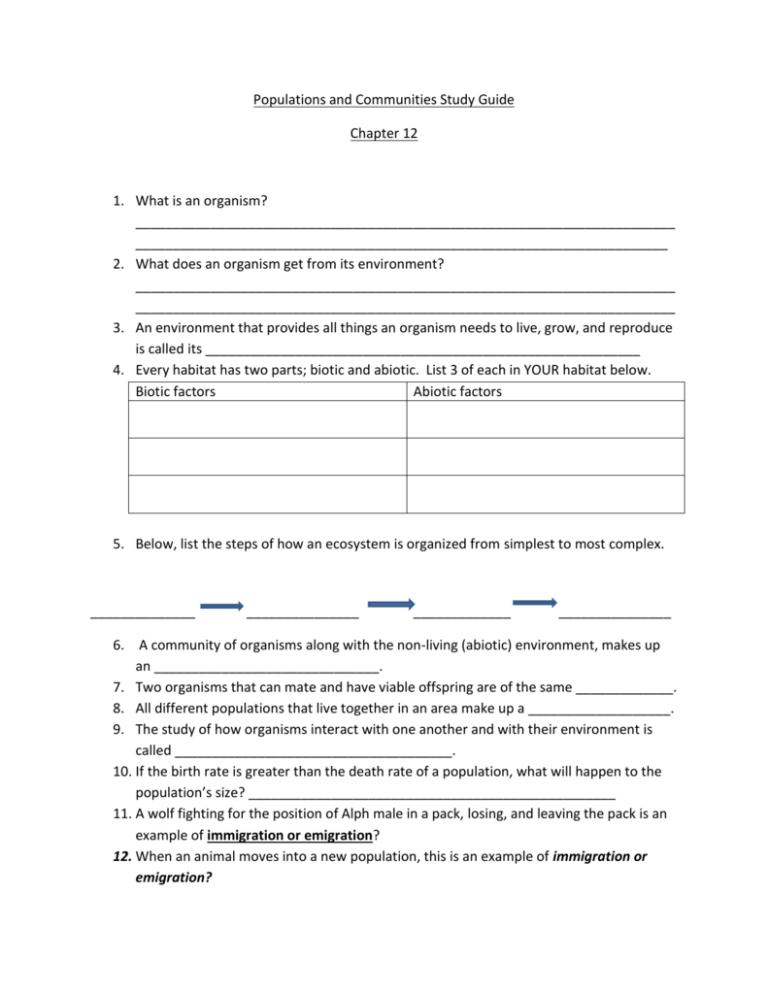
Populations and Communities Study Guide Chapter 12 1. What is an organism? ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 2. What does an organism get from its environment? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 3. An environment that provides all things an organism needs to live, grow, and reproduce is called its __________________________________________________________ 4. Every habitat has two parts; biotic and abiotic. List 3 of each in YOUR habitat below. Biotic factors Abiotic factors 5. Below, list the steps of how an ecosystem is organized from simplest to most complex. ______________ _______________ _____________ _______________ 6. A community of organisms along with the non-living (abiotic) environment, makes up an ______________________________. 7. Two organisms that can mate and have viable offspring are of the same _____________. 8. All different populations that live together in an area make up a ___________________. 9. The study of how organisms interact with one another and with their environment is called _____________________________________. 10. If the birth rate is greater than the death rate of a population, what will happen to the population’s size? _________________________________________________ 11. A wolf fighting for the position of Alph male in a pack, losing, and leaving the pack is an example of immigration or emigration? 12. When an animal moves into a new population, this is an example of immigration or emigration? 13. An example of an abiotic factor in an ecosystem is – a. Insects b. Trees c. Fungi d. Sunlight 14. Look at the graph below to answer the questions. a) Which population was greater, wolf or moose, in 1975? ______________ b) When the wolf population was at its highest in 1980, what was the moose population? ____________________________________ c) Why do you think the wolf-moose population sizes keep alternating, and when one is high, the other is low? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ d) Which species is the predator? ___________________________________ e) Which species is the prey? ______________________________________ 15. What is a limiting factor for a population? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 16. The role of an organism in its habitat is called its _____________________________ 17. If two organisms occupy the same niche, one may die off. This struggle for limited resources is known as _______________________________________________. 18. When one organism kills another for food/resources, this is known as ______________________________________________________________ 19. Below, label the predator/prey in the picture. Predator _____________________________ Predator _______________________ Prey ________________________________ Prey __________________________ Predator ____________________________ Predator ______________________ Prey _______________________________ Prey _________________________ 20. Identify the 3 types of symbiosis below: mutualism, commensalism, parasitism _____________________ _______________ ____________________ 21. The type of symbiosis when one organism benefits and the other neither benefits or is harmed is called ______________________________________________________ 22. The type of symbiosis when one organism benefits and the other is harmed is called ________________________________________________________________ 23. Birds and insects sharing the same tree as a shelter is an example of – a. Homeostasis b. Cyclic behavior c. Cooperative behavior d. Competitive behavior 24. The first species to populate an area once uninhabited by living organisms, are called? _________________________________________ 25. This type of succession happens when an ecosystem has been disturbed, but there is soil and still some organisms that exist __________________________________________ 26. Some causes of the type of succession from question #25, might be: __________, _____________________, ________________, and ______________________. 27. This type of succession happens where no soil exists and no living organisms live. ______________________________________________________________ 28. Label the pictures below as ready to go through primary or secondary succession. ________________________________ _____________________________