Study Guide
advertisement

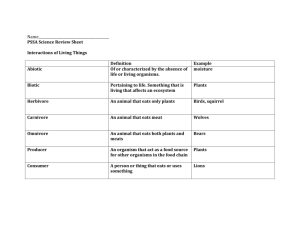
Study Guide Ecology and Biomes Test Ecology - The study of the interactions between living and non-living factors in an environment. biotic - all living factors in an environment; animals, plants, bacteria abiotic - all non-living factors in an environment; weather, sun, water, temperature Symbiosis - a close long-term association between two or more species. 3 types of symbiotic relationships mutualism - symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit ex: the clownfish and sea anemone. Sea anemone provides protection for the fish and the fish provides scrapes of food for anemone. parasitism – symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed ex: heartworms in dogs, fleas and ticks on animals. commensalism – symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected ex: shark and remora. Remora benefits from feeding off sharks scrapes, protection and transportation, the shark is not affected. Food chain – a diagram that shows how energy flows from food molecules from one organism to the next. Energy from sun producer Producer herbivore Herbivore carnivore Carnivore scavenger Scavenger Food web - a complex diagram showing the many energy pathways in a real ecosystem Producers: grass and trees Herbivores: a type of consumer that eats plants ex: rabbit, deer, grasshopper, chipmunk Carnivores: a type of consumer that eats animals ex: fox, owl, eagle Omnivore: a type of consumer that eats plants and animals ex: humans Scavenger: a type of consumer that eats remains of dead organisms ex: vulture (not shown in picture) Energy Pyramid - is a diagram shaped like a triangle that shows the loss of energy at each level of the food chain. -Producers are the plants that convert sunlight energy into chemical energy in sugar -Primary Consumers or herbivores eat the producers -Secondary consumers or carnivores eat the primary consumers. -Tertiary consumers eat secondary consumers. If there were as many tertiary consumers as the number of producers then there would not be enough food for all the higher level consumers. Carbon Cycle – The diagram to the left represents the carbon cycle. Every living thing is made up of carbon and carbon plays an important role in the cells of all living things. Carbon enters the environment by: Decomposing of dead plants and animals Respiration of plants and animals Burning of fossil fuels If too much carbon enters the atmosphere in a form that is not useable (gas), then it accumulates and causes an imbalance in the environment. Some scientists believe carbon emissions are the major cause of our ocean and land temperatures increasing. Scientists call this global warming. The Nitrogen Cycle All living things need nitrogen. Plants get the nitrogen they need from the ground. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria change the nitrogen from the atmosphere into a form that plants can use. Nitrogen gets into the environment by: Animal waste Fertilizers Decaying of plants and animals Nitrogen enters waterways and causes algae blooms. This increase in plant growth depletes oxygen from the water and other animals and plants die because they do not get the oxygen they need to survive and grow. The Water Cycle – evaporation, condensation and precipitation are three components of this cycle. MAJOR CHARACTERISTCS OF BIOMES Rainforest Warm, very rainy, near equator, most biologically diverse animals include: poison dart frog, orangutan, monkey Tundra Located at far Northern or Southern latitudes (or at high elevations). Permafrost, very cold, thin soil. Animals include: caribou, arctic fox, polar bear Coniferous forest Evergreen (coniferous) trees, long cold winters, short cool summers. Animals include: red fox, moose, owl, hare. Temperate deciduous forest Four seasons, deciduous trees, moderate temperatures. Animals include: eagle, deer, bear, and squirrel. Temperate grassland Grasses, few trees, four seasons. Animals include: coyotes, bobcats, and bison. Desert Very hot days, cool nights, very dry, little rainfall. Animals include: lizard, snake. Tropical savanna Dry season and rainy season, located near the equator, tall grasses. Animals include: hawks, lions, leopards, and zebra. Marine Salt water Animals include: blue whale, sea otters, fish. Freshwater Little to no salt. Ponds, streams, lakes, rivers. Animals include: bluegill, frogs Habitat – the environment where an organism lives. Niche – an organisms way of life and its relationships with its abiotic (nonliving) and biotic (living) environments. All organisms need food, shelter, living space, and water to survive. These resources are called limiting factors. The availability of these limiting factors have an affect on the number of organisms that can live in an area at the same time. The carrying capacity is the largest population that an environment can support. Competition – two or more species or individuals trying to use the same limited resource. Organism is a member of a species ex: a wolf Population is a group individuals of the same species living together in the same area at the same time ex: pack of wolves Community are all of the populations of different species living together in the same area at the same time. Ex: wolves and bears Ecosystem all nonliving (abiotic) and living (biotic) factors in an environment ex: bear, wolves, ice, weather Biomes- a large region characterized by a specific type of climate and certain types of plant and animal communities Biosphere the part of the Earth on which life exists and includes all of the different ecosystems.