Ecology Skeleton Notes
advertisement

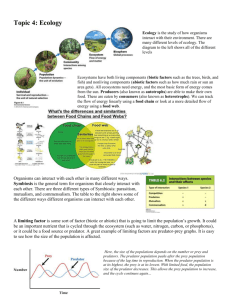
Name _____________________________________________ Period _________ Date ____________________ Chapter 18 -- Ecology What is Ecology? Ecology: the scientific study of interactions between organisms and their environments, focusing on energy transfer Known as the science of relationships What makes up the environment? The environment is made up of two factors: o Biotic factors All living organisms inhabiting the Earth o Abiotic factors Non-living parts of the environment Ex: temperature, soil, sunlight, moisture *This is totally NOT photoshopped. Organism Any unicellular or multicellular form exhibiting all of the characteristics of life The lowest level of organization Population Group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time that interbreed Produce fertile offspring Compete with each other for resources o Ex: food, mates, shelter Community Several interacting populations that inhabit a common environment and are interdependent Ecosystem Populations in a community and the abiotic factors with which they interact o Ex: marine, terrestrial Biosphere All life supporting portions of Earth composed of air, land, fresh water, and salt water 1 The highest level of organization Habitat vs. Niche Habitat o Place in which an organism lives out its life Niche o Role a species plays in a community o Determined by the tolerance limitations of an organism or limiting factor Limiting factor o Any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence of organisms in a specific environment o Ex: amount of water, food, temperature, space, and mates Feeding Relationships There are three main types of feeding relationships o Producer – Consumer Ex: grass cow o Predator – Prey Ex: mouse snake o Parasite – Host Ex: tick deer 2 Producer All autotrophs (plants) that trap energy from the sun Bottom of the food chain Consumer All heterotrophs Organisms that ingest food containing the sun’s energy o Herbivores o Carnivores o Omnivores o Decomposers Primary consumers Eat plants (herbivores) Secondary, tertiary … consumers Prey on animals (carnivores) Predators o Hunt prey for food Scavengers o Feed on carrion, dead animals Omnivores o Eat both plants and animals Decomposers o Breakdown the complex compounds of dead and decaying plants and animals into simpler molecules that can be absorbed Symbiotic Relationships Symbiosis o Commensalism o Parasitism o Mutualism Commensalism o One species benefits and the other is neither harmed not helped o Ex: polar bears and cyanobacteria Parasitism o One species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host) o Parasite – host relationship Ex: tick on an animal Mutualism o Beneficial to both species Ex: cleaning birds and cleaner shrimp 3 Trophic Levels Each link in a food chain is known as a trophic level Represent a feeding step in the transfer of energy and matter in an ecosystem Food web Shows all possible feeding relationships in a community at each trophic level Represents a network of interconnected food chains Food chain One pathway of energy paths Food Web All possible energy 4 Nutrient Cycles Cycling maintains homeostasis in the environment Three cycles o Water cycle o Carbon cycle o Nitrogen cycle Water Cycle Evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation Carbon Cycle Photosynthesis and respiration cycle carbon and oxygen through the environment 5 Nitrogen Cycle Atmospheric nitrogen (N2) makes up nearly 78-80% of air Organisms cannot use it in that form Lightning and bacteria convert nitrogen in usable forms 6