BIO101 Unit 4
advertisement

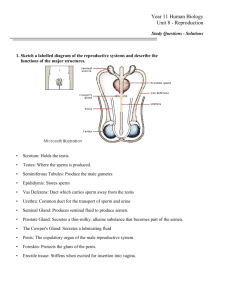
BIO102 Unit 10 Reproductive System Glossary AIDS Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome is caused by a group of related retroviruses known as HIV (human immunodeficiency viruses); a disease which effects the immune system by effecting the normal development of T lymphocytes; usually spread by sexual contact or sharing of intravenous needles. bulbourethral gland Either of two small structures located below the prostate gland in males sometimes called the cowper’s gland that adds secretions to semen. cervix the narrow end of the uterus which leads into the vagina; the portion of the uterus which dilates during childbirth. chlamydia a bacterial STD that is one of the most common usually asymptomatic; men experience a mild burning sensation and females experience a vaginal discharge. circumcision the surgical removal of the prepuce or foreskin of the penis usually on a newborn male baby. clitoris a small mass of erectile tissue that lies anterior to the urethral opening in the vulva of a female; can respond to sexual stimulation. coitus interruptus a usually unsuccessful method of birth control that requires the male to withdraw his penis from the woman’s vagina prior to ejaculation. condom (vaginal pouch) a rubber sheath that either covers the penis or lines the vagina; prevents sperm from entering the uterus; can offer some protection from sexually transmitted diseases. corpus luteum A yellow body that forms in the ovary from a follicle that has discharged its egg; it is the structure that secretes progesterone. diaphragm or cervical cap which is placed over the entrance to the cervix before intercourse which prevents the sperm from entering the uterus; does not offer protection against sexually transmitted diseases. diploid a term applied to a cell which has the normal chromosome number of a species such as 46 chromosomes in human body cells. ejaculatory ducts these ducts receive sperm from the vas deferens and secretions from the seminal vesicles and empty into the urethra. endometrium coiled tubule near the testes where sperm mature and may be stored until ejaculation. erection the result of the filling of the spongy, erectile tissue of the penis with blood during sexual arousal. estrogen a hormone secreted by the ovaries that promotes the maturation of an ovarian follicle, thickening of the endometrium during the menstrual cycle and female secondary sexual characteristics. fallopian tube the two tubes that transport the eggs towards the uterus; also called uterine tubes and oviducts. fimbriae fingerlike extensions from the fallopian tube near the ovaries that aid the eggs movement into the tubes. follicle several hundred thousand structures in the females ovaries that contain potential mature ova (eggs) follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) a hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the development of an ovarian follicle in a female or the production of sperm in a male.. genital herpes caused by herpes simplex virus of two types; type 1 causes cold sores and fever blisters and type 2 causes genital sores. gonnorrhea a bacterial STD that is usually characterized by a unpleasant discharge during its early stages; treatable with antibiotics. haploid a term applied to a cell which has one half the normal chromosome number of a species such as sperm or eggs. hepatitis B usually spread by sexual contact, but like HIV can be contracted through blood transfusions and contaminated needles; the disease is preventable with a new HBV vaccine. labia majors & labia minors two pairs of skin folds that form a covering for the vaginal and the urethral openings and also hoods the clitoris. luteinizing hormone (LH) a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland that causes ovulation and converts the ruptured follicle to form the corpus luteum in the female and stimulates the testes to produce testosterone in males; called ICSH (interstitial cell stimulating hormone) in males. meiosis the cell division process which occurs to cells in the testes or ovaries resulting in the production of sperm or eggs menstruation loss of blood and tissue from the uterus at the end of the menstrual cycle; sometime referred to as the females period. menstrual cycle the monthly changes that occur to the ovary and uterus in a female that are determined by the levels of several sex hormones in the body; sometimes referred to as the ovarian cycle. mons pubis a pad of fatty tissue over the pubic symphysis that is covered with skin and pubic hair; considered part of the females external genitals. ovary female gonad; the organ that produces ova (eggs), and the hormones estrogen and progesterone. ovulation release of a mature ovum (egg) from ovarian follicle. oxytocin a hormone released by the posterior pituitary that promotes the release of milk by the mammary glands. penis external organ in males through which the urethra passes that serves as the organ of sexual intercourse. progesterone a female hormone secreted by the corpus luteum that promotes the thickening of the endometrium and helps maintain pregnancy. prolactin a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary that promotes production of milk after child birth. prostate gland a gland located around the male urethra below the urinary bladder that adds secretions to semen. scrotum the saclike structure that house the two testes in males which along with the penis compose the male external genitals. semen a thick, whitish fluid consisting of sperm and secretions from the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland and the bulbourethral glands that makes up the male ejaculate. seminal vesicle a pair of glands whose secretions contribute to semen; these glands join with the vas deferens to form the ejaculatory ducts. seminiferous tubules the tubular structures in the testes that contain the cells which will develop into sperm. spermatogenesis the process of meiosis that occurs in the testes in males which results in the production of sperm. syphilis a STD caused by a bacteria which during its early stages forms open sores called chancres; can be treated with penicillin; if this condition is left untreated it can lead to death. testes the male gonads; the organ that produces sperm and the male hormone testosterone. testosterone the hormone produced by the interstitial cells in the testes that promotes the maturation of sperm and promotes male secondary sexual characteristics such as body shape and facial hair. tubal ligation a surgical sterilization procedure performed on females where the fallopian tubes are tied closed or cut; prevents the sperm from reaching the ovum. uterus the womb or organ that lies between the fallopian tubes and the vagina which houses the developing fetus. vagina a muscular tube that serves as the birth canal and the organ of sexual intercourse in females. vas deferens the sperm ducts that lead from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in males. vasectomy a surgical sterilization procedure performed on a male where a portion of the vas deferens is removed; prevents sperm from becoming part of semen. vulva the female external genitals which includes the mons pubis, clitoris, labia major and labia minor that forms a covering for the vaginal and urethral openings.