1 - Seattle Central College
advertisement
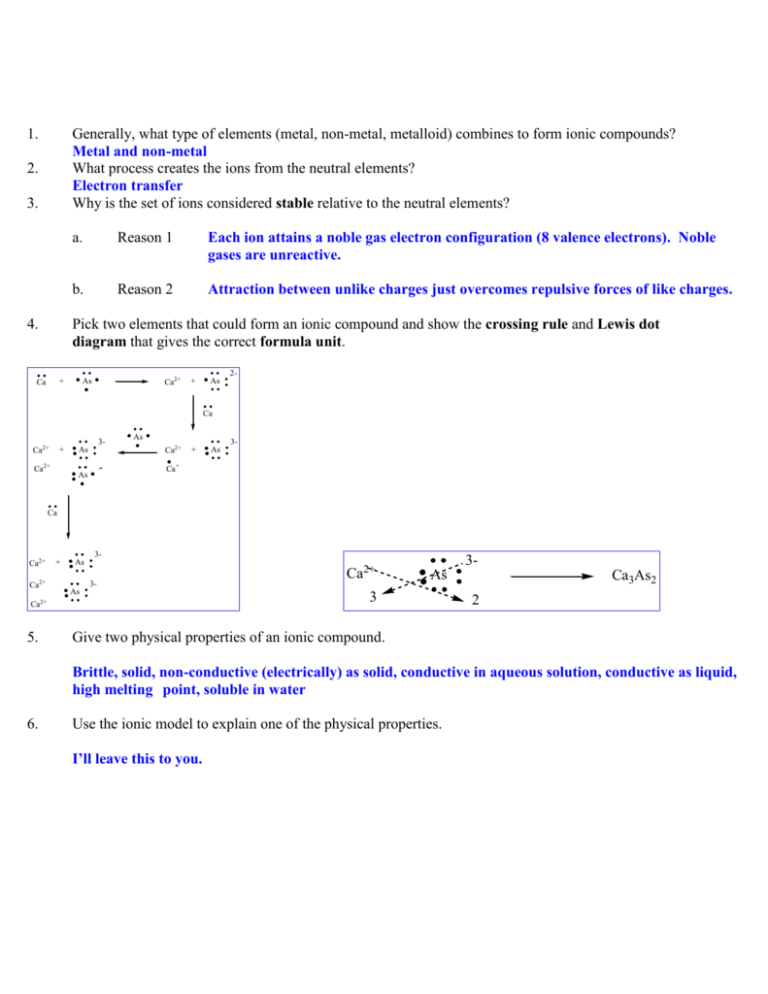
1. Generally, what type of elements (metal, non-metal, metalloid) combines to form ionic compounds? Metal and non-metal What process creates the ions from the neutral elements? Electron transfer Why is the set of ions considered stable relative to the neutral elements? 2. 3. 4. a. Reason 1 Each ion attains a noble gas electron configuration (8 valence electrons). Noble gases are unreactive. b. Reason 2 Attraction between unlike charges just overcomes repulsive forces of like charges. Pick two elements that could form an ionic compound and show the crossing rule and Lewis dot diagram that gives the correct formula unit. + Ca Ca2+ As 2+ As Ca 3- Ca2+ + Ca2+ As - As As Ca2+ 3+ As Ca+ Ca Ca2+ Ca2+ 3+ As 3As Ca2+ 5. Ca2+ 3As 3 Ca3As2 2 Give two physical properties of an ionic compound. Brittle, solid, non-conductive (electrically) as solid, conductive in aqueous solution, conductive as liquid, high melting point, soluble in water 6. Use the ionic model to explain one of the physical properties. I’ll leave this to you. 1. 2. 3. 4. Generally, what type of elements (metal, non-metal, metalloid) combines to form covalent compounds? Non-metal and Non-metal or Non-metal and Metalloid What process creates the covalent bonds from the neutral elements? Overlap of atomic orbitals Why is the set of bonded atoms considered stable relative to the neutral elements? a. Reason 1 Each atom attains a noble gas electron configuration (8 valence electrons). Noble gases are unreactive. b. Reason 2 Attraction between electrons of both atoms to protons of both atoms just overcomes repulsive forces of like charges (electron-electron and proton-proton). Pick two elements that could form a covalent compound and show a Lewis dot diagram that gives the correct molecular formula O 5. C O Give two physical properties of a covalent compound. Non-conductive of heat or electricity and low melting point 6. Use the covalent model to explain one of the physical properties. I’ll leave this to you.