Earth Science
advertisement

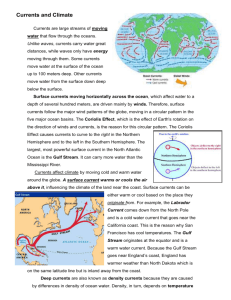
Earth Science Chapter 13 Section 4 A. Surface Currents: A current is a large stream of moving water that flows through the oceans. Unlike waves a current moves water from one place to another over great distances. Some currents move water at the surface, while other currents move deep water. Surface currents, which affect water to a depth of several hundred meters, are driven mainly by winds. Surface currents move in circular patterns east or west and then double back to complete a circle. Surface currents and winds move in circular patterns due to the Coriolis effect, which is caused by the Earth’s rotation. Currents are deflected to the right in the N. Hemisphere and to the left in the S. Hemisphere. The largest and most powerful surface current in the North Atlantic is the Gulf Stream. Caused by strong winds from the west. The Gulf Stream is about 30 Km wide and 300 meters deep. It carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico, to the Caribbean then north along the U.S. coast then turns east out to sea. B. How Surface Currents Affect Climate: Climate is the pattern of temperature and precipitation typical of an area over a long period of time. A surface current warms or cools the air above it, influencing the climate of the land near the coast. C. Deep Currents: Deep currents are caused by differences in density rather than surface winds. Deep currents move and mix water around the world. They carry cold water from the poles back toward the equator. D. Upwelling: Upwelling is the upward movement of cold water from the ocean depths. This occurs as the wind blows warm surface water away from the coast, and cold water rises to replace it. Upwelling brings up tiny ocean organisms, minerals and other nutrients from the deep. Which supports large schools of fish, which in turn supports the fishing industry and other creatures. One major area of upwelling is along the west coast of S. America. E. El Nino: Change in winds and currents can greatly impact the oceans and the neighboring land. El Nino, is an abnormal climate event that occurs every 2-7 years in the Pacific Ocean. El Nino begins when an unusual pattern of winds form over the western Pacific. This causes a vast sheet of warm water to move eastward toward S. America. What happens? 1. El Nino prevents upwelling along the coast. 2. Fish and food supplies are depleted 3. Weather patterns are changed, often bringing unusual or severe conditions to different areas.