Radiation
advertisement
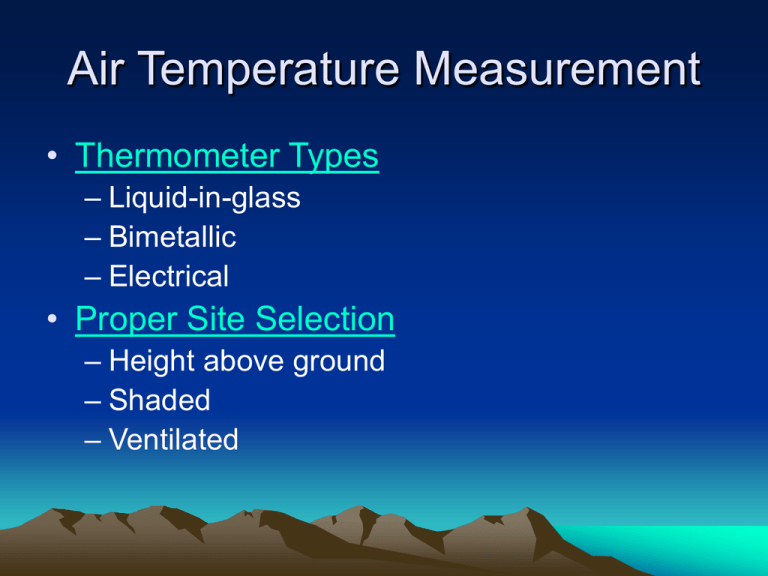
Air Temperature Measurement • Thermometer Types – Liquid-in-glass – Bimetallic – Electrical • Proper Site Selection – Height above ground – Shaded – Ventilated Temperature Change with Elevation • Generally decreases with increasing elevation in the troposphere • Vertical Temperature Profile- Atmosphere • Importance of elevation of surroundings – Denver vs. State College – Denver vs. WV mountains Seasonality • Temperature difference between warm and cold season • Generally greater over land than water • Generally increases with distance from water – – – – Heat capacity difference Penetration of solar radiation in water Mixing and currents in water Evaporation of water • Cloud cover amount Prevailing Wind Direction • Blowing from water or land? – Charleston, SC vs. San Diego, CA Ocean Currents • Water temperature – Cold currents on west coasts, in general – Warm currents on east coasts, in general Air Masses • A large volume of air (thousands of miles across by several miles deep) with similar temperature and moisture characteristics throughout • Source Regions = High Pressure Areas – Air acquires attributes of underlying surface – Continental vs. Maritime (moisture) – Polar vs. Tropical (temperature) Key Figures • 3.1, 3.2, 3.10, 3.17, 3.20, 3.38