WG10C - Lesson 3 The Agrarian Way
advertisement
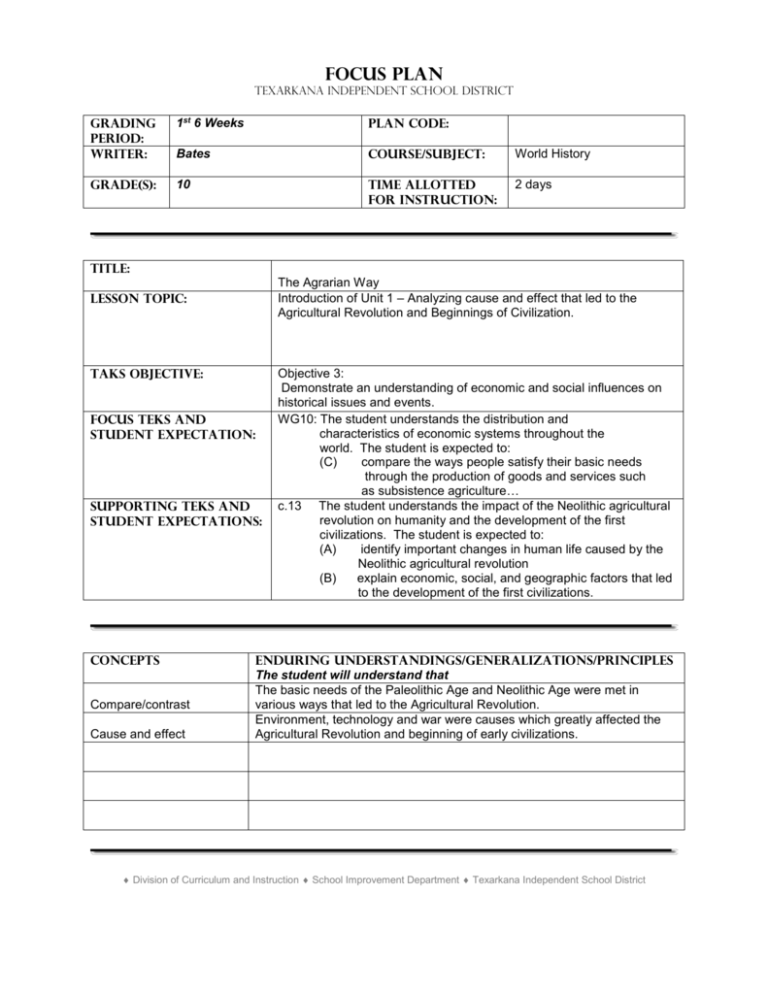
Focus Plan Texarkana Independent School District GRADING PERIOD: writer: 1st 6 Weeks PLAN CODE: Bates Course/subject: World History Grade(s): 10 Time allotted for instruction: 2 days Title: The Agrarian Way Introduction of Unit 1 – Analyzing cause and effect that led to the Agricultural Revolution and Beginnings of Civilization. Lesson TOPIC: TAKS Objective: FoCUS TEKS and Student Expectation: Supporting TEKS and Student Expectations: Concepts Compare/contrast Cause and effect Objective 3: Demonstrate an understanding of economic and social influences on historical issues and events. WG10: The student understands the distribution and characteristics of economic systems throughout the world. The student is expected to: (C) compare the ways people satisfy their basic needs through the production of goods and services such as subsistence agriculture… c.13 The student understands the impact of the Neolithic agricultural revolution on humanity and the development of the first civilizations. The student is expected to: (A) identify important changes in human life caused by the Neolithic agricultural revolution (B) explain economic, social, and geographic factors that led to the development of the first civilizations. Enduring Understandings/Generalizations/Principles The student will understand that The basic needs of the Paleolithic Age and Neolithic Age were met in various ways that led to the Agricultural Revolution. Environment, technology and war were causes which greatly affected the Agricultural Revolution and beginning of early civilizations. Division of Curriculum and Instruction School Improvement Department Texarkana Independent School District I. Sequence of Activities (Instructional Strategies) A. Focus/connections/anticipatory set The History Facts of the Day # 8 will be displayed on an overhead projector using a transparency OR using a computer generated inFocus projector. Students have recorded the History Facts of the Day in previous classes and are familiar with the procedure. B. C. Instructional activities (demonstrations, lectures, examples, hands-on experiences, role play, active learning experience, art, music, modeling, discussion, reading, listening, viewing, etc.) 1. Objectives: Students will apply their definition of civilization to two different eras and report their findings to the class. 2. Procedures: The teacher will ask the students for their definition of civilization. Their responses should include: A civilization is a group of people living and working together for the purpose of creating an organized society. People living in civilizations have the ability to use tools, work together cooperatively, and communicate with each other. People living in civilizations have the ability to advance culturally and technologically. 3. Modeling: The teacher will facilitate a Power Point Presentation describing Prehistory to Early Civilization. The teacher will print out a black and white copy of each slide with speaker notes prior to the presentation. Guided activity or strategy The teacher will divide the class into small groups of two or three students. Each group will research civilizations of the Paleolithic Age and Neolithic Age. II. D. Accommodations/modifications E. Enrichment STUDENT PERFORMANCE A. Description 1. 2. The students will research early civilizations and prepare a Venn diagram to compare and contrast the two periods. Each group will select one person to report its finding to the class. B. Accommodations/modifications C. Enrichment Division of Curriculum and Instruction School Improvement Department Texarkana Independent School District iii. Assessment of Activities A. Description The teacher will use a three-criteria rubric to evaluate students’ work during this lesson. B. Rubrics/grading criteria The teacher will explain the three criteria to the students. Criteria 1 – Students had difficulty completing their research and made an incomplete presentation to the class - 50 points. Criteria 2 – Students completed their research and made an accurate and complete presentation to the class – 75 points. Criteria 3 – Students completed their research carefully and thoroughly and made a thoughtful, accurate, and complete presentation to the class – 100 points. C. Accommodations/modifications D. Enrichment E. Sample discussion questions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Were tools used by members of the civilization? Did members of the civilization work together? What form of communication – oral, written or both - did each civilization have? Did either civilization advance culturally and technologically? Explain. How would you describe the civilization? IV. TAKS Preparation A. Transition to TAKS context Demonstrate an understanding of economic and social influences on historical issues and events. The teacher will explain the economic influences of farming that led to the Agricultural Revolution. B. Sample TAKS questions History Facts of the Day question (TAKS 2003) The basic characteristic of the economics of most traditional agrarian societies is: A B C D surplus crops subsistence farming large reserves of investment capital a variety of crops for export Answer: B V. Key Vocabulary Vocabulary terms were assigned the previous day and will be reviewed. (See FoCUS PLAN – 2: Talk Like a Historian) Division of Curriculum and Instruction School Improvement Department Texarkana Independent School District VI. Resources A. Textbook B. Supplementary materials Transparency: History Fact of the Day Rubric: Early Civilization Rubric Power Point: Early Civilization C. Technology Overhead projector InFocus projector Computer VII. follow up activities (reteaching, cross-curricular support, technology activities, next lesson in sequence, etc.) VIII. Teacher Notes Only the TEKS listed on the Curriculum Map relating to Pre-History toward Civilization will be the focus of these lessons. TEKS WG10 (C) correlates with WH14 (C). The student understands the historic origins of contemporary economic systems. The student is expected to: WG10(C) compare the ways people satisfy their basic needs through the production of goods and services such as subsistence agriculture WH14(C) compare the relationships between and among contemporary countries with differing economic systems Division of Curriculum and Instruction School Improvement Department Texarkana Independent School District