4.1.03 Cooling tower Plant w/2 Speed Cells, Sequence of Operation
advertisement

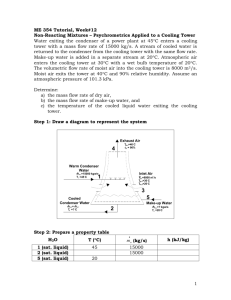
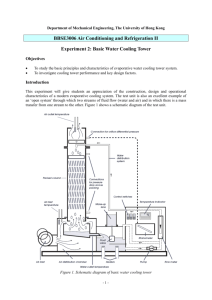
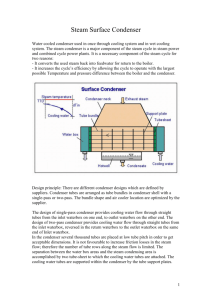
Applications (Field Installed) GPEC Cooling Tower Plant – w/ 2 Speed Cells Cooling Tower Plant / Sequence of Operations Note: 1) The following is a sample of a typical sequence of operation that may be adapted for a particular project. This is provided as a suggestion on how to write a sequence of operation for a specific project. The cooling tower controller includes the ability for the operator to select some different sequences. Consult your Carrier representative if the sample sequence requires alterations. 2) Limit the number of motor starts, or speed changes, per hour to ensure that the fan motor insulation does not become overheated. Consult with the manufacturer to determine the recommended minimum and maximum number of starts per hour and to configure the on and off time delays for each of the discrete output points that controls a fan. 4.3 Cooling Tower Plant – w/ 2 Speed Cells A. Description: 1. General: Cooling tower (fluid cooler) shall be directly controlled and monitored by a EMS compatible dedicated stand-alone programmable logic General Purpose Electronic Controller (GPEC). 2. Occupancy Status: The flow switch determines the occupancy status. When the flow switch is closed (enabled), there is proof of condenser flow, indicating that the cooling tower plant is in the occupied mode. When the flow switch is open (disabled), there is no condenser flow, indicating that the cooling tower plant is in the unoccupied mode. 3. Sequence of Operation During Occupied Hours: When the flow switch is enabled, the cooling tower algorithms are enabled. The diverting valve will be modulated and the cooling tower fans will be enabled in sequence to maintain the condenser water temperature setpoint. The AO—Adaptive Control algorithm will control the diverting valve and the DO—Staging algorithm will control the cooling tower fan speeds. The AO—Adaptive Control algorithm should use a control temperature setpoint (occupies low setpoint) approximately two degrees less than the setpoint used for the DO—Staging algorithm (occupies high setpoint) to properly sequence the condenser valve with the cooling tower fans. 4. Sequence of Operation During Unoccupied Hours: When the flow switch is disabled, the cooling tower algorithms are disabled. The diverting valve will be positioned to full bypass to the cooling towers. The cooling tower fans will be disabled. For cold starts the cooling towers to be bypassed on startup. 5. CWS – Condenser Water Supply Temperature: The sensor will be located after the condenser water bypass tee to properly sense the mixed water temperature. Both the AO–Adaptive Control algorithm and the DO–Staging algorithm require the CWS sensor to be the master sensor. 6. FS – Flow Switch: A paddle type flow switch is required to provide a discrete signal to the AO—Adaptive Control algorithm and the DO—Staging algorithms to indicate whether the condenser system is enabled or disabled. The paddle type flow switch must be located after the condenser water bypass tee.