Ancient Civilizations – Unit 1 and Unit 2
advertisement

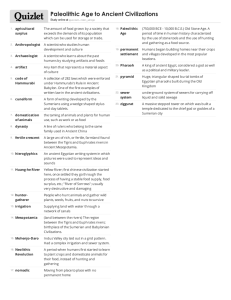
Ancient Civilizations – Unit 1 and Unit 2 Test Study Guide and Practice Exercises Name: _______________________ Period: _____ Overall description: The test will consist of 8 sections. Each section in this study guide provides helpful information on each of the test sections. Section 1: Chronology and chronological terms. Part A: You will be asked to arrange four events that we’ve studied in a chronological order on the timeline. Below, you will find a practice exercise: Events: (a) Neanderthal species perish (b) Sargon establishes the first empire in Mesopotamia (c) The Zhou overthrow the Shang in China (d) Assyrian empire falls after the destruction of Nineveh by Chaldeans 30,000 2350 1027 612 BCE BCE Part B: You will be asked to indicate the range of years for each century and to identify centuries of the dates given in years. Here is an example: Year(s) Century 2350 B.C.E. 1). __________ 2). ____________________ 1st Century A.D. 601-700 C.E. 3). __________ 4). ____________________ 8th Century B.C.E. 29 B.C.E. 5). ___________ Helpful handout to review: Historic Dates, Terms, and Definitions Section 2 and Section 5: Map Skills: Section 2: You will be asked to identify four river valley civilizations, major rivers, and their geographic locations. Section 5: You will also be asked to identify geographic locations of empires/societies mentioned in your presentations. You will also be asked to match writing systems to their geographic location. Finally, review major bodies of water shown on the second map. Helpful handout to review: Warm Up #3: It is All About Geography Section 3: Matching: Unit 1 Section 4: Matching: Unit 2 Out of the terms listed below, you will be asked to match 10 terms to their correct definitions/explanations for each unit. Agricultural Revolution Artifacts Clan Domestication Hunter-Gatherer Neolithic Prehistory Unit 1: Key Terms: Agriculture Ancestors Carbon 14 Dating Community Fossil Jericho Nomad Stone Henge Catalhoyuk Cro-Magnon Hominid Artisans Paleolithic Surplus Archeology Civilization Culture Homo Sapiens Neanderthal Pastoralism Technology Helpful handout to review: Your notes on Ch.1, sec.1, 2, and 3 + Warm Ups #1 and #2 Abraham Theocracy Cuneiform Moses Dynastic Cycle Papyrus Nubia Ramses II Assyrians Unit 2: Key Terms: Alphabet Animism City-States Empire Exile Fertile Crescent Polytheism Monotheism Mandate of Heaven Torah Jerusalem Hieroglyphs Pictograms Sumer Phoenicians Hebrews Delta Meroe Cultural Diffusion Diaspora Silt Ten Commandments Hammurabi Huang He Valley Hatshepsut Mummification Ziggurat Here is how it will look like on the test (EXAMPLE) Key Term/Vocabulary Definition: _____ Hammurabi A. Process of Taming _____ Domestication B. Lifestyle that specifically refers to wandering herders who moved their animals to new pastures and watering places _____ Pastoralism C. Part of the Code of Laws delivered to Moses that included rules regulating social and religious behavior _____ Ten Commandments D. Famous Babylonian king famous for issuing uniform set of laws for his diverse subjects Helpful handouts to review: Your notes on Ch.2, sec.1-4 + pp. on all empire for Unit 2 project. Important Note: Many of the terms that will not be used in the matching sections of the test will appear in questions or as possible answers in the multiple choice section of the test. Section 6: Multiple Choice. Besides the key terms mentioned above, for the multiple choice section of the test, consider reviewing: 1. 2. 3. 4. Location of early civilizations Features of a civilization Meaning of Mesopotamia Common religious characteristics of ancient societies 5. Difference between the status of rulers (kings/pharaohs) in ancient civilizations 6. Societies famous for ancient Codes of Laws 7. The way slavery was perceived by ancient peoples 8. Great accomplishments of the Phoenicians 9. Religious beliefs of the Hebrews 10. Babylonian captivity 11. Features of physical geography and climate of Indian subcontinent 12. Chinese dynasties and their chronological order 13. Flooding patterns of major rivers 14. Mandate of Heaven 15. Interactions between Egypt and Nubia (including Meroe) 16. Important religious figures of Judaism 17. Important Pharaohs Helpful Handouts to Review: All notes!!! Section 7: Primary Source Analysis: You will be asked to read a primary source and answer several questions related to it. If you would like to practice, here is one: The Code of Hammurabi [18th Century BCE] – excerpts: Read the excerpt and answer questions based on your interpretation of the source. …197: If he breaks another noble-man's bone, his bone shall be broken. 198: If he put out the eye of a commoner, or break the bone of a commoner, he shall pay one silver mina. 199: If he put out the eye of a man's slave, or break the bone of a man's slave, he shall pay one-half of its value. 200: If a man knock out the teeth of his equal, his teeth shall be knocked out. 201: If he knocks out the teeth of a commoner, he shall pay one-third of a silver mina. Questions: 1. What region/empire did Hammurabi rule? _______________( not based on this source!!!) 2. Is this a formal/legal document or informal document? Explain. 3. What can be concluded about social classes in this ancient society? Helpful handouts to review: Primary Source Analysis: Ancient Civilizations of Mesopotamia and Egypt Section 8: Thesis writing (Review your thesis writing assignments (Egalitarian vs. Hierarchical lifestyles as well as impact of Cuneiform.) Grading Rubric on the test: Thesis addresses the question Argumentative (presents a position/statement on the topic) – 1 Includes more than 1 idea - 1 Grammar/sentence structure accurate - 1