Titolo: ciclodestrine nel trasporto attivo di farmaci antitumorali
advertisement

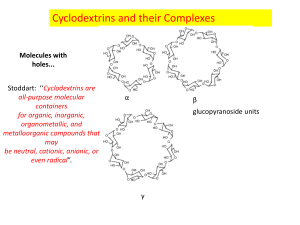
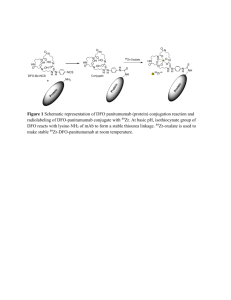
Cyclodextrin bioconjugates for site specific drug delivery Salmaso S.a, Carofiglio T.b, Fornasier R.c, Sonvico F.d, Couvreur P.d and Paolo Calicetia a Department of Pharmaceutical Science-University of Padua. bDipartimento di Chimica Inorganica, Metallorganica ed Analitica- University of Padua. c Dipartimento di Chimica Organica, Centro Meccanismi Reazioni Organiche del CNR-University of Padua. dUMR CNRS 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy, Châtenay-Malabry, University of Paris–Sud XI-France. Abstract. Conjugate of three components, cyclodextrin-Poly(ethylene glycol)-folic acid (CDJFA), was synthesized by a carbodiimide-mediated coupling of FA to CD-PEG-NH2 which was previously obtained reacting mono-tosil activated cyclodextrins with excess NH2-PEG-NH2 (Jeffamine). The conjugate CDJFA was characterized by 1H NMR and ESI-TOF. Inclusion complex ability of conjugate was compared to non-conjugate cyclodextrins using different probe chemicals: Estradiol, Rhodamin B and Chlorambucil. Results showed a different inclusion properties of the new conjugate. Further studies displayed lower emolitic effect of conjugate CDJFA when compared to cyclodextrins. The specific interaction between the conjugate CDJFA and folate-binding protein was evaluated by Surface Plasmon Resonance. This analysis confirmed a specific binding of CDJFA to folate-binding proteins which did not occur with non-conjugate cyclodextrins used as control. In vitro binding studies were performed with sub-lines MCF7 (human breast carcinoma) which express negligible level of FR (folate receptor), and KB (human epidermal carcinoma) which express high level of FR. CDJFA strongly binds to tumour cells and displays a binding constant of the same order of non-conjugate folate. Non-conjugate cyclodextrins were used as control. To examine wheatear newly synthesized carrier might deliver included molecules to the citosolic compartment, Rhodamin B was employed as probe molecule and uptake test on KB cells monolayer was performed. Fluorescence of cellular lisate was measured. Cell associated fluorescence proved to be higher when Rhodamin B was included into CDJFA than nonconjugate cyclodextrins. MCF7 cells were used as control. Rhodamin B charged endosomes were displayed by confocal microscopy into KB cells treated with Rhodamin B included CDJFA. Low intensity diffused red fluorescence was observed when Rhodamion B was complexed to non-conjugate cyclodextrins. Thus folate-linked cyclodextrins represent a potential new drug carrier for tumour cellselective targeting.